Kustomize
In this section we will learn about Kustomize, and how to use it deploy and make modifications to Kubernetes resources across different environments.
Problem Statement & Idealogy
We have to first know what problem Kustomize is solving. So, assume we have the following deployment:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
component: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
We will have multiple environments e.g. dev, stg, prod. We want to kustomize our deployment so it behaves differently in each one of our environments. E.g. replicas count is per environment bases.
One of the simplest solutions is to create separate directories for each environment and have a separate deployment file in each directory. We will end up duplicating the configs across all our environments.
A better solution is to use Kustomize: We need to reuse our k8s configs and only modify what needs to be changed. Keep it DRY.
Kustomize has two key terms that we have to understand:
- Base: The base config represents the common configuration that is shared across all environments. And provides default values.
- Overlay: The overlay allows us to customize the behavior on a per-environment basis.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
component: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
spec:
replicas: 1
spec:
replicas: 2
spec:
replicas: 3
Folder Structure
k8sdirectory:basedirectory:kustomization.yaml.nginx-deploy.yaml.service.yaml.redis-deploy.yaml.
overlaysdirectory:devdirectory:kustomization.yaml.deployment.yaml.
stgdirectory:kustomization.yaml.deployment.yaml.
proddirectory:kustomization.yaml.deployment.yaml.
Base Config: Shared of default across all environments. Overlay Config: Environment specific configurations that add or modify the base config.
Workflow
We will have our Base Configs and Overlay Configs as inputs to kustomize then it will Output the Final Manifests files.
Kustomize comes built-in with kubectl. We may need to install it tho. As the one that comes with kubectl is not always the latest version.
We are not making any use of complex and hard to read templating engines like Helm.
Helm vs Kustomize
Helm solves the same issue by making use of go templates to allow assigning variables to properties.
But helm way more than just a tool to customize configurations on a per-environment basis. Helm is also a complete package manager for your app. E.g. yum, apt, npm, etc.
Helm is complex and comes with extra features like conditionals, loops, functions, and hooks.
Install Kustomize
pre-requisite:
- kubernetes cluster.
- kubectl installed on local machine and configured to connect to the cluster.
curl -s "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes-sigs/kustomize/master/hack/install_kustomize.sh" | bash
kustomize version --short
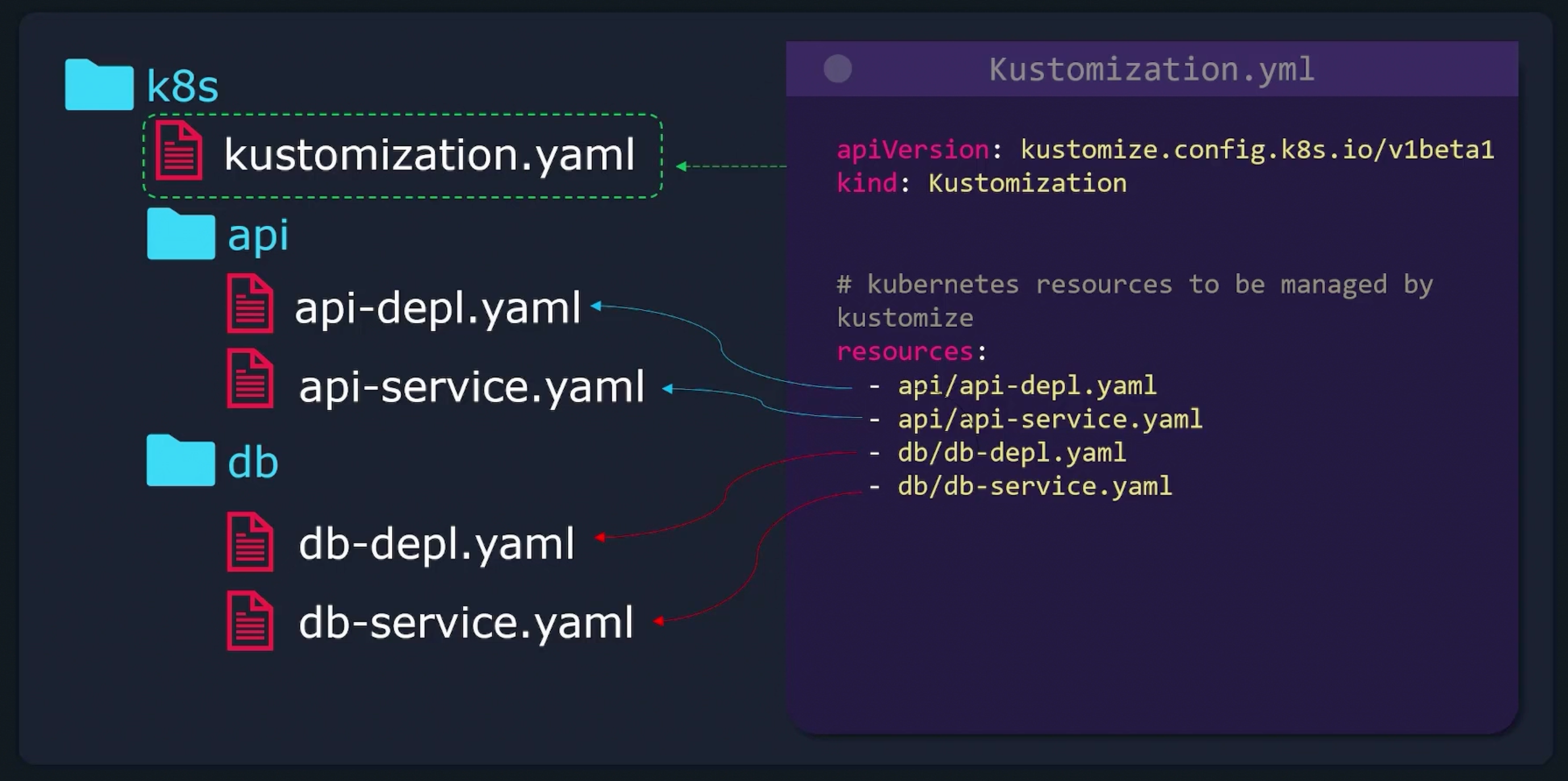
kustomization.yaml
Kustomize looks for kustomization.yaml file in the directory where it is run. You can not change its name. And there are two things that needs to exist in it:
resources: List of all the resources to be managed by kustomize.commonLabels: Customizations that need to be made.
resources:
- nginx-deploy.yaml
- nginx-service.yaml
commonLabels:
compony: KodeKloud
kustomize build k8s
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
labels:
company: KodeKloud
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
component: nginx
company: KodeKloud
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: nginx
company: KodeKloud
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-loadbalancer-service
labels:
company: KodeKloud
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 3000
selector:
component: nginx
company: KodeKloud
type: LoadBalancer
What we learned:
- Kustomize will look for a
kustomization.yamlfile that contains two things:resources: List of all kubernetes manifests kustomize should manage.- All the customizations that should be applied to the resources.
- The kustomize build command combines all the manifests and applies the defined transformations.
- The
kustomize buildcommand does not apply/deploy the kubernetes resources. It only generates the final manifests. - (TO APPLY) take output and redirect it to
kubectl apply -f -to apply the changes.
Kustomize Output
kustomize build k8s
kustomize build k8s | kubectl apply -f -
# Or
kubectl apply -k k8s
kustomize build k8s | kubectl delete -f -
# Or
kubectl delete -k k8s
Kustomize API version and Kind
# (Optional)
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
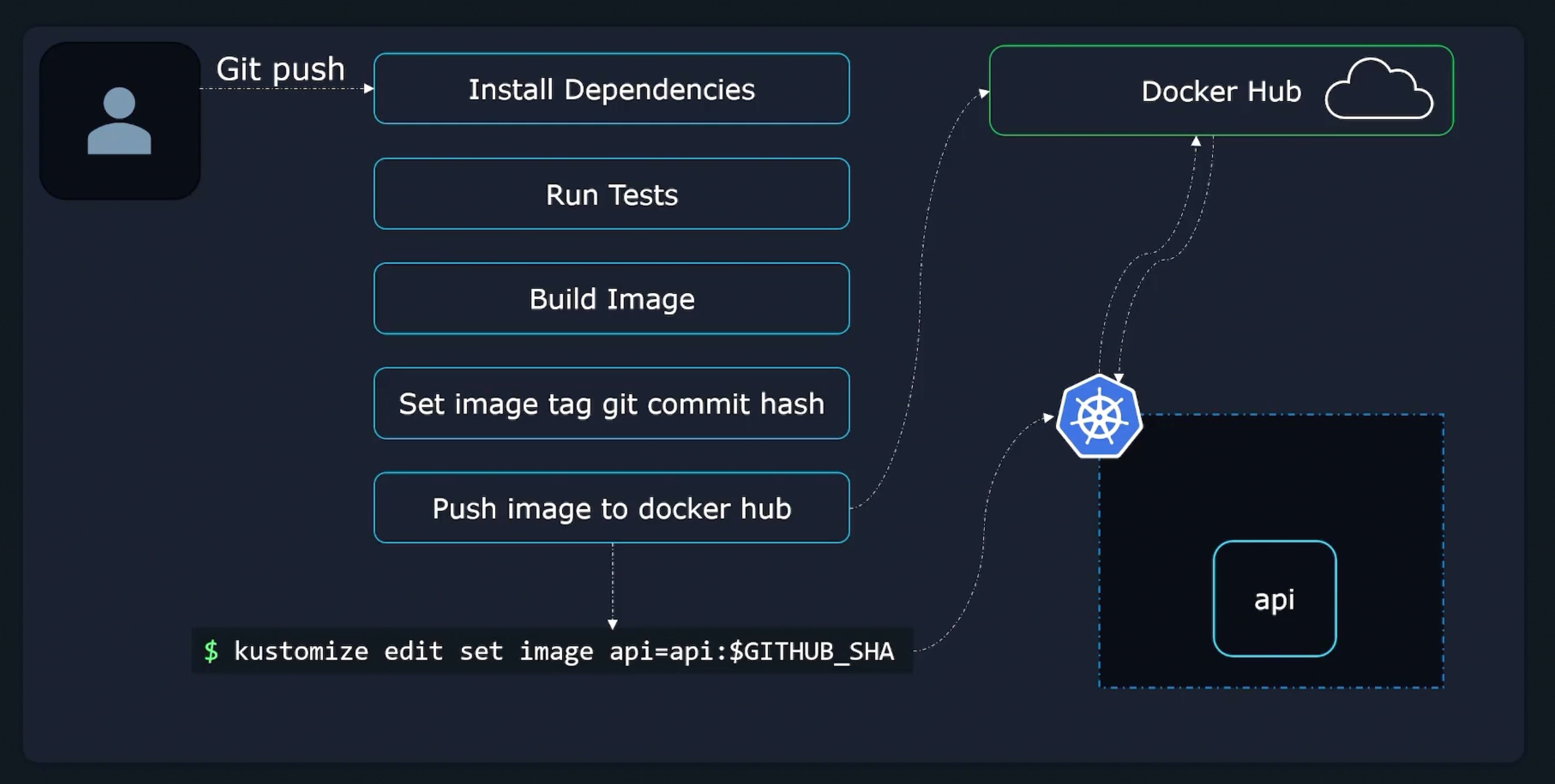
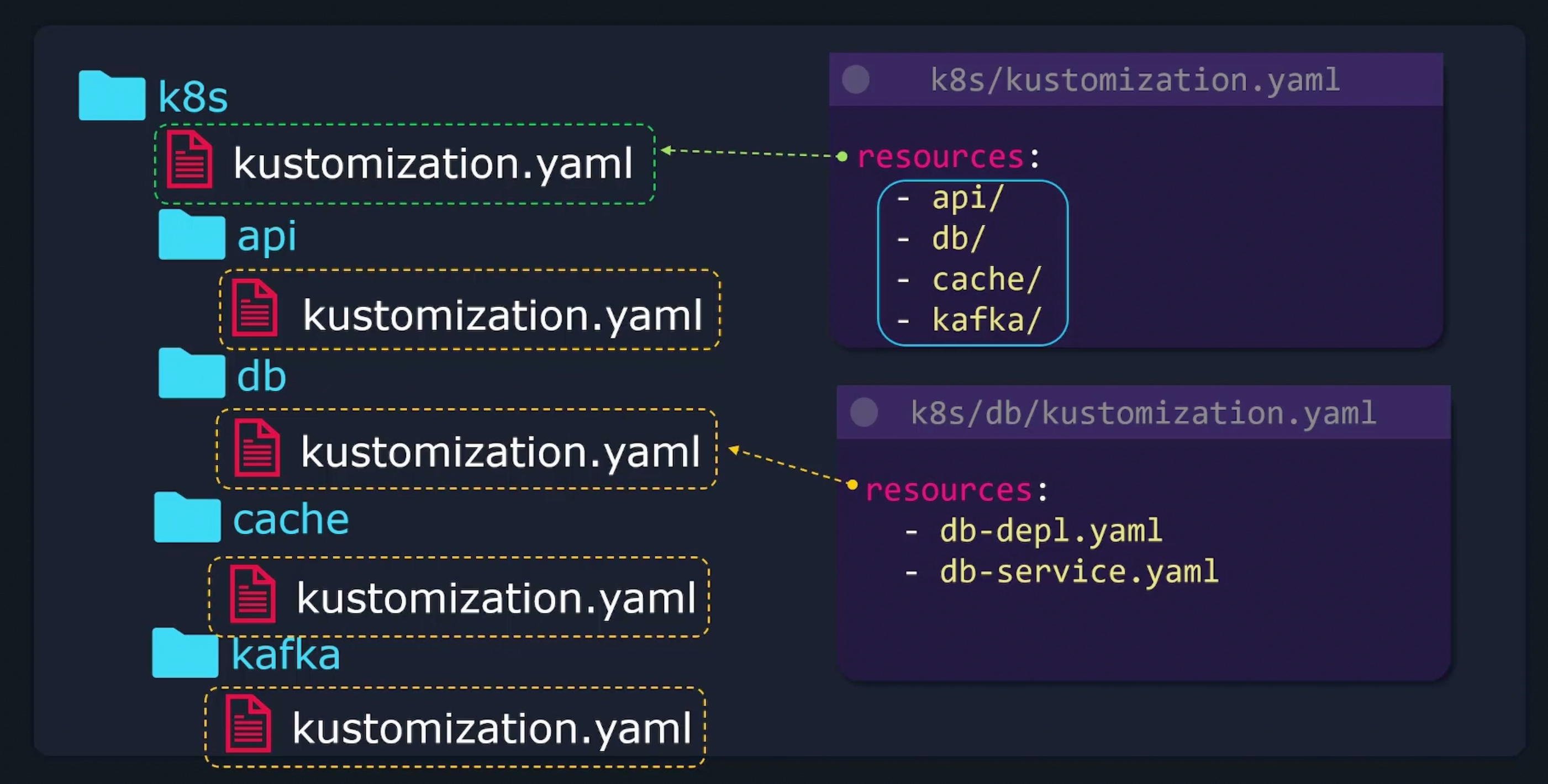
Managing Directories
kustomize build k8s | kubectl apply -f -
kubectl apply -k k8s
Common Transformers
commonLabels: Add labels to all resources.commonAnnotations: Add annotations to all resources.namePrefix/nameSuffix: Add a prefix or suffix to the name of all resources.namespace: Set the namespace for all resources.
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
commonLabels:
org: KodeKloud
namespace: lab
namePrefix: KodeKloud-
nameSuffix: -dev
commonAnnotations:
branch: master
Image Transformers
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Kustomization
images:
- name: nginx
newTag: 1.16
newName: haproxy
Patches Intro
kustomize patches provides another method to customize kubernetes resources. Unlike common transformers, patches provides a more "surgical" approach to targeting one or more sections in a kubernetes resource.
To create a patch we have to provide three different parameters:
Operation type: Add, Remove, Replace, ...etc.Target: What resource should this patch be applied to:kind: The kind of resource.name: The name of the resource.- Version/Group
- Namespace
- LabelSelector
- AnnotationSelector
Value: The value to be patched.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
component: api
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: api
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
patches:
- target:
kind: Deployment
name: api-deployment
patch: |-
- op: replace
path: /metadata/name
value: web-deployment
- target:
kind: Deployment
name: api-deployment
patch: |-
- op: replace
path: /spec/replicas
value: 5
Define a Patch
in Kustomize there are two ways to define a patch:
Json 6902: You need to provided target and the patch details. RFC 6902.Strategic Merge Patch: Uses regular kubernetes configs to define the patch.
patches:
- patch: |-
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
replicas: 5
Different Patch Types
Basically, Json 6902 Inline vs Separate File. Before we saw the Inline method. Now we will see the Separate File method.
patches:
- path: replica-patch.yaml
target:
kind: Deployment
name: nginx-deployment
- op: replace
path: /spec/replicas
value: 5
SAme with Strategic Merge Patch:
patches:
- replica-patch.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
replicas: 5
Patches Examples
Dictionary Patch
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
component: api
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: api
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
- Json 6902
- Strategic Merge Patch
patches:
- target:
kind: Deployment
name: api-deployment
patch: |-
- op: replace
path: /spec/template/metadata/labels/component
value: web
patches:
- patch: |-
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: web
Add a new Key
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
component: api
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: api
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
- Json 6902
- Strategic Merge Patch
patches:
- target:
kind: Deployment
name: api-deployment
patch: |-
- op: add
path: /spec/template/metadata/labels/org
value: KodeKloud
patches:
- patch: |-
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
org: KodeKloud
Remove
- Json 6902
- Strategic Merge Patch
patches:
- target:
kind: Deployment
name: api-development
patch: |-
- op: remove
path: /epc/template/metadata/labels/org
patches:
- patch: |-
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
template:
metadata:
labels:
org: null
Patches List
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
component: api
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: api
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
The container section expects a list.
- Json 6902
- Strategic Merge Patch
patches:
- target:
kind: Deployment
name: api-deployment
patch: |-
- op: replace
path: /spec/template/spec/containers/0
value:
name: haproxy
image: haproxy
patches:
- patch: |-
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: haproxy
Add List
- Json 6902
- Strategic Merge Patch
patches:
- target:
kind: Deployment
name: api-deployment
patch: |-
- op: add
# "-" means append to the end
# "0" means insert at the beginning
# "i" means insert at index i
path: /spec/template/spec/containers/-
value:
name: haproxy
image: haproxy
patches:
- patch: |-
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: haproxy
image: haproxy
Replace List
- Json 6902
- Strategic Merge Patch
patches:
- target:
kind: Deployment
name: api-deployment
patch: |-
- op: replace
path: /spec/template/spec/containers/0
value:
name: haproxy
image: haproxy
patches:
- patch: |-
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: haproxy
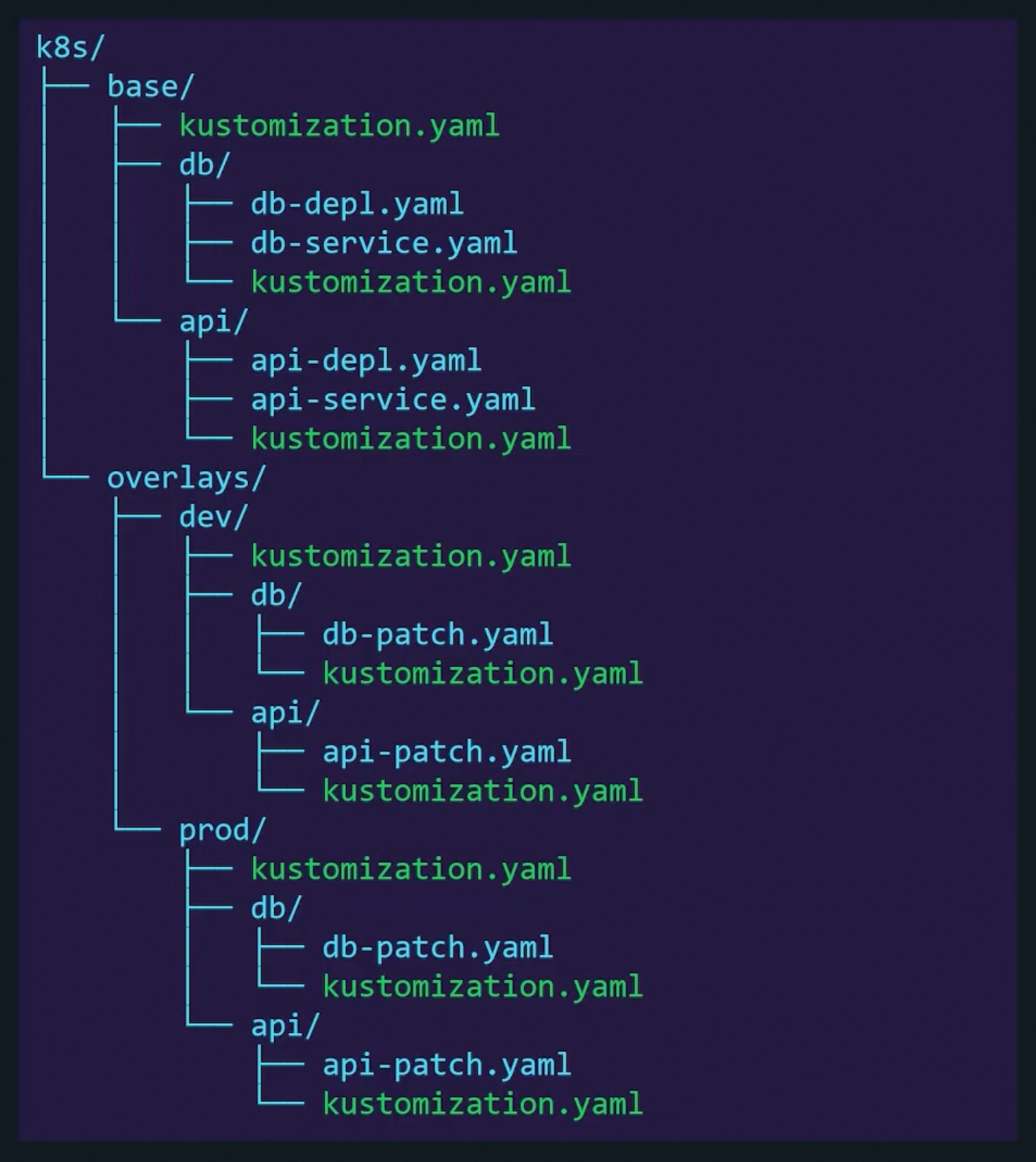
Overlays
tree k8s
k8s
├── base
│ ├── kustomization.yaml
│ ├── nginx-deploy.yaml
│ ├── redis-depl.yaml
│ └── service.yaml
└── overlays
├── dev
│ ├── config-map.yaml
│ └── kustomization.yaml
├── prod
│ ├── config-map.yaml
│ ├── grafana-depl.yaml
│ └── kustomization.yaml
└── stg
├── config-map.yaml
└── kustomization.yaml
5 directories, 11 files
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
We want to change replicas per environment basis:
resources:
- nginx-deploy.yaml
- redis-depl.yaml
- service.yaml
bases:
- ../../base
patches:
- target:
kind: Deployment
name: nginx-deployment
patch: |-
- op: replace
path: /spec/replicas
value: 2
bases:
- ../../base
resources:
- grafana-depl.yaml
patches:
- patch: |-
- op: replace
path: /spec/replicas
value: 3
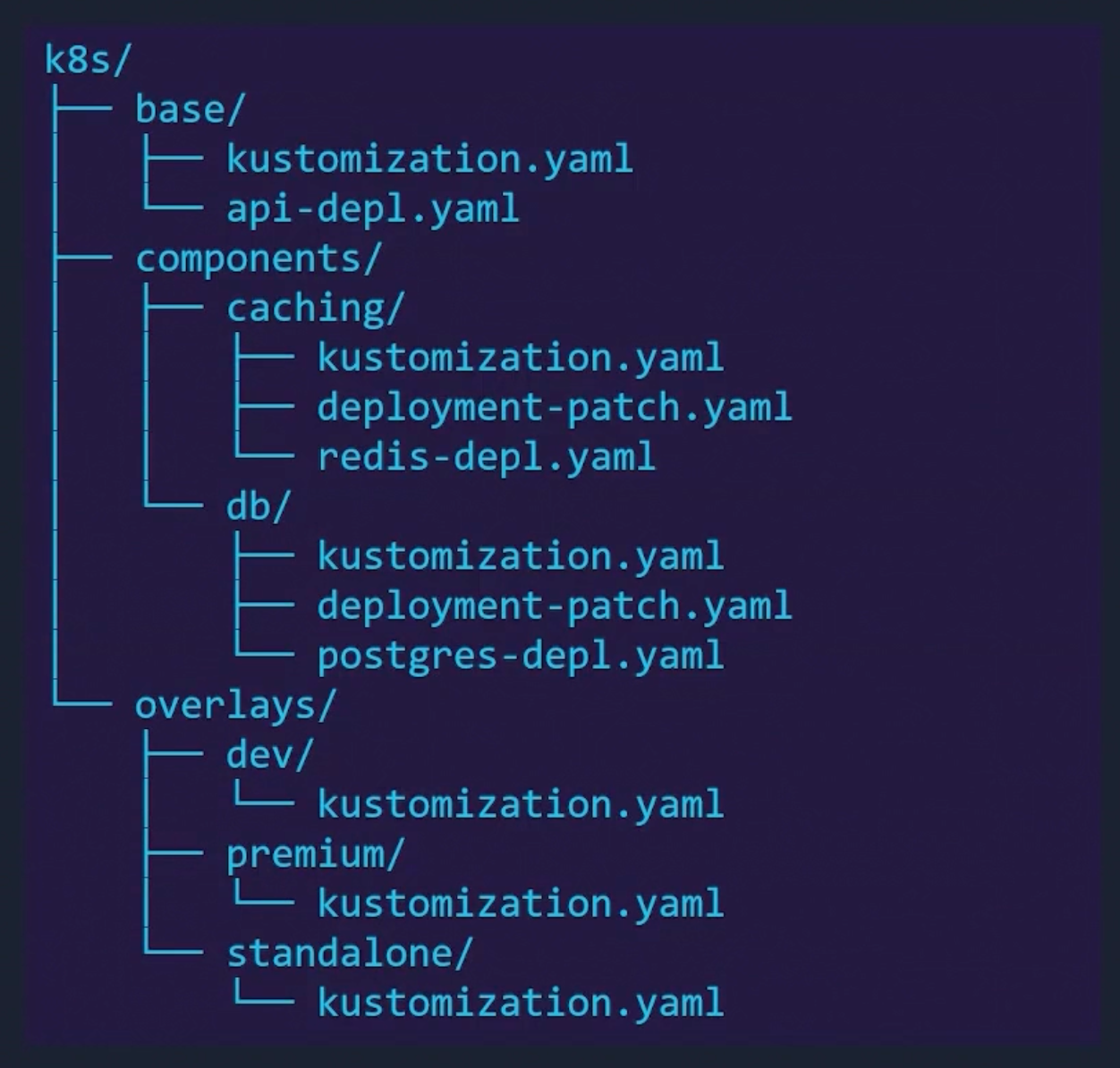
Directory Structure
Components
Components provides the ability to define reusable pieces of configuration logic(resources + patches) that can be included in multiple overlays.
Components are useful in situations where applications support multiple optional features that need to be enabled only in a subset of overlays.
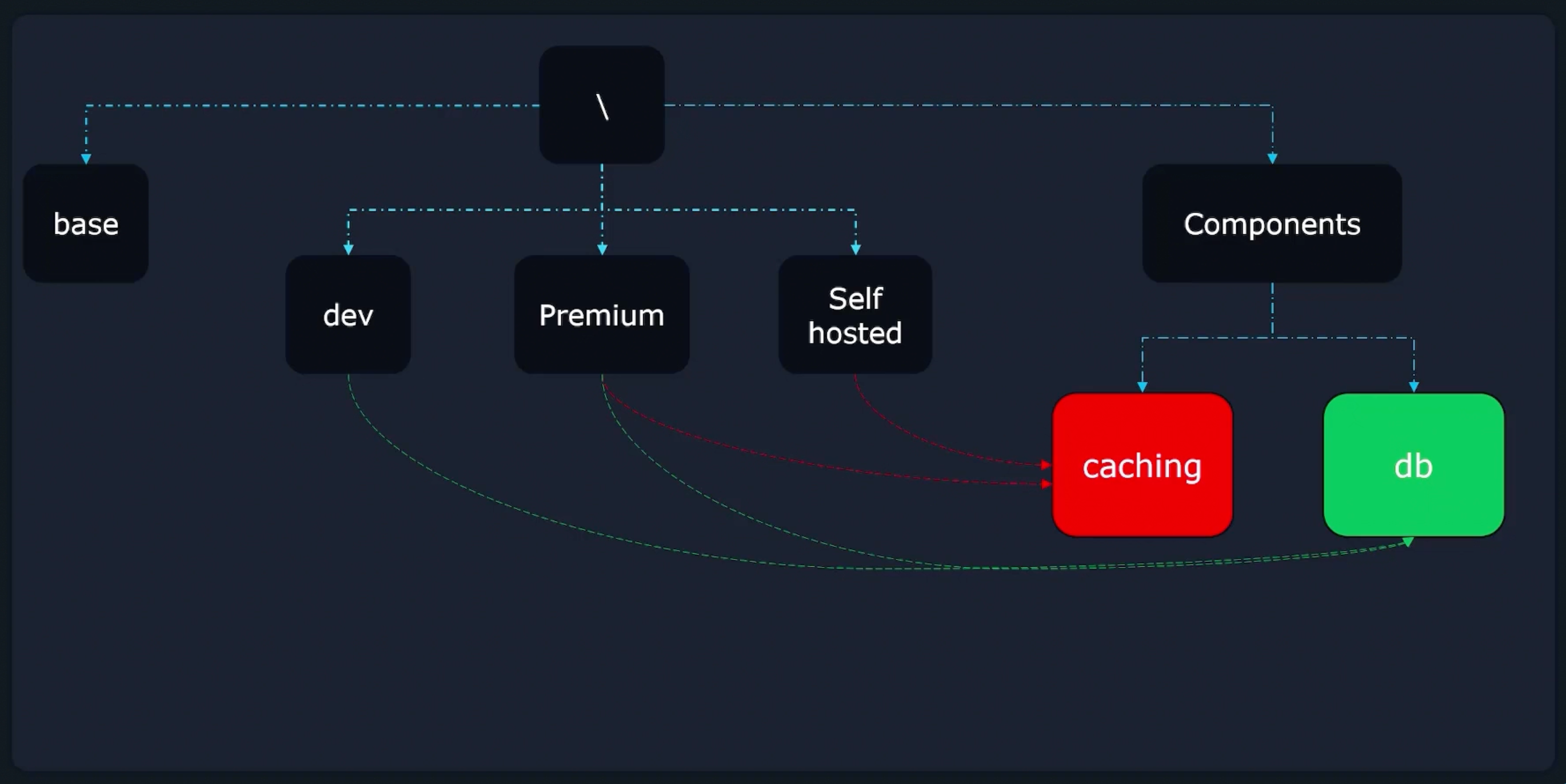
Example
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: postgres-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
component: postgres
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: postgres
spec:
containers:
- name: postgres
image: postgres
apiVersion: kustomize.config.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Component # Important
resources:
- postgres-depl.yaml
secretGenerator:
- name: postgres-cred
literals:
- password=postgres123
patches:
- deployment-patch.yaml
# A Strategic Merge Patch
# Targeting the `api-depl` in the `k8s/base` directory
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: api-deployment
spec:
template:
spec:
containers:
- name: api
env:
- name: DB_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: postgres-cred
key: password
bases:
- ../../base
components:
- ../../components/db
Generators
What problem does secretGenerator and configMapGenerator solve? In this example we have:
k8s/api-depl.yamlk8s/db-configMap.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: db-credentials
data:
# You want to do that inside a secret actually
# Anything we do in this demo also applies to
# secrets
password: "password1"
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
component: nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
component: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx
env:
- name: DB_PASSWORD
valueFrom:
configMapKeyRef:
name: db-credentials
key: password
kubectl exec nginx-deployment-xxxx -- env | grep DB_PASSWORD
kubectl exec nginx-deployment-xxxx -- printenv | grep -i db
A couple of month later we wanted to change the password of our database.. We have to tell kubernetes we updated this. You will change the db-configMap.yaml file and then apply it. But the nginx-deployment is unchanged.
kubectl rollout restart deployment nginx-deployment
Secret / Config Generator
When you define a generator in kustomize. It is going to create a ConfigMap or Secret resource for you. But it appends a hash to the name of the resource. e.g. db-credentials-xxxxx. When you create a deployment.yaml file you just reference the db-credentials and kustomize will automatically update the deployment.yaml file with the new name of the ConfigMap or Secret.
Overtime we wanted to update the password of the database. Our generator will create a new ConfigMap or Secret with a new name. And then update the deployment.yaml file with the new name of the ConfigMap or Secret. That will trigger a rollout of the deployment ^^.
Configure generators
configMapGenerator:
- name: db-credentials
literals:
- password=password1
Result:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: db-credentials-xxxxx
data:
password: password1
File Generators
configMapGenerator:
- name: nginx-config
files:
- nginx.conf
configMapGenerator:
- name: ingress-nginx-14314
files:
- ingress-nginx-14314.json
options:
disableNameSuffixHash: true
labels:
grafana_dashboard: "1"
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
}
}
Result:
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-config-xxxxx
data:
nginx.conf: |
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:3000;
}
}
Secret Generators
secretGenerator:
- name: db-cred
literals:
- password=password1
Result:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
type: Opaque
metadata:
name: db-cred-xxxx
data:
password: cGFzc3dvcmQx
Garbage Collection
Setup kubernetes to automatically clean stale configs.
kubectl apply -k k8s/overlays/prod --prune -l app-config=my-config
Imperative Commands
kustomize provides the ability to imperatively update the kustomization.yaml files using edit command.
kustomize edit --help
kustomize edit set image nginx=nginx:1.2.2
kustomize edit set namespace staging
kustomize edit set label org:KodeKloud env:staging
kustomize edit set replicas nginx-deployment=3
kustomize edit add configmap db-creds --from-literal=password=password1 --from-literal=username=root
kustomize edit add resource db/db-depl.yaml
images:
- name: nginx
newTag: 1.2.2
namespace: staging
commonLabels:
org: KodeKloud
env: staging
replicas:
- count: 5
name: nginx-deployment
configMapGenerator:
- name: db-creds
literals:
- password=password1
- username=root
resources:
- db/db-depl.yaml
Which kustomization.yaml file are we updating?! the one in the directory you ran the command from.
Example