ArgoCD
In this section we will discuss:
- What GitOps is?
- GitOps Principles
Intro
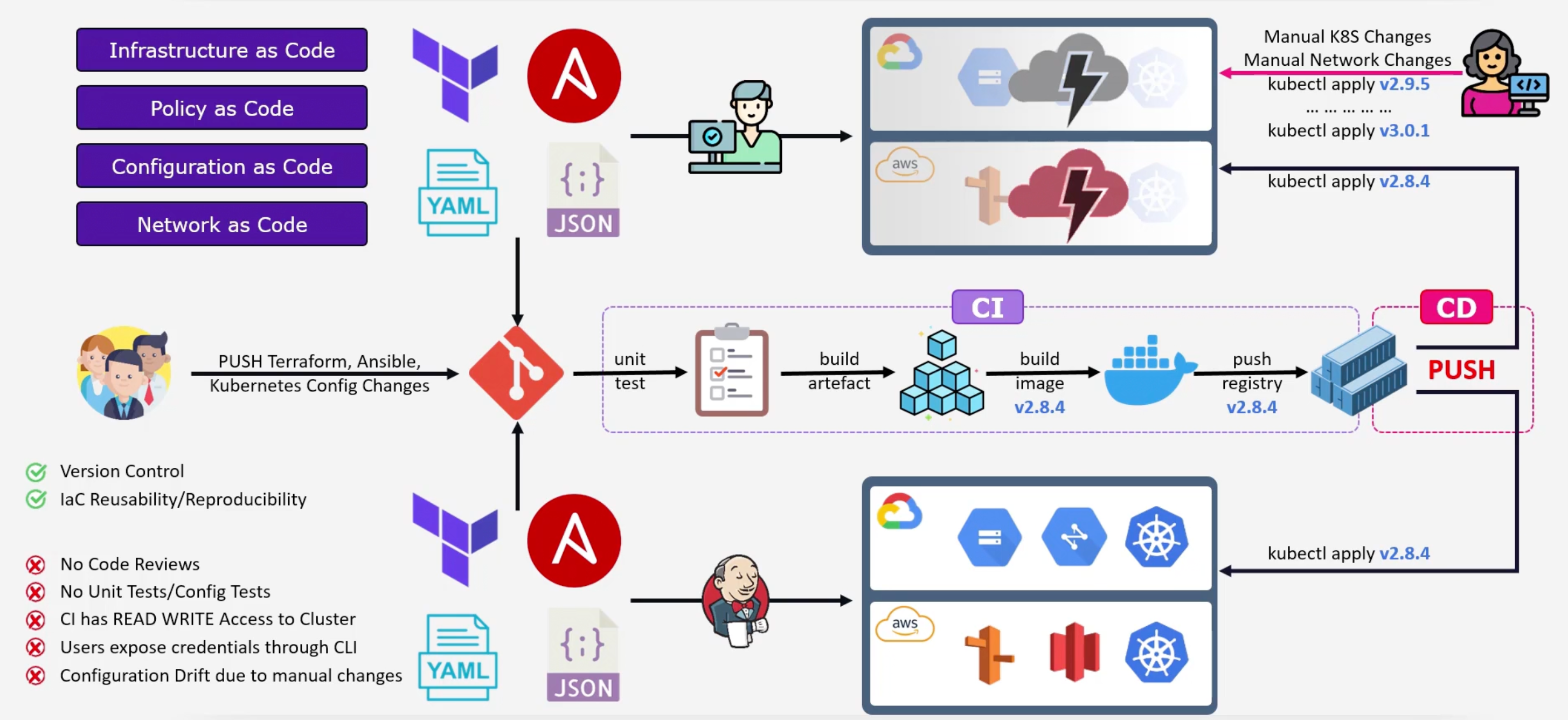
- Infrastructure as Code
- Policy as Code
- Configuration as Code
- Network as Code
X as code approach. Plus, No code reviews and no unit tests or config tests. And most importantly the problem of `Manual k8s/Network changes" like who the F did this?
GitOps Methodology
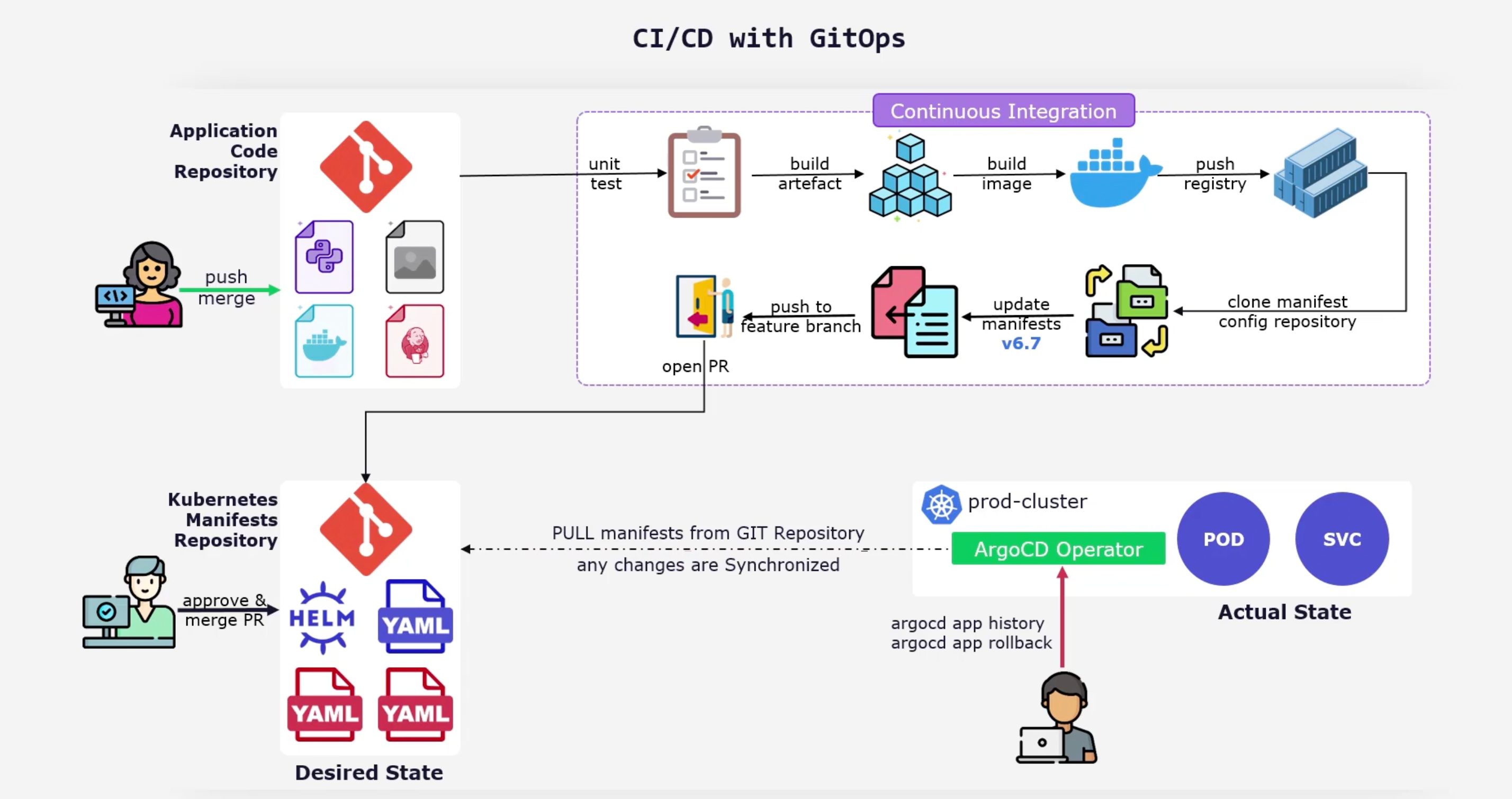
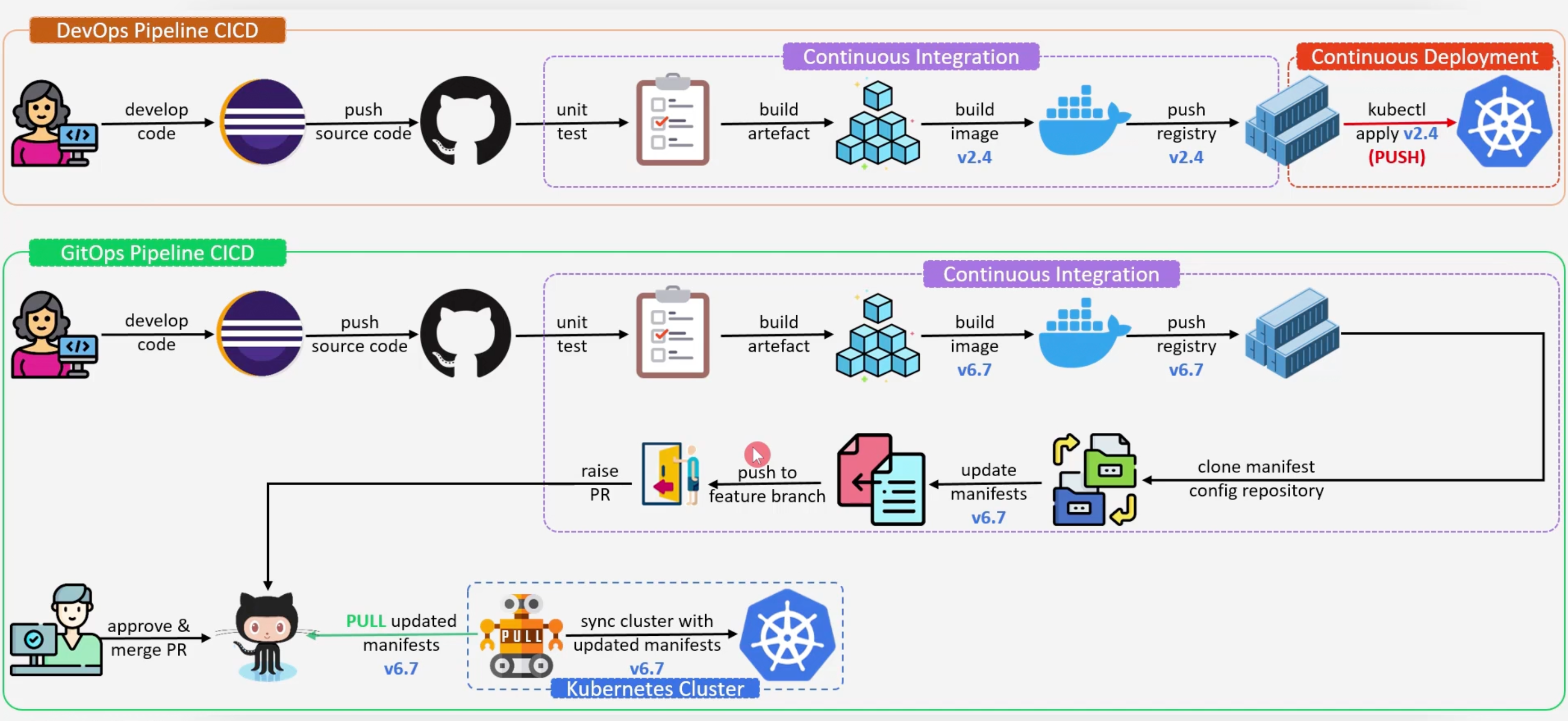
GitOps is a framework where the entire code delivery process is controlled by Git. GitOps can be considered as an extension of Infrastructure as Code (IaC) that uses Git as the version control system.
A GitOps Operator runs in the cluster and ensures that the desired state of the cluster matches the state defined in the Git repository. The GitOps Operator can also apply them in a different cluster as well.
GitOps Principles
GitOps has four principles:
- GitOps Is
Declarative. - GitOps Apps Are
VersionedandImmutable. Source of truth is Git. - GitOps Apps Are
Pulled Automatically. GitOps Operator or Software agents, pull the changes from the Git repository. - GitOps Apps Are
Continuously Reconciled. Three statesObserve,Diff, andAct.
DevOps vs GitOps
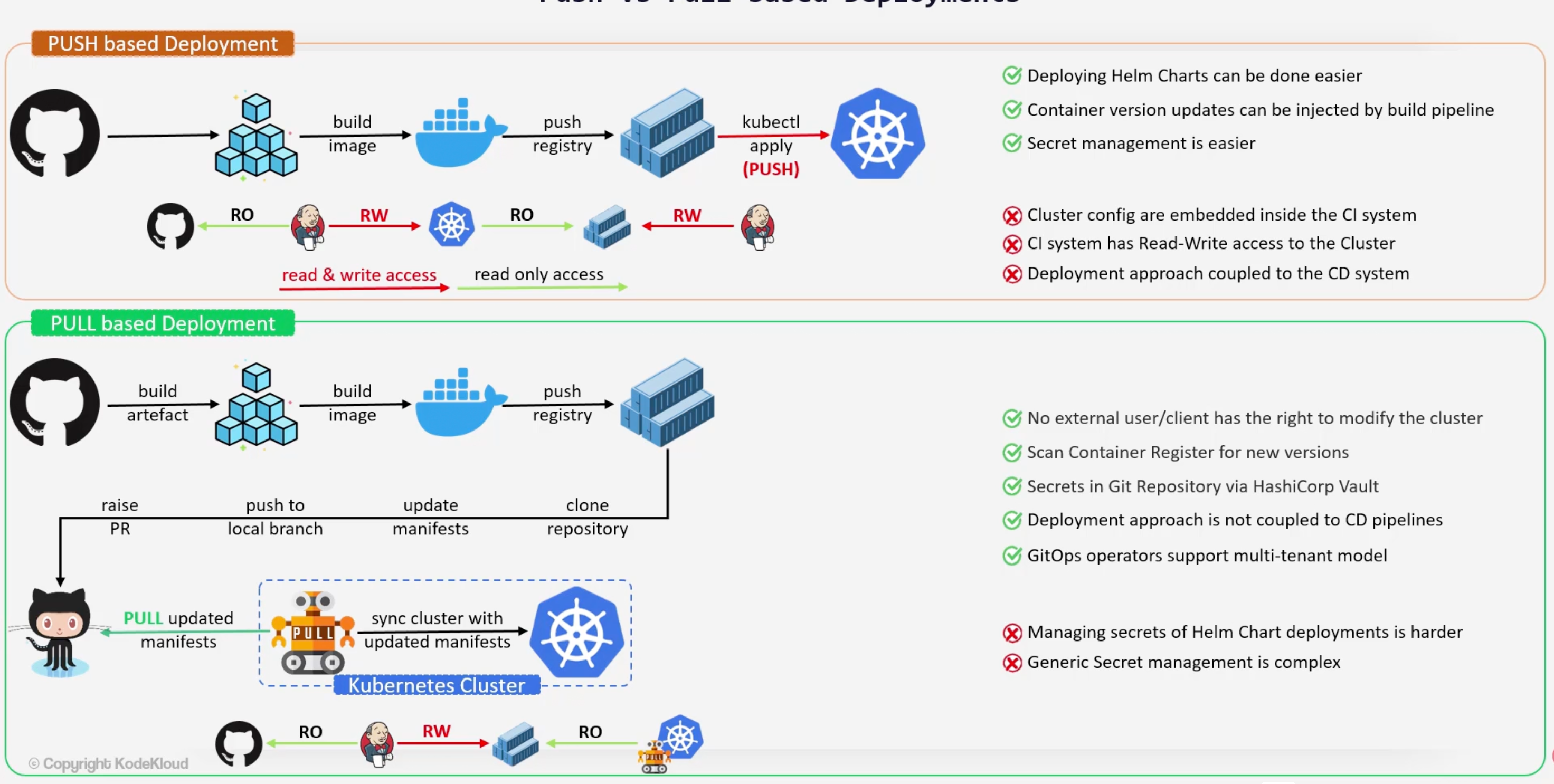
Push vs Pull Deployments
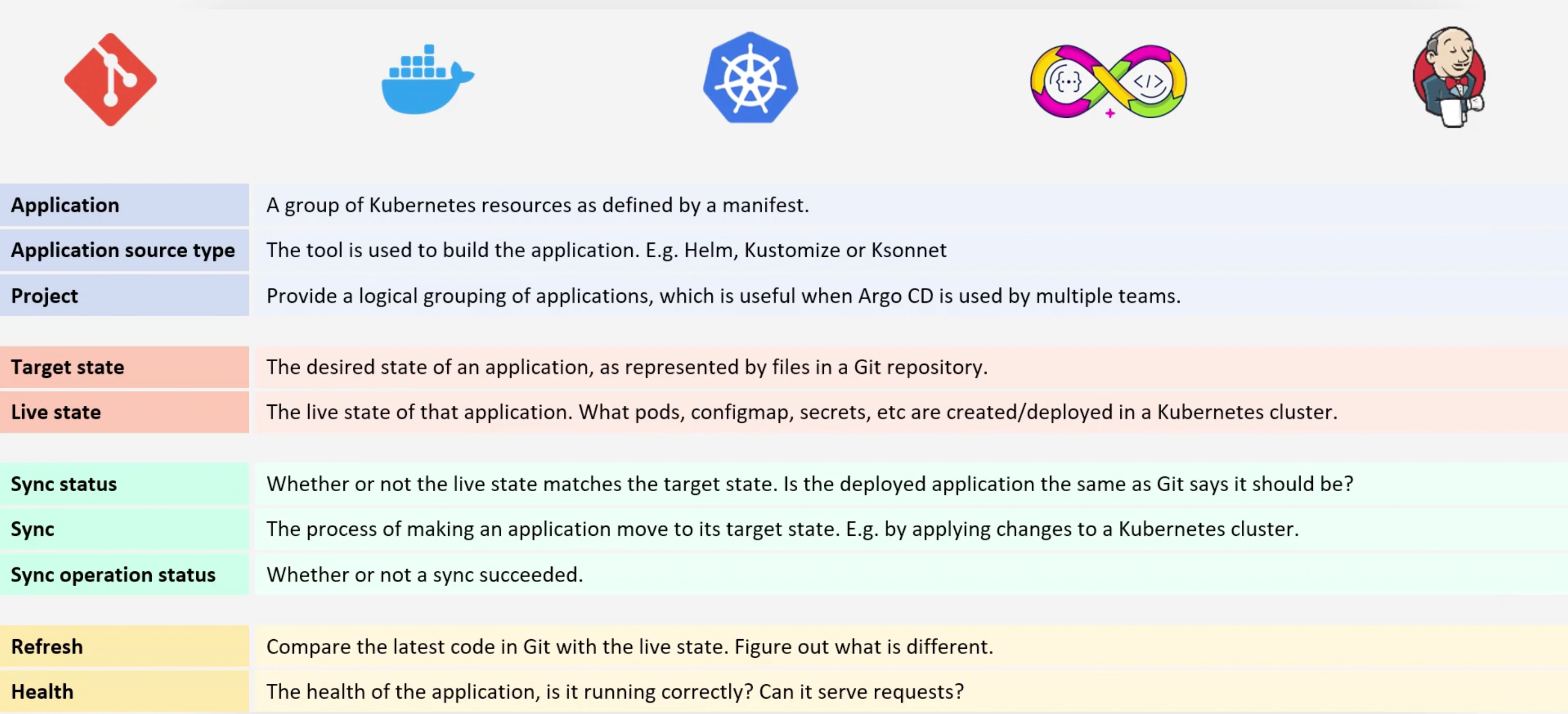
Concepts and Terminologies
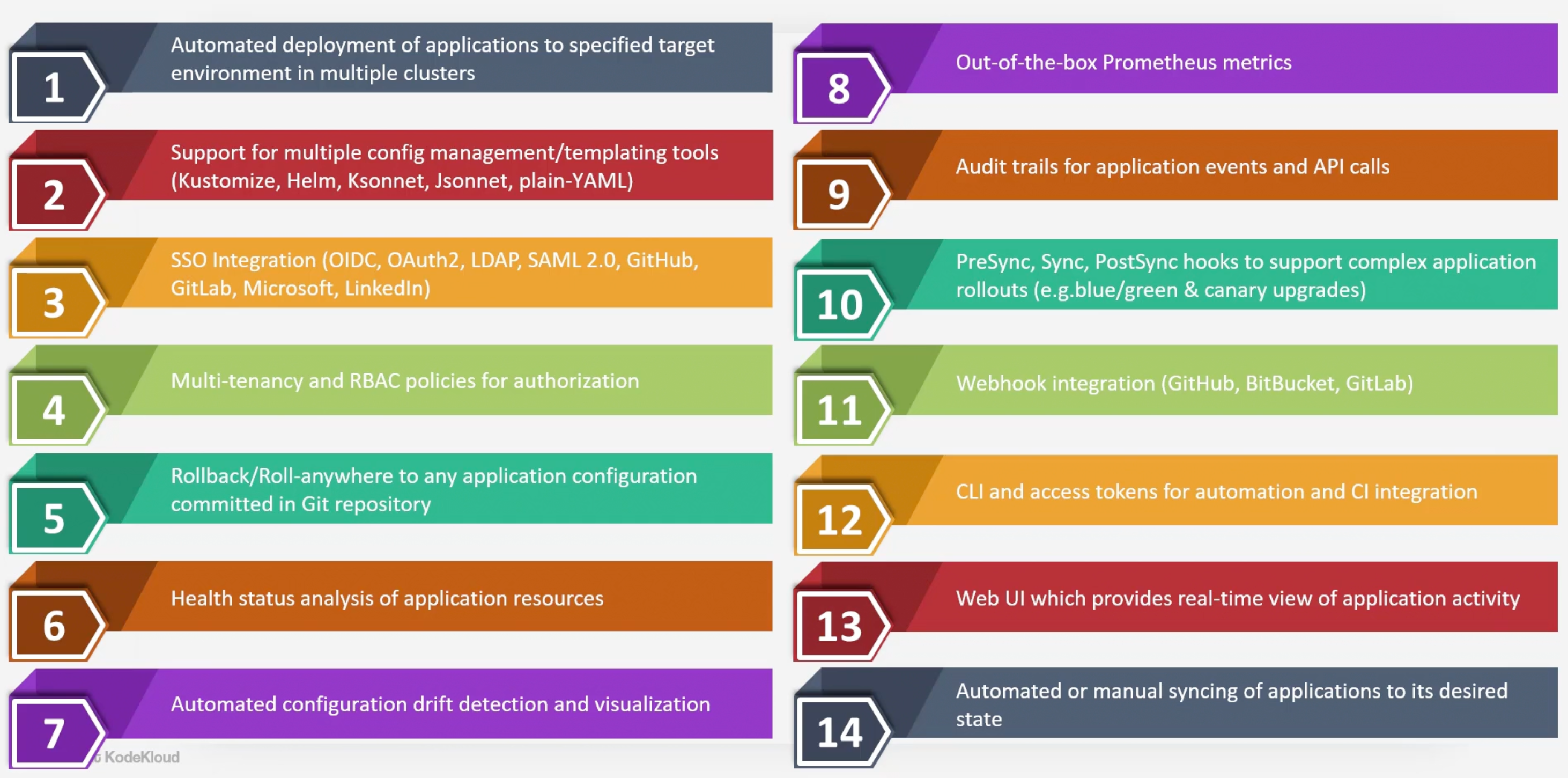
Features
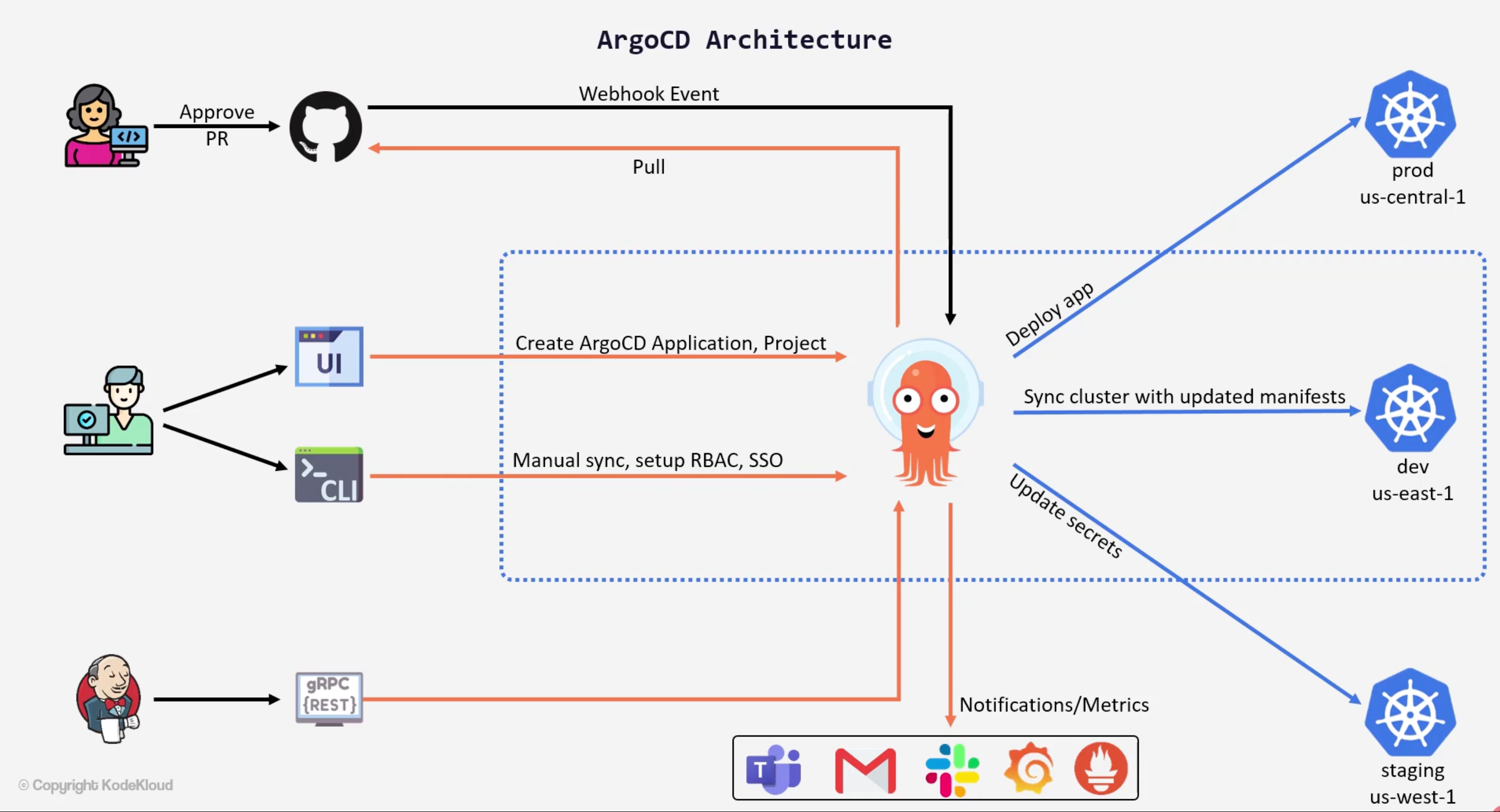
Architecture
Installation Options
kubectl create namespace argocd
kubectl apply -n argocd -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
helm repo add argo https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm
helm update
helm search repo argo
helm install my-argo-cd argo/argo-cd --version 4.8.0 # Default is the non HA version
To interact with the ArgoCD API server, we need to download the CLI.
curls -sSL -o /usr/local/bin/argocd https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/latest/download/argocd-linux-amd64
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/argocd
Applications
An application is a Kubernetes Custom Resource Definition (CRD) which represents a deployed application in a cluster. An application is defined by two pieces of information:
- The source: A Git repository and a path within that repository. Where the desired state of the kubernetes manifests live.
- The destination: A target cluster and namespace.
- Also: Project Name, Sync Policy, ...etc.
We can have in the source helm charts, kustomize, jsonnet, ...etc.
An application can be created using the CLI Yaml specification or the UI.
argocd app create color-app \
--repo https://github.com/sid/app-1.git \
--path team-a/color-app \
--dest-namespace color \
--dest-server https://kubernetes.default.svc
Once the application is created is pulls the application manifests from the git repository and applies them to the target cluster.
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: color-app
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/sid/app-1.git
targetRevision: HEAD
path: team-a/color-app
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: color
syncPolicy:
automated:
selfHeal: true
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
Demo CLI
argocd app create
argocd app list
argocd app create color-app \
--repo https://github.com/sid/app-1.git \
--path team-a/color-app \
--dest-namespace color \
--dest-server https://kubernetes.default.svc
argocd app sync color-app
Project
Create a custom project.
# The default project can deploy applications
# to any destination cluster and ALL namespaces
# and the B*tch can connect to any source!
# Wild, hmmm!
argocd proj list
k -n argocd get applications,appproj
# Let us create a better project ;)
argocd app create solar-system-app-2 \
--repo https://3000-port-6e66d15b8add4d94.labs.kodekloud.com/bob/gitops-argocd \
--path solar-system \
--dest-namespace solar-system \
--dest-server https://kubernetes.default.svc
Reconciliation loop
The reconciliation function tries to bring the actual state of the cluster to the desired state.
The reconciliation loop is how often your argoCD application will sync from git.
The default timeout is 3 minutes. It is called the application reconciliation timeout.
kubectl -n argocd describe po argocd-repo-server | grep -i reconciliation
kubectl -n argocd patch configmap argocd-cm -p '{"data": {"timeout.reconciliation": "300s"}}'
kubectl -n argocd rollout restart deploy argocd-repo-server
# Now it will check for changes in GIT repo every 5 minutes
kubectl -n argocd describe po argocd-repo-server | grep -i reconciliation -B1
The api-server can be setup to receive webhooks events in order to remove the pulling delay.
Within our git provider we can setup a webhook to send a POST request to the argoCD api-server.
Health Checks

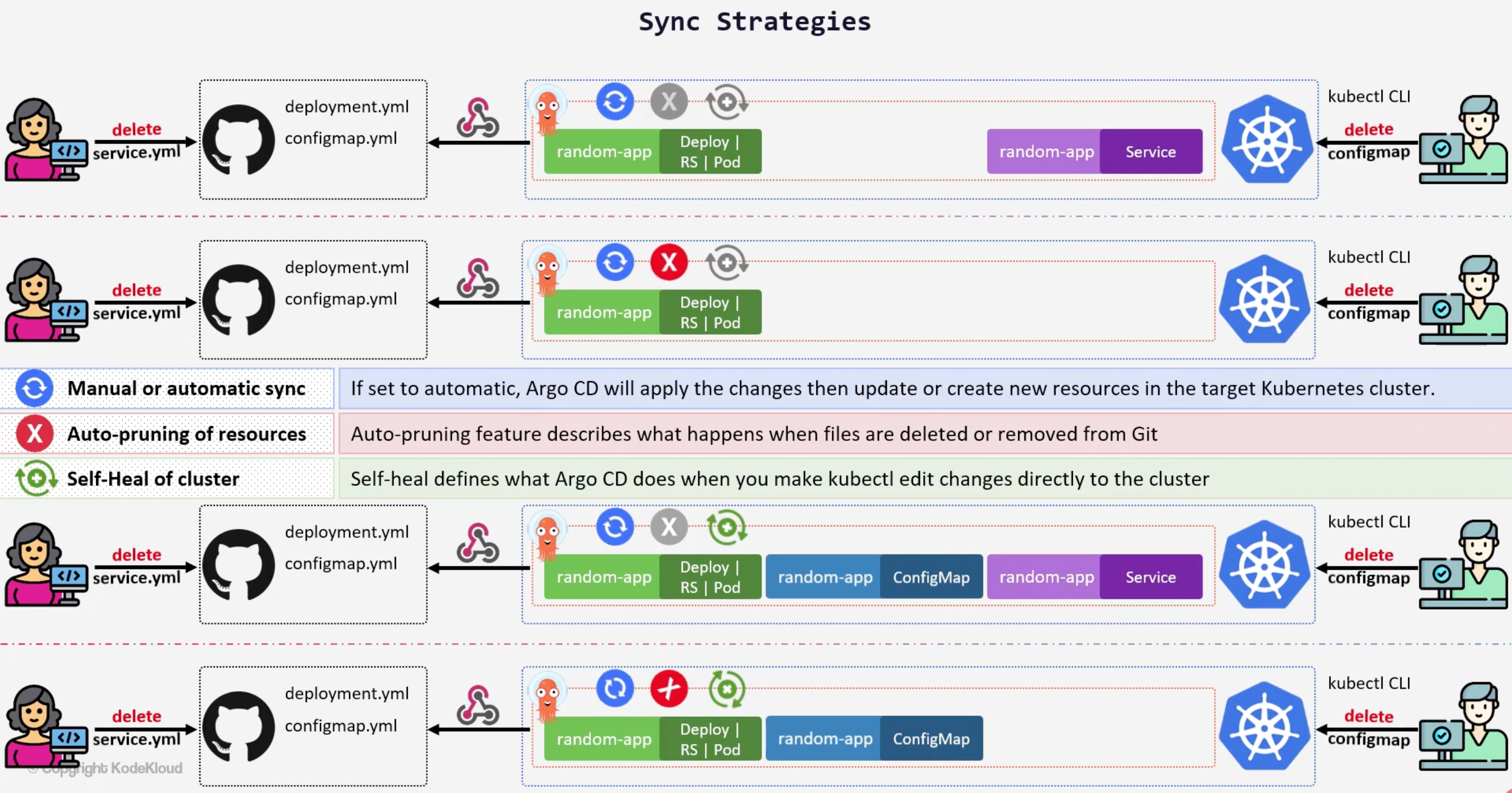
Sync Strategies
Declarative
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: geocentric-model-app
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/sidd-harth/test-cd.git
targetRevision: HEAD
path: ./declarative/manifests/geocentric-model
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: geocentric-model
syncPolicy:
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
App of Apps
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: app-of-apps
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/sidd-harth/test-cd.git
targetRevision: HEAD
path: ./declarative/app-of-apps
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: argocd
syncPolicy:
automated:
prune: true
selfHeal: true
apiVersion: argoproj.io/v1alpha1
kind: Application
metadata:
name: circle-app
namespace: argocd
spec:
project: default
source:
repoURL: https://github.com/sidd-harth/test-cd.git
targetRevision: HEAD
path: ./declarative/manifests/circle
destination:
server: https://kubernetes.default.svc
namespace: circle
syncPolicy:
syncOptions:
- CreateNamespace=true
kubectl -n argocd apply -f app-of-apps.yaml
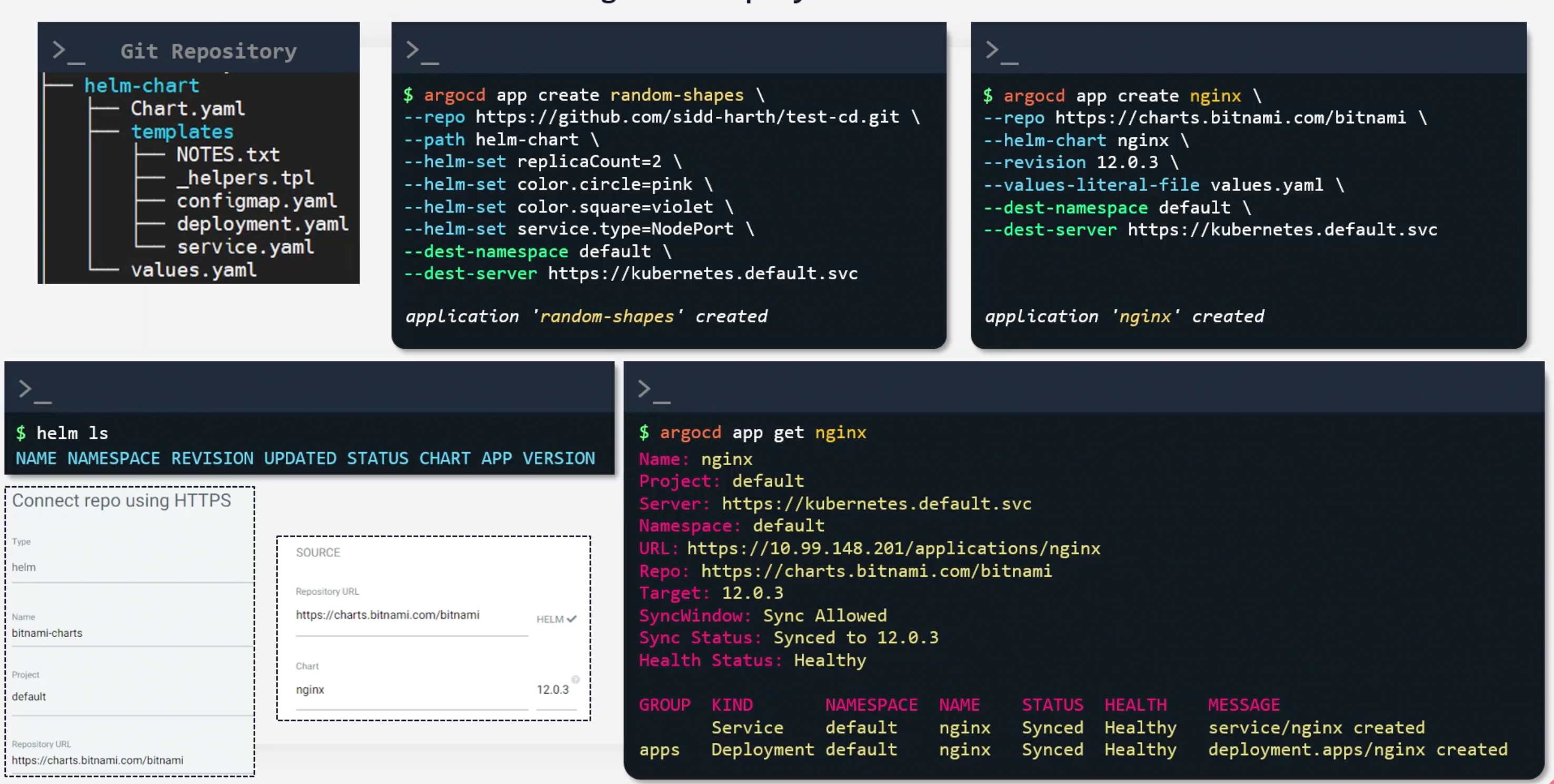
Helm�
Remember:
Chart.yaml.templates/NOTES.txt.templates/_helpers.tpl.
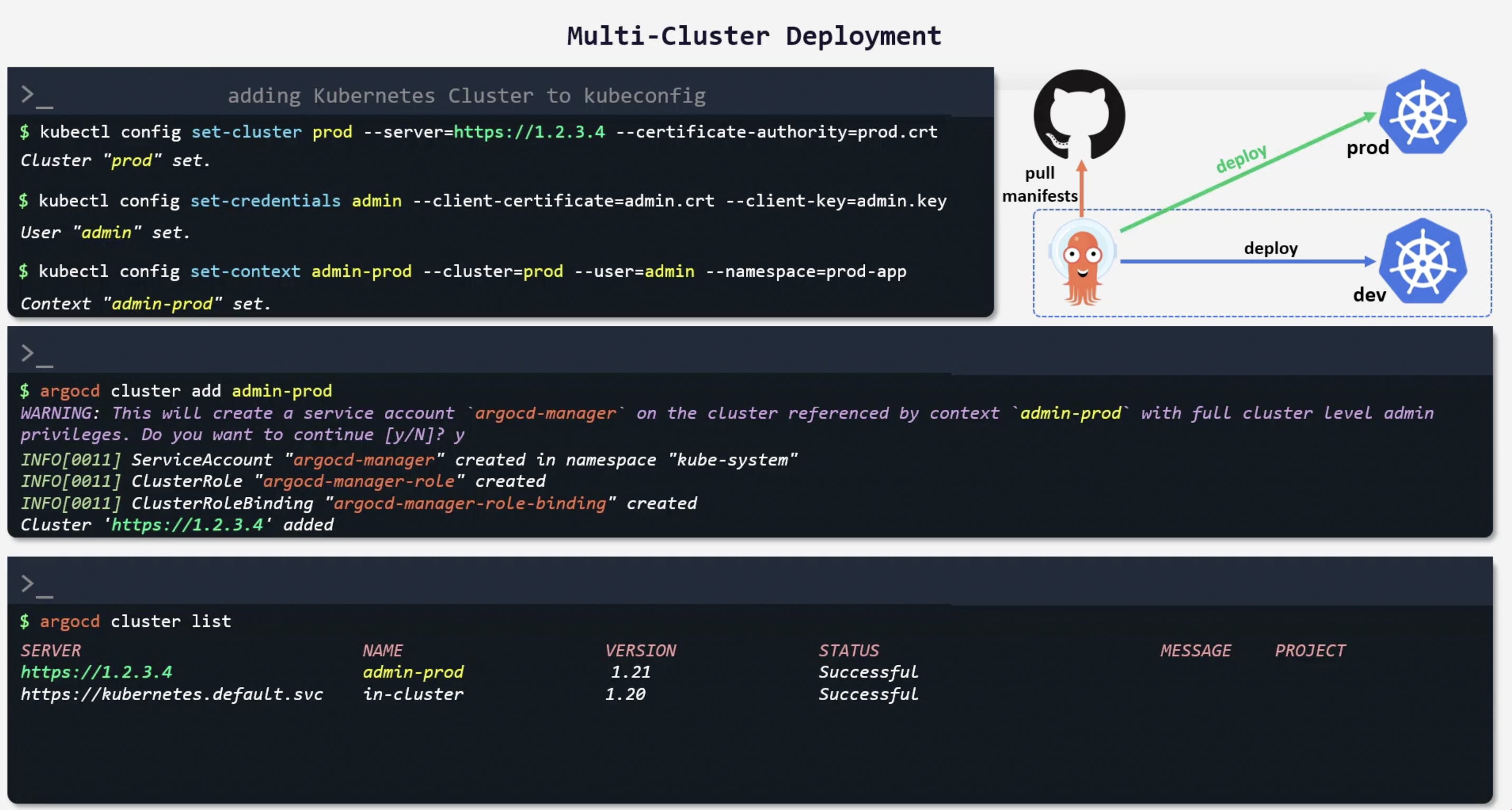
Multi Cluster Deployment
RBAC

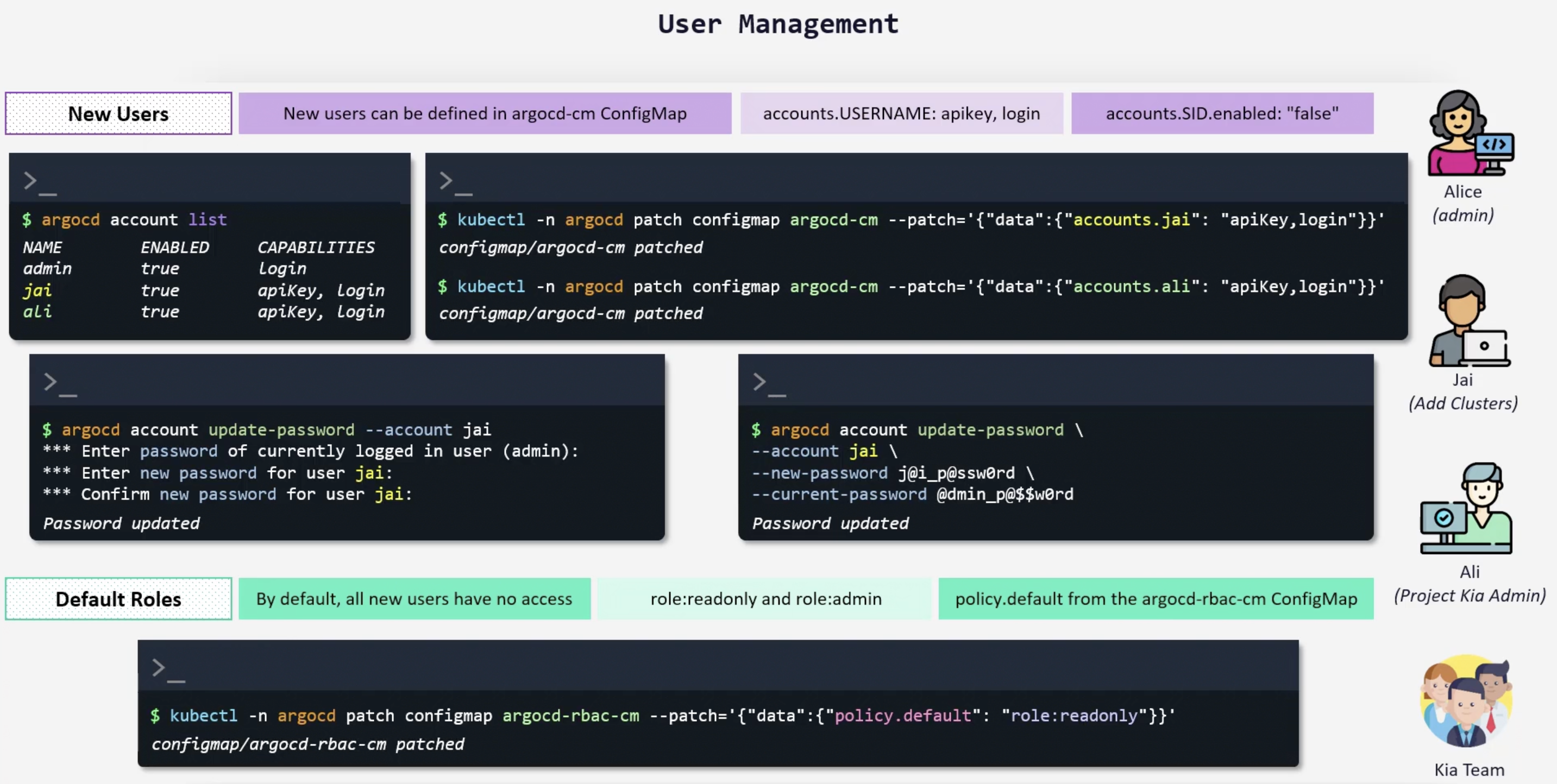
User Management
Local user management
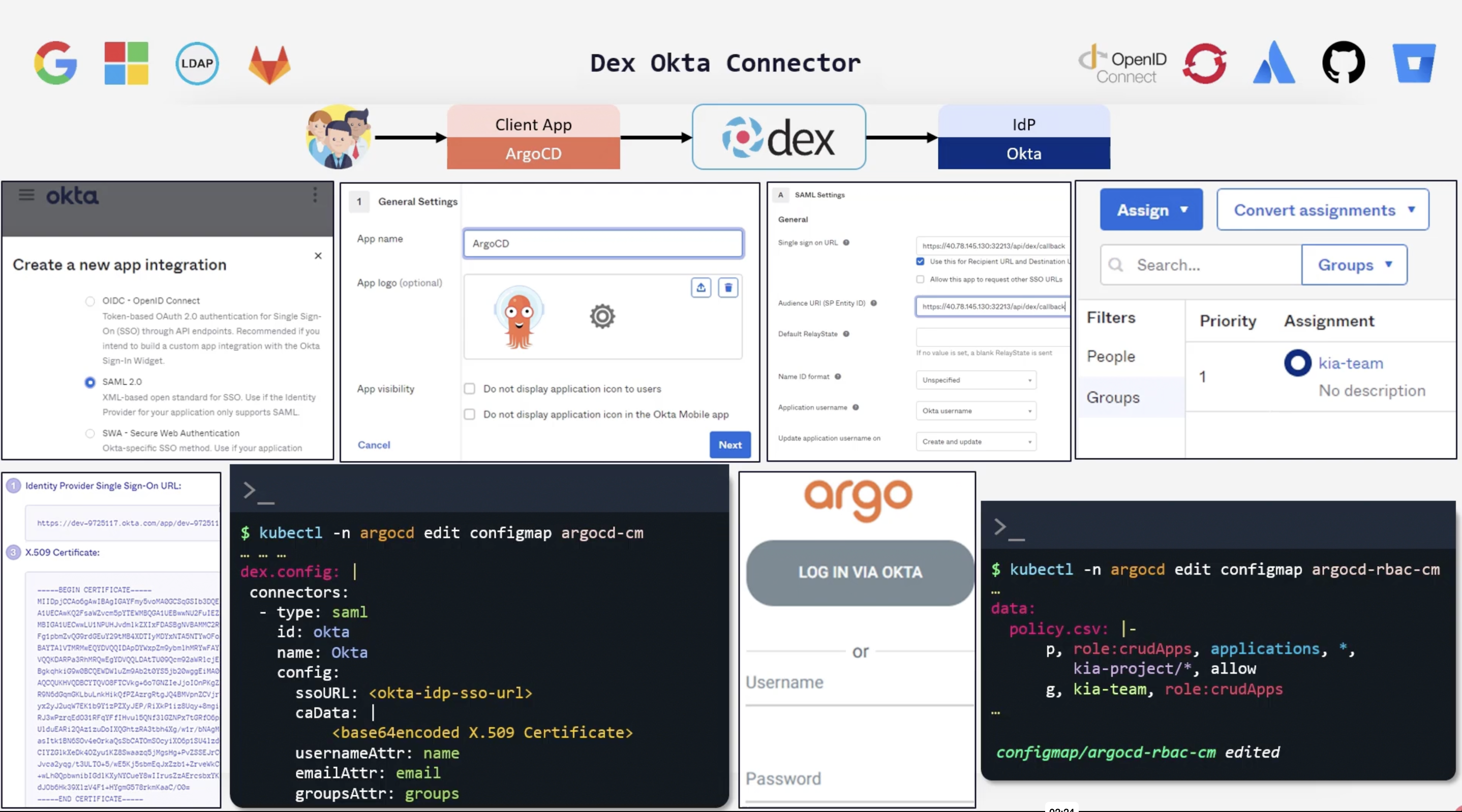
Dex Okta Connector
Dex is an identity service that uses OpenID Connect to drive authentication for other apps. When a user logs in using dex, the user's identity is usually stored and authenticated by an external identity provider iDp like Okta, Google, GitHub, ...etc.
Dex acts as a shim between client application and the identity provider. In this example, the client application is ArgoCD and the IdP is Okta.
Dex supports multiple IdPs. If we go with okta we can go with a SAML application.
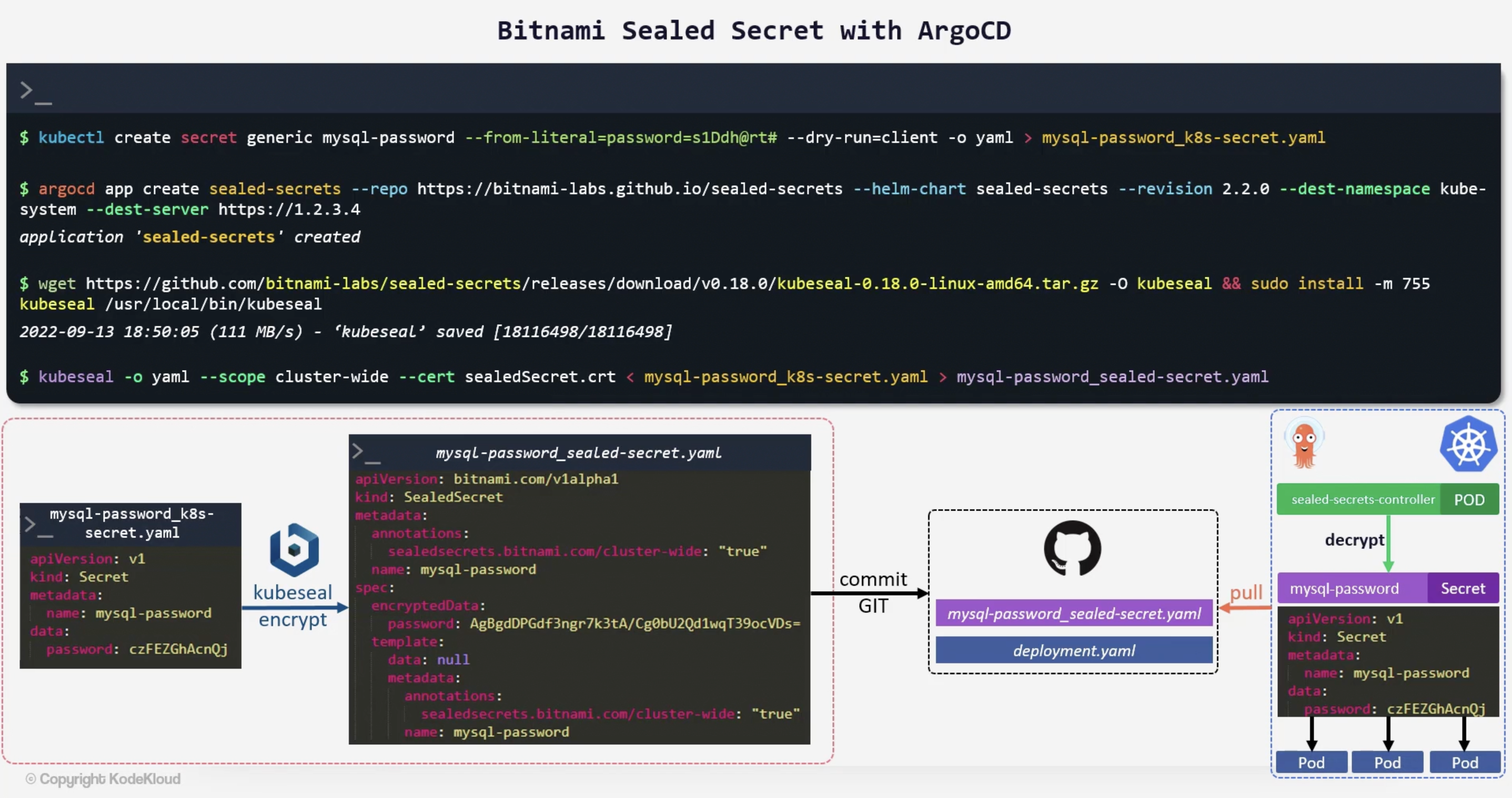
Bitnami Sealed Secrets
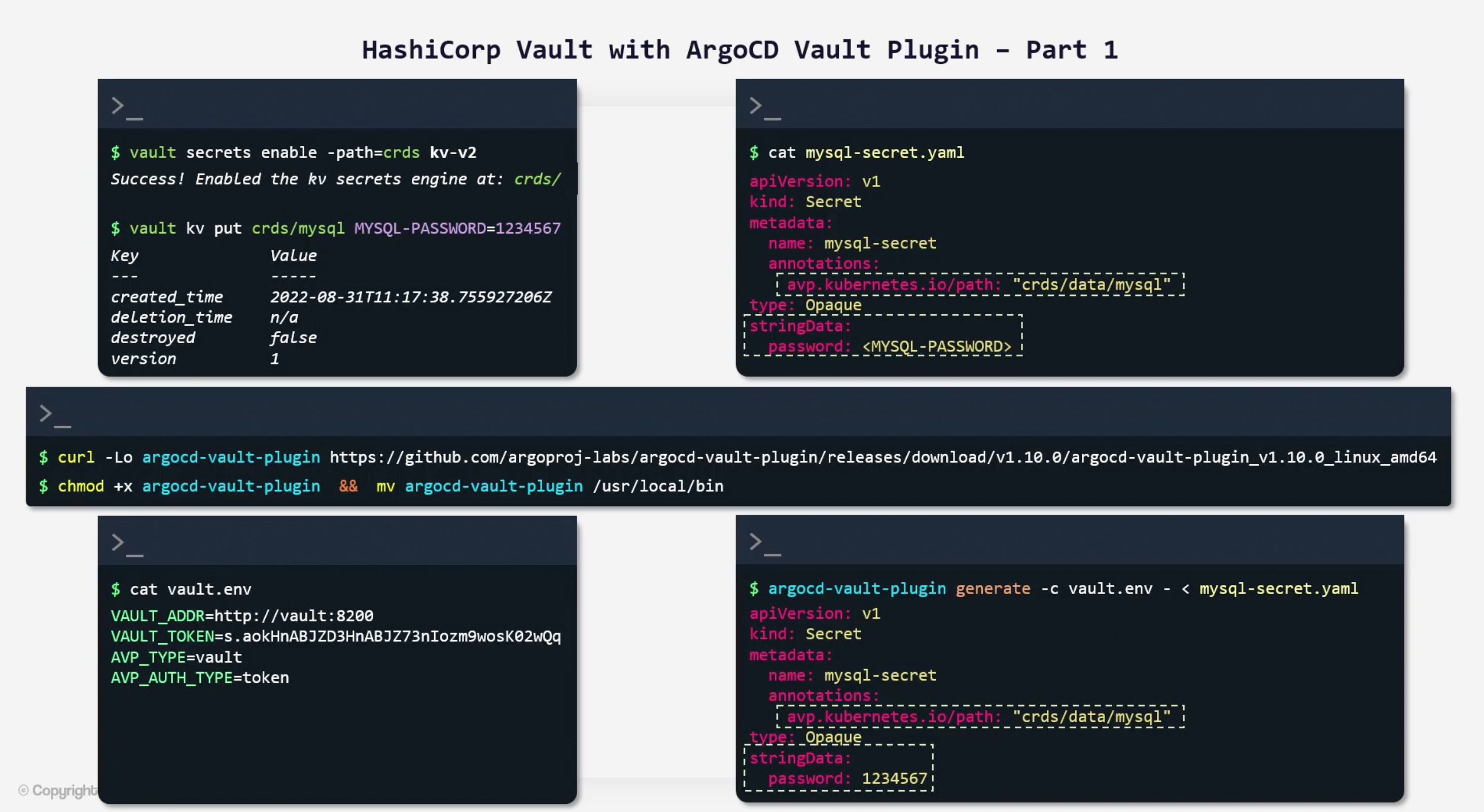
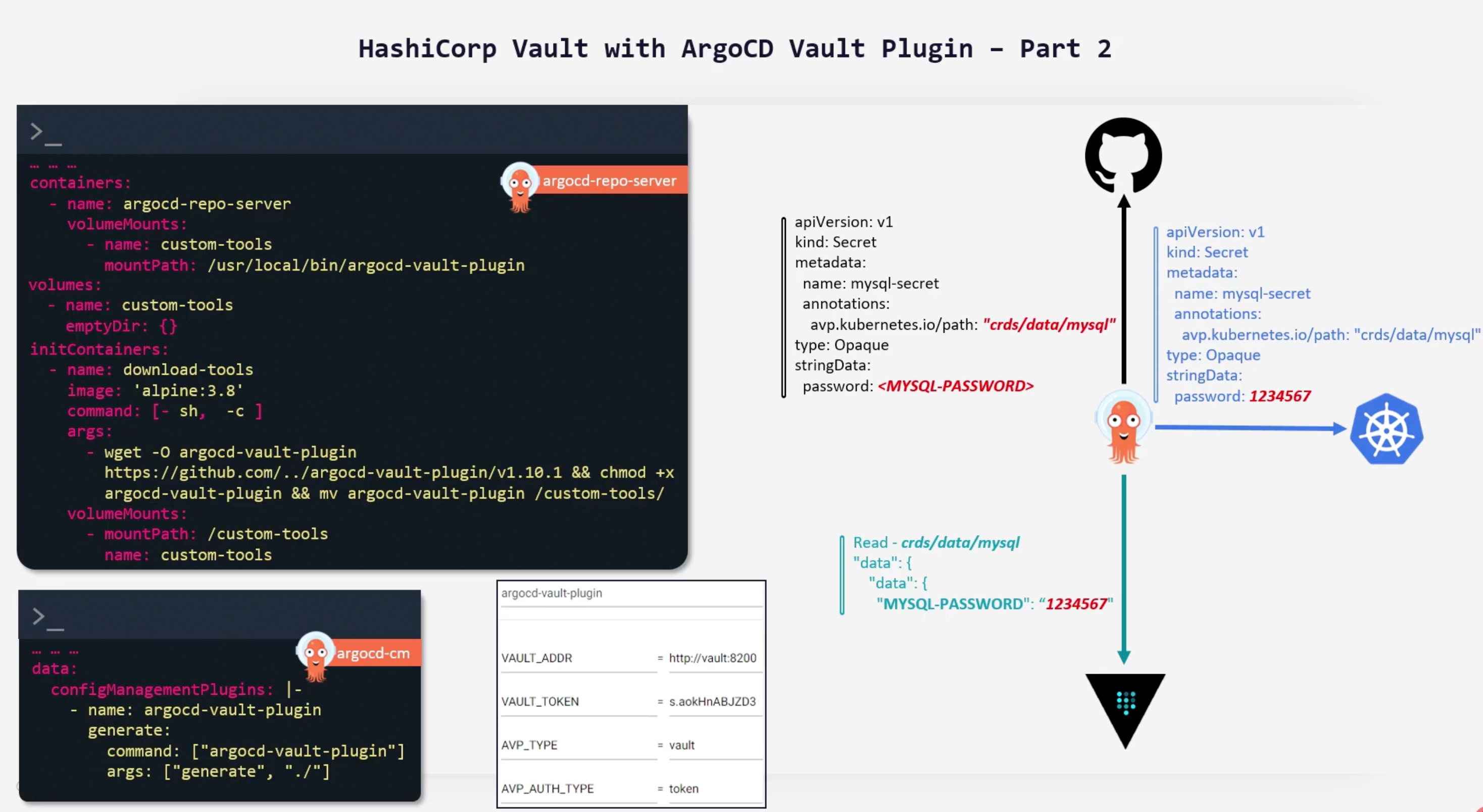
Vault
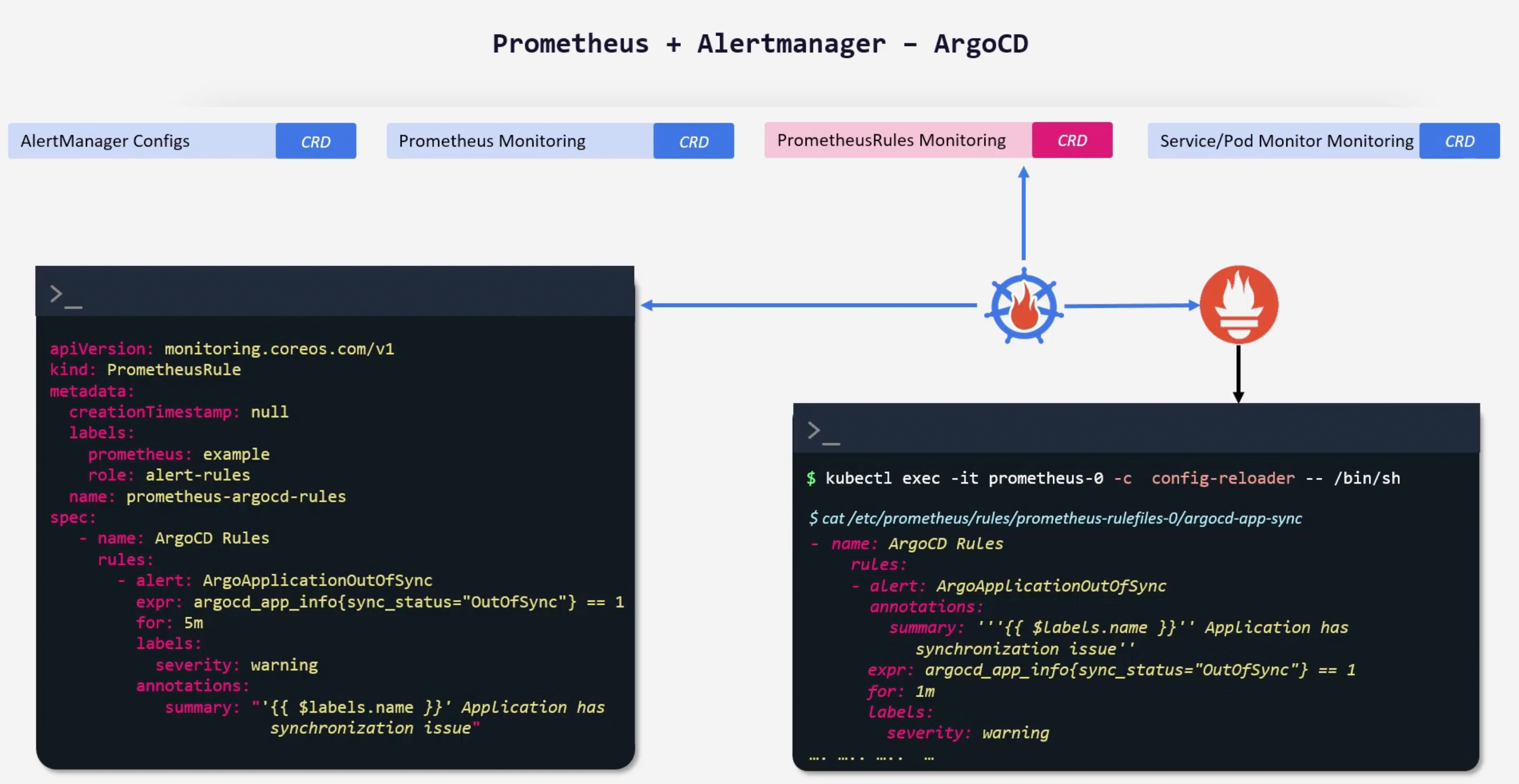
Alertmanager
Notification
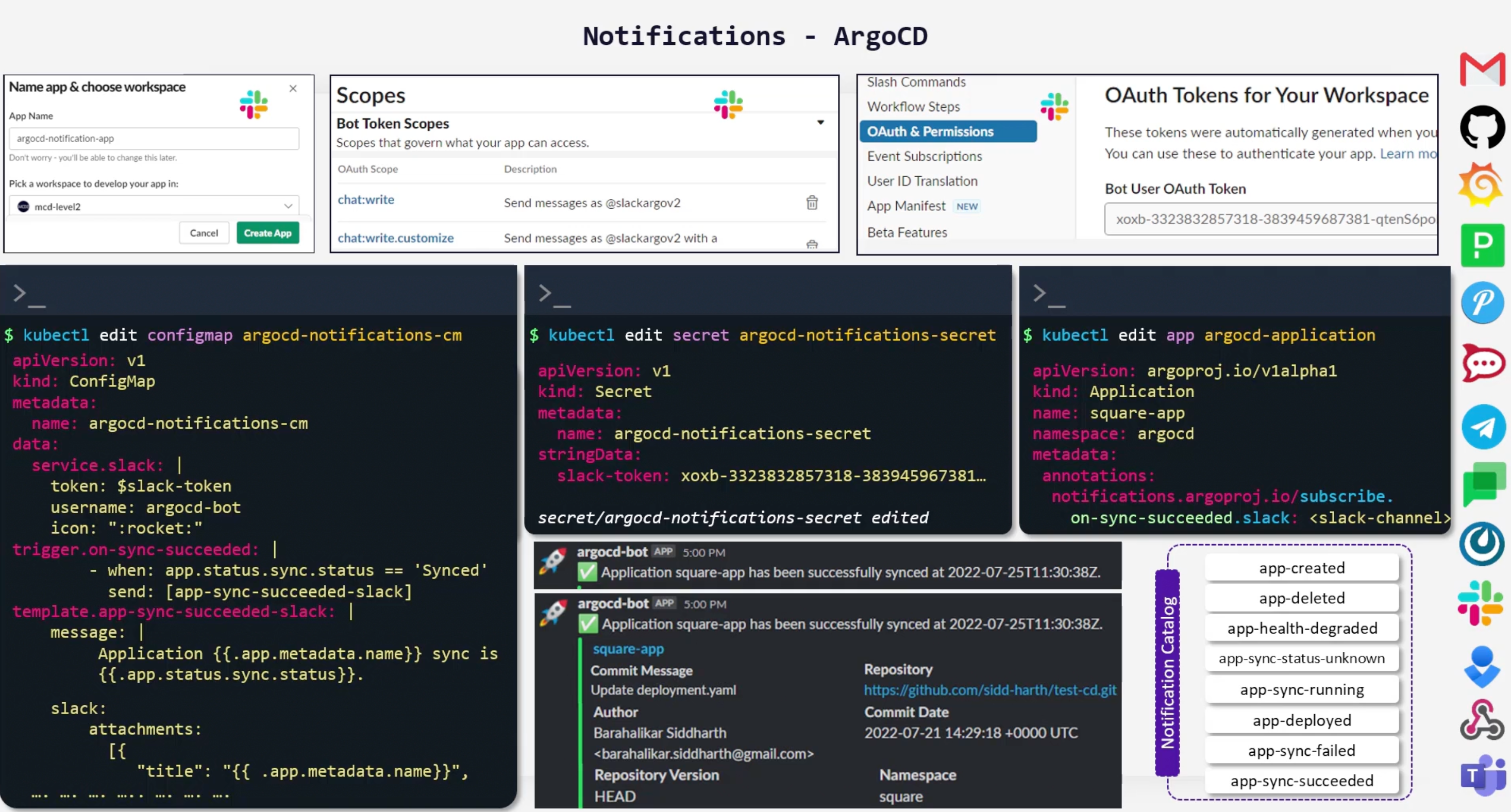
CICD & GitOps