Network Services
Perquisites
| Prefix | First Ip Address | Last Ip Address | Number of Addresses |
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.0.0.0/8 | 10.0.0.0 | 10.255.255.255 | 16,777,216 |
| 172.16.0.0/12 | 172.16.0.0 | 172.31.255.255 | 1,048,576 |
| 192.168.0.0/16 | 192.168.0.0 | 192.168.255.255 | 65,536 |
- For TCP and UDP, a port number is a 16-bit unsigned integer, thus ranging from 0 to 65535.
- Ephemeral ports are
1024to65,535.
| Port Range | Description |
|---|---|
| 0 - 1023 | Well Known Ports |
| 1024 - 49,151 | Registered Ports |
| 49152 - 65,535 | Dynamic and/or Private Ports |
VPC
Stands for Virtual Private Cloud. Allows us to isolate recourses from other resources. VPC gives you full control over networking in the cloud:
- Subnetting.
- Routing.
- Firewalls "NACLS, Security Groups".
- Gateways.
VPCs are region specific. They can't span more than one region.
VPCs by default act as network boundaries.
- Every VPC has a
CIDR blockthat defines the range of IP addresses that resources in the VPC can use. - A CIDR can be anywhere from
/16to/28.
- You can enable an
Optionalsecondary IPv4 CIDR block. - You can enable
IPv6/56CIDR block. - You can have up to
5 IPv6CIDR blocks, but this limits is adjustable.
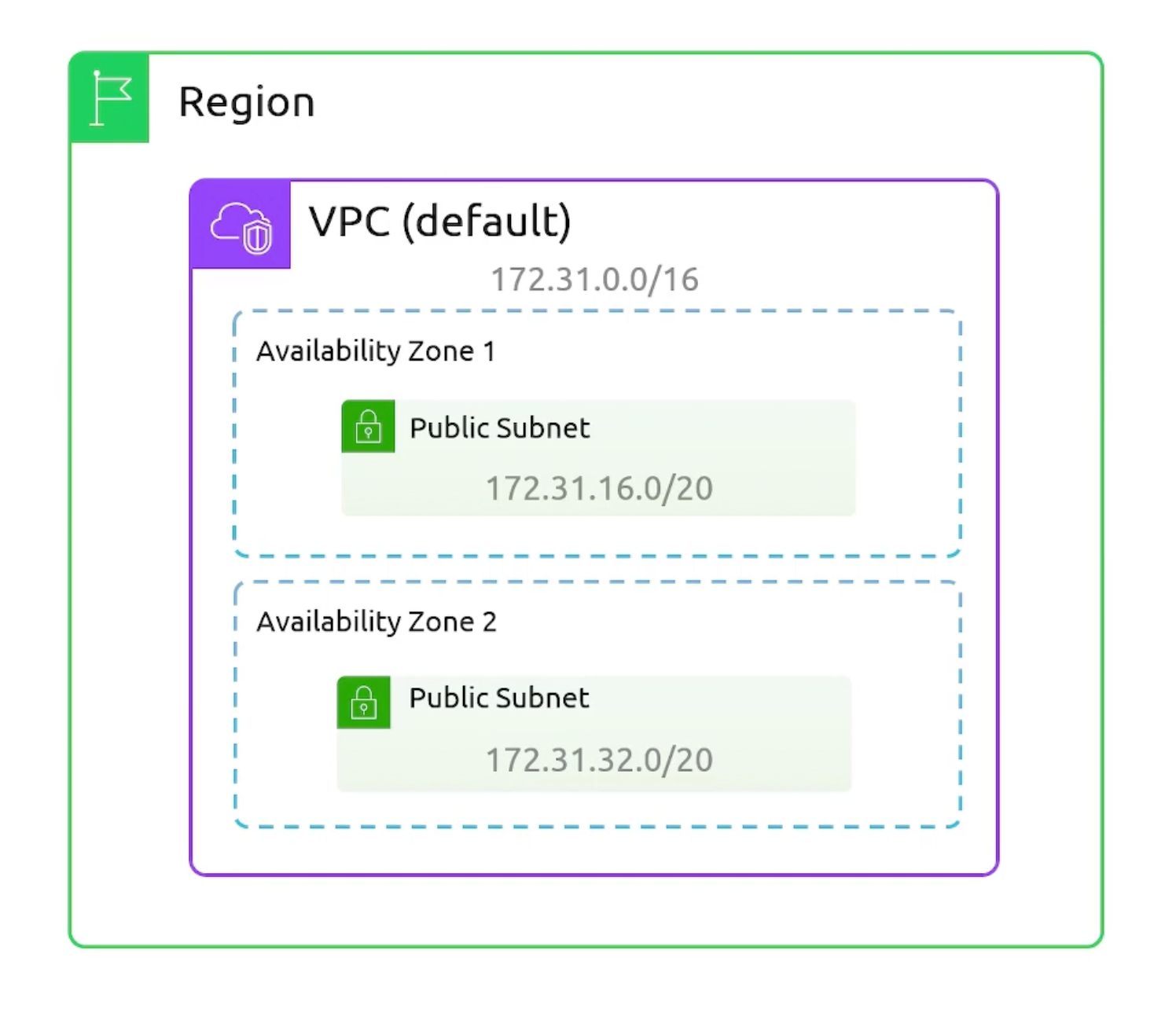
Default VPC
Default VPCs allow internet connectivity for all your resources by default.
/16IPv4 CIDR block172.31.0.0/16(65,536 addresses).
- For every availability zone: One
/20default subnet (4,096 addresses) iscreated. - Auto-assign public IP addresses is
enabledby default inside each default subnet.
- Default VPCs have an
Internet Gatewayattached by default. - A route that points all traffic
0.0.0.0/0to the Internet Gateway. - Devices in the default subnets will be accessible from the internet.
- Default Security Group that allows all outbound traffic.
- Default
Network Access Control List - NACLthat allows all traffic in and out.
Subnets
Are groups of IP addresses within your VPC.
- Subnets reside within a single AZ.
- Subnets within a VPC must be within the CIDR range.
- subnets can't overlap with other subnets in the VPC.
- Subnets block size must be between
/16and/28. - subnets can be made
publicorprivate.
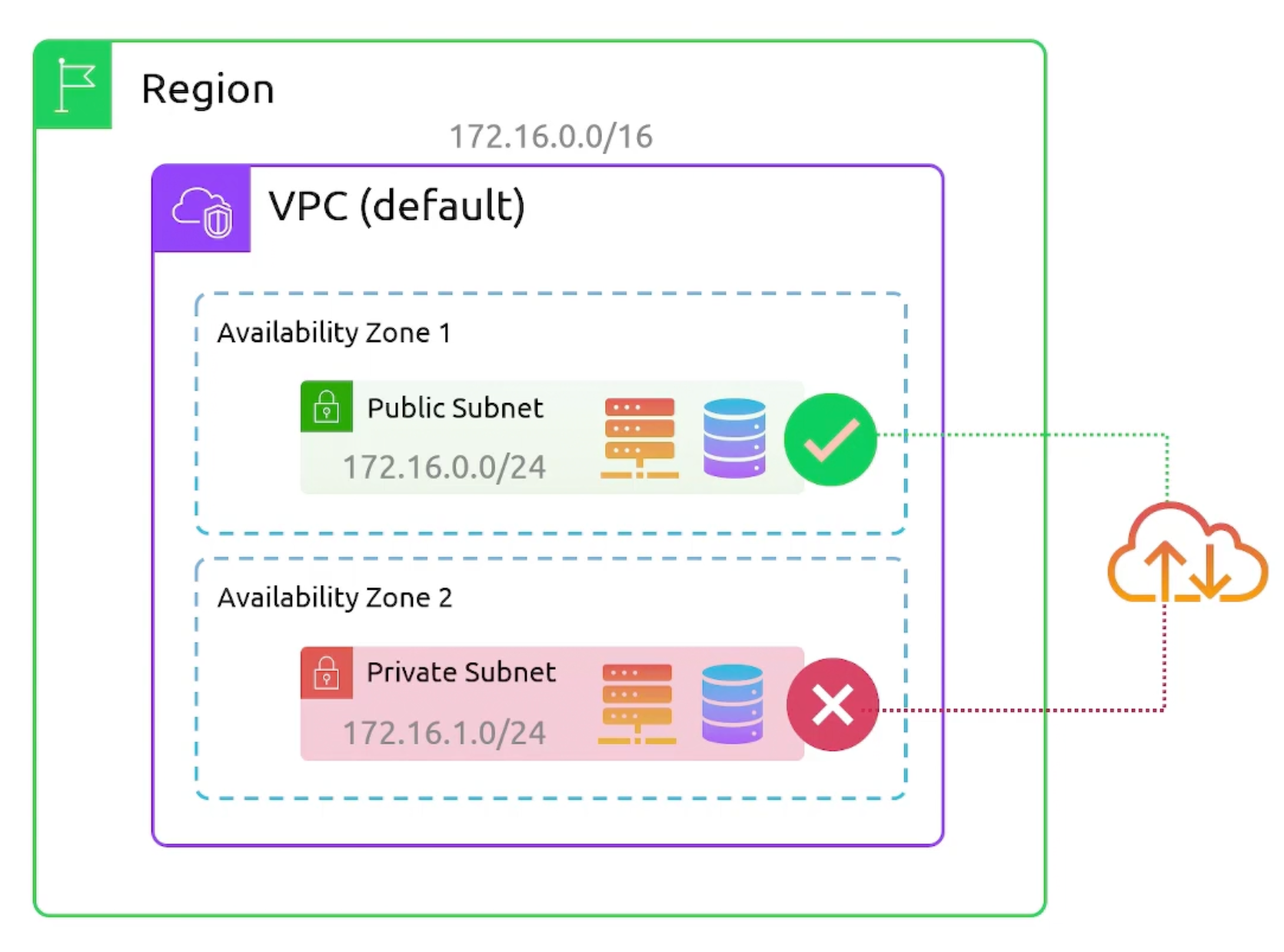
- A subnet allows for an
Optional IPv6 /56CIDR block. - A subnet can be configured to be IPv6 only.
- By default, subnets can talk to other subnets within the same VPC. Without the need for anything.
The first four IP addresses and the last IP address in each subnet CIDR block are reserved by AWS.
Example 192.168.10.0/24:
192.168.10.0Network Address.192.168.10.1(VPC Router) Reserved byAWS.192.168.10.2(DNS) Reserved byAWS.192.168.10.3(Future use) Reserved byAWS.- last IP address of a subnet (
192.168.10.255) is reserved as the broadcast address.
Routing in a VPC
- Every VPC has a
vpc-router. - This router has an interface in each subnet.
- Can be reached for
network+1Ip address.- For subnet
192.168.1.0/24the router interface in the subnet is192.168.1.1.
- For subnet
- The purpose of the router is to direct traffic between subnets and in/out of the VPC.
- You can configure the router with
Route Tables.
Route Tables
- A set of rules that the router uses to forward network traffic.
- One default route table is created automatically for each VPC.
- Each rule is called a
route. - The router will compare the destination IP address of the packet to the routes in the route table.
In case of overlapping routes, pick the rule that has a larger prefix. /16 is larger than /8.
All route tables have exactly one route by default. This route sends all traffic to the local VPC.
- A subnet can only be associated with one route table at a time.
- Multiple subnets can be associated with the same route table.
Why would we need multiple route tables?
You might have different rules:
- Public subnets associated with public-route-table.
- Private subnets associated with private-route-table.
Internet Gateway
- An
Internet Gatewayis a virtual router that connects a VPC to the internet. - When you create a subnet, it will be
privateby default. - Internet Gateway is attached to the VPC.
region-resilient: Cover all AZs in the region.A VPC can have up to one Internet Gateway attached to it.- An Internet Gateway can only be attached to a single VPC at a time.
- Public Subnet
- Private Subnet
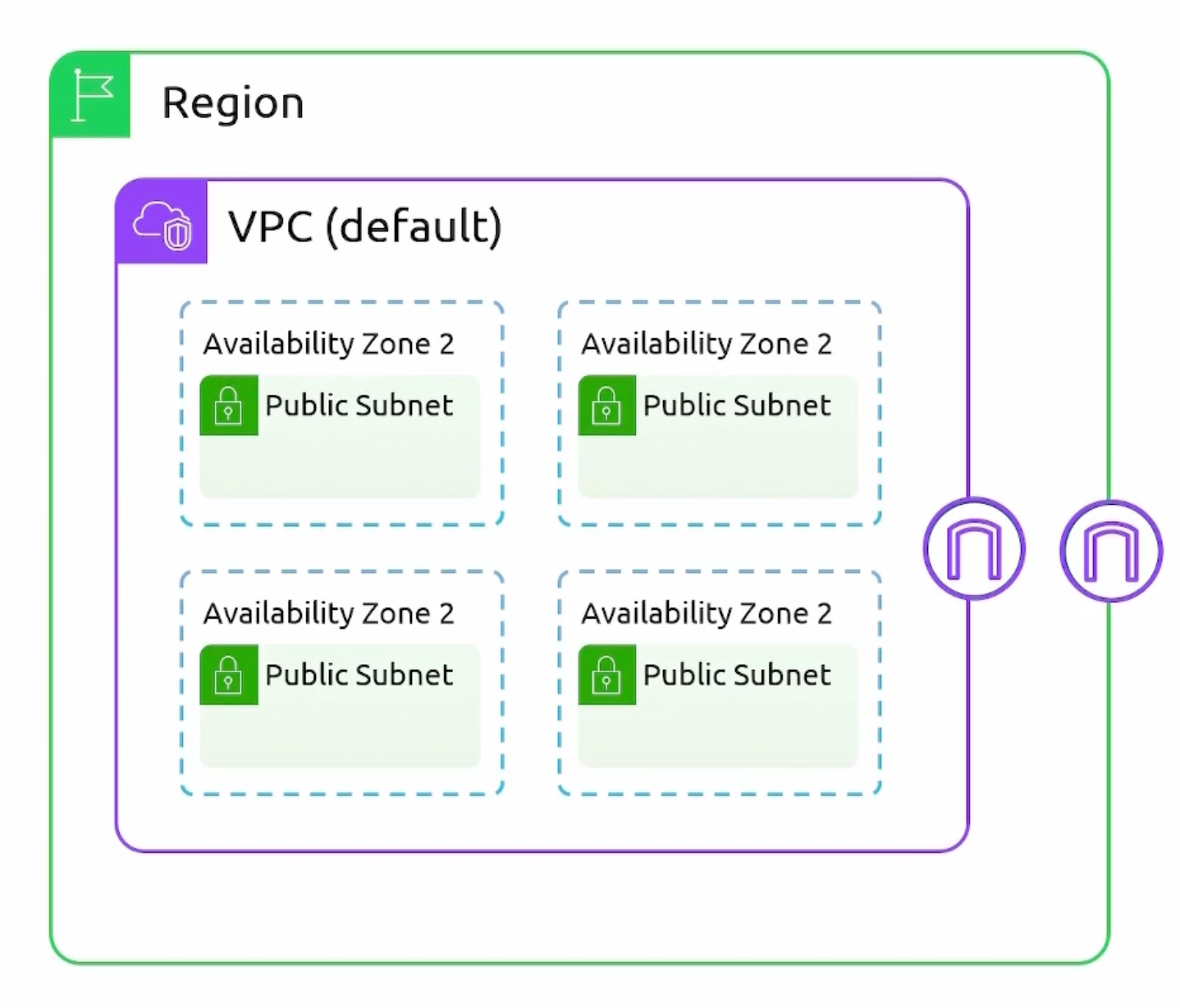
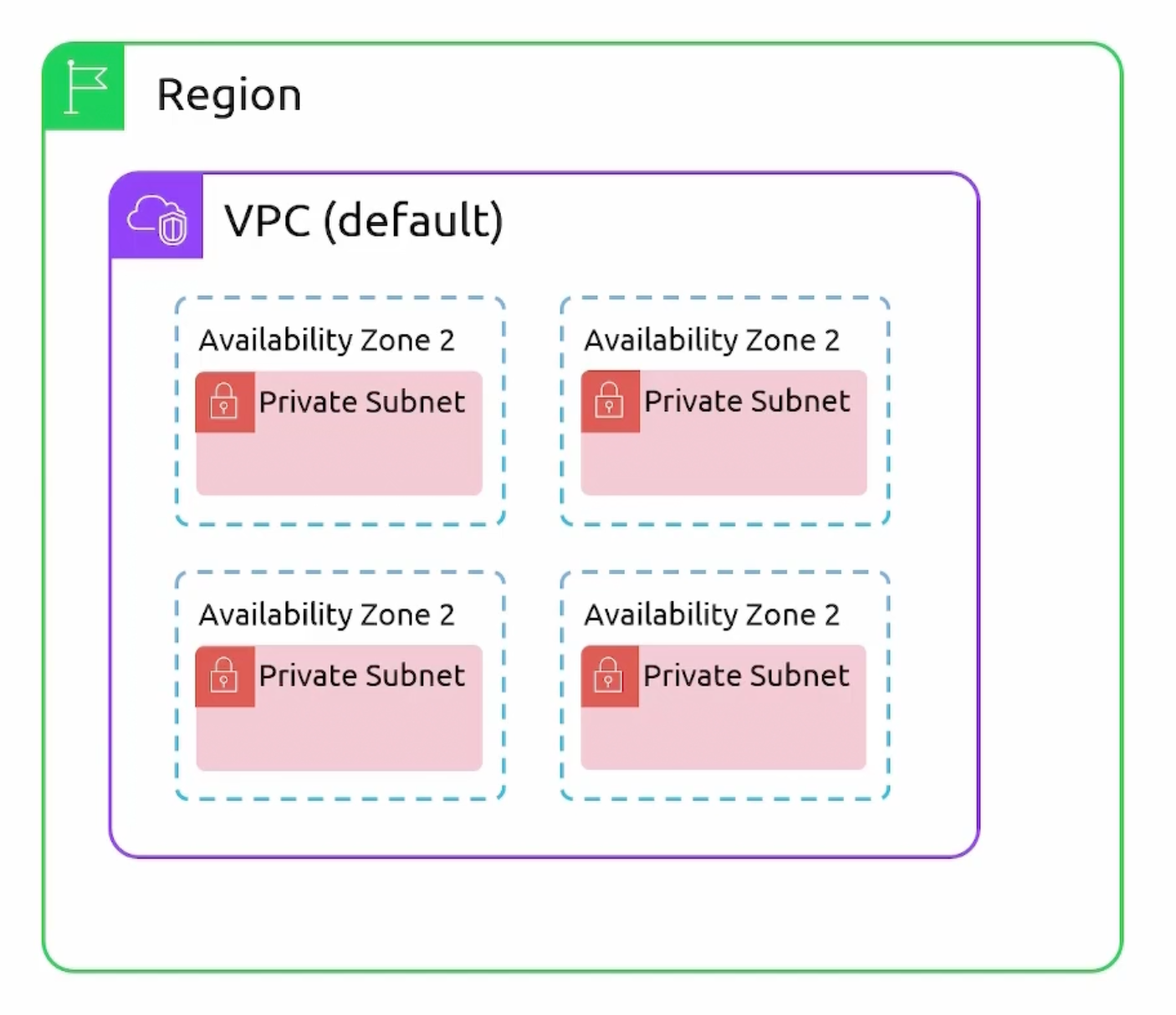
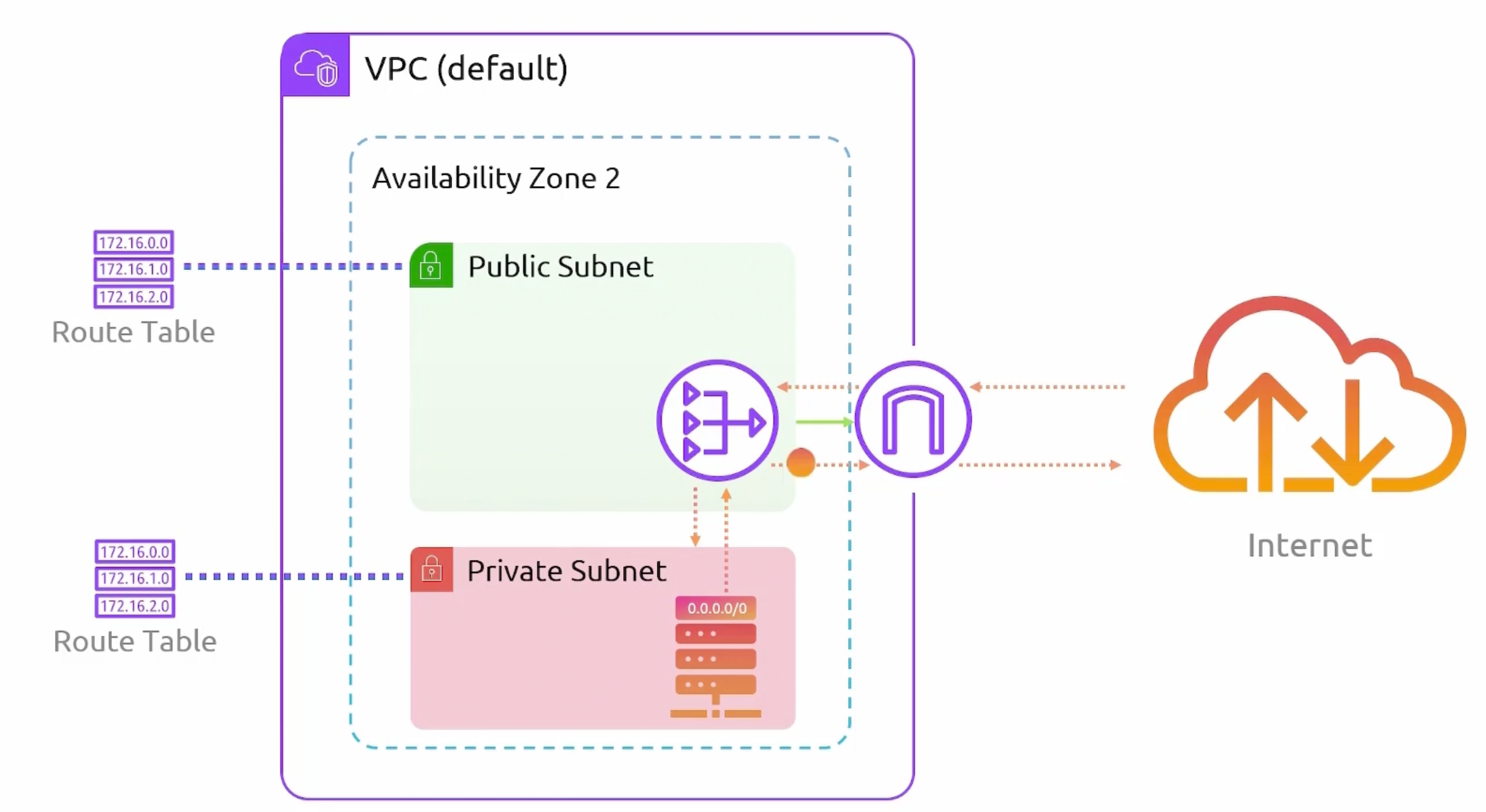
How to make a subnet public?
- Create an Internet Gateway (
IGW). - Attach the
IGWto the VPC. - Create a custom route table. Configure a
default routepointing to theIGW. - Associate the public subnet with the custom route table.
Your public IP is associated to your private IP. Linked together.
If you have multiple interfaces, each can have a public IP.
NAT Gateway
NATstands forNetwork Address Translation.- A NAT Gateway is a highly available AWS
managed servicethat allows your resources in a private subnet to access the internet. - Pricing: You pay hourly for the NAT Gateway and for the data processed.
NAT Gatewayis NOT region-resilient. AZ-reliant service. Need one NATGW per AZ.NAT Gatewayuses anElastic IPaddress.NAT Gatewaysare deployed to a public subnet to have internet access.- Route tables for private subnets should have a default route pointing to the
NAT Gateway. - A
NAT Gatewaysupports up to5 Gbpsof bandwidth and automatically scales up to100 Gbps.
- NAT Gateway
- NAT Gateway HA
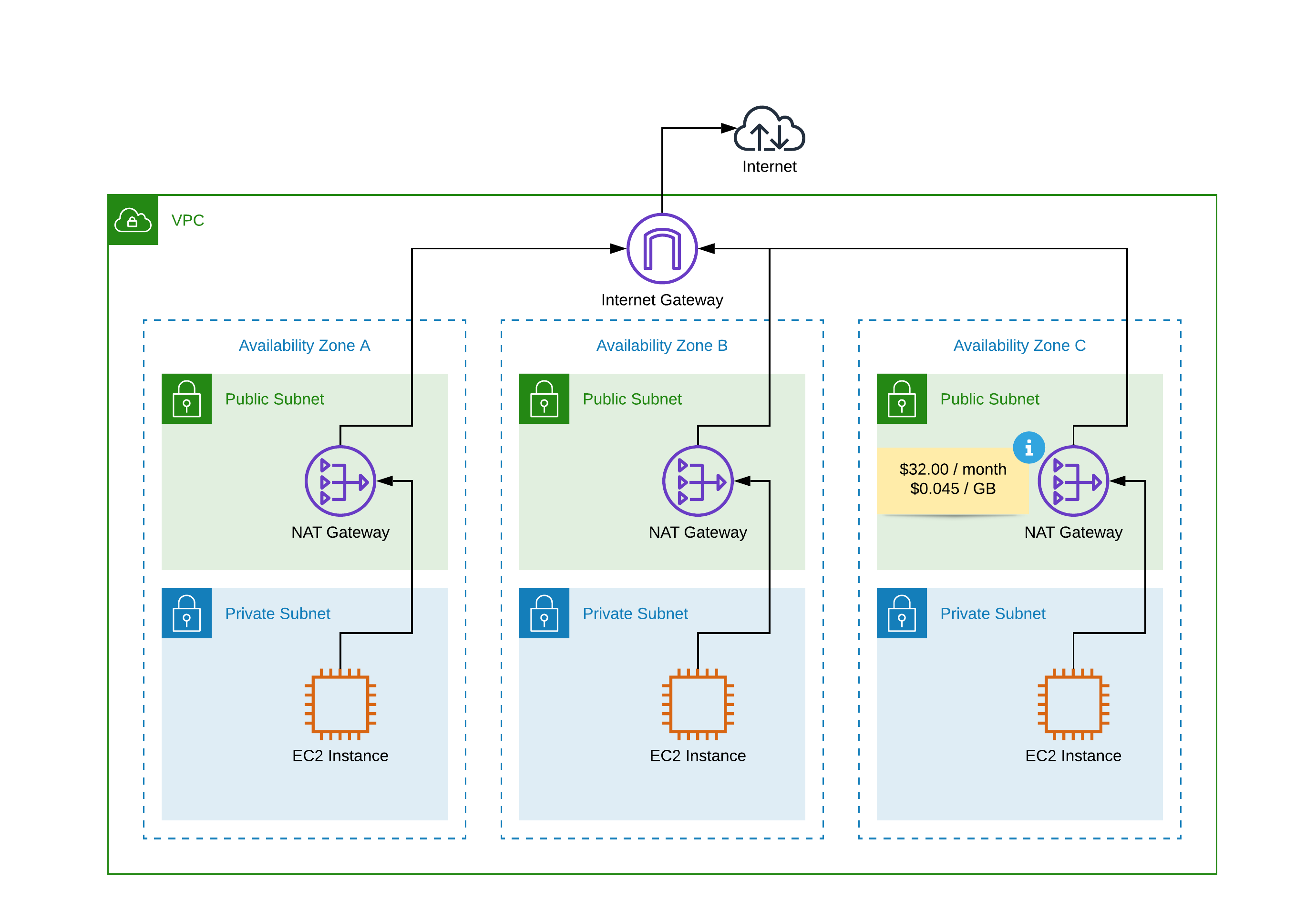
If you need to egress traffic via a NATGW that is not in the same AZ you will incur intra-AZ bandwidth costs of 0.01 USD/GB in addition to the 0.045 USD/GB NATGW bandwidth.
DNS Resolution in VPCs
- Query
169.254.169.253for DNS resolution. - Second IP address of the
VPC.
By default, only private IP addresses will get a domain name. You can enable domain names for public IP addresses by:
- Enabling
enableDnsHostnameswhen you craete aVPC. - Enabling
enableDnsSupportwhen you create aVPC.
Elastic IP Addresses
A static IP address designed for dynamic cloud computing.
When you stop and start or reboot an EC2 instance, the public IP address will change.
- You can assign security groups to an Elastic IP.
- They are specific to a region.
- Comes from
Amazon's pool of public IP addressesor you can bring your own IP address.
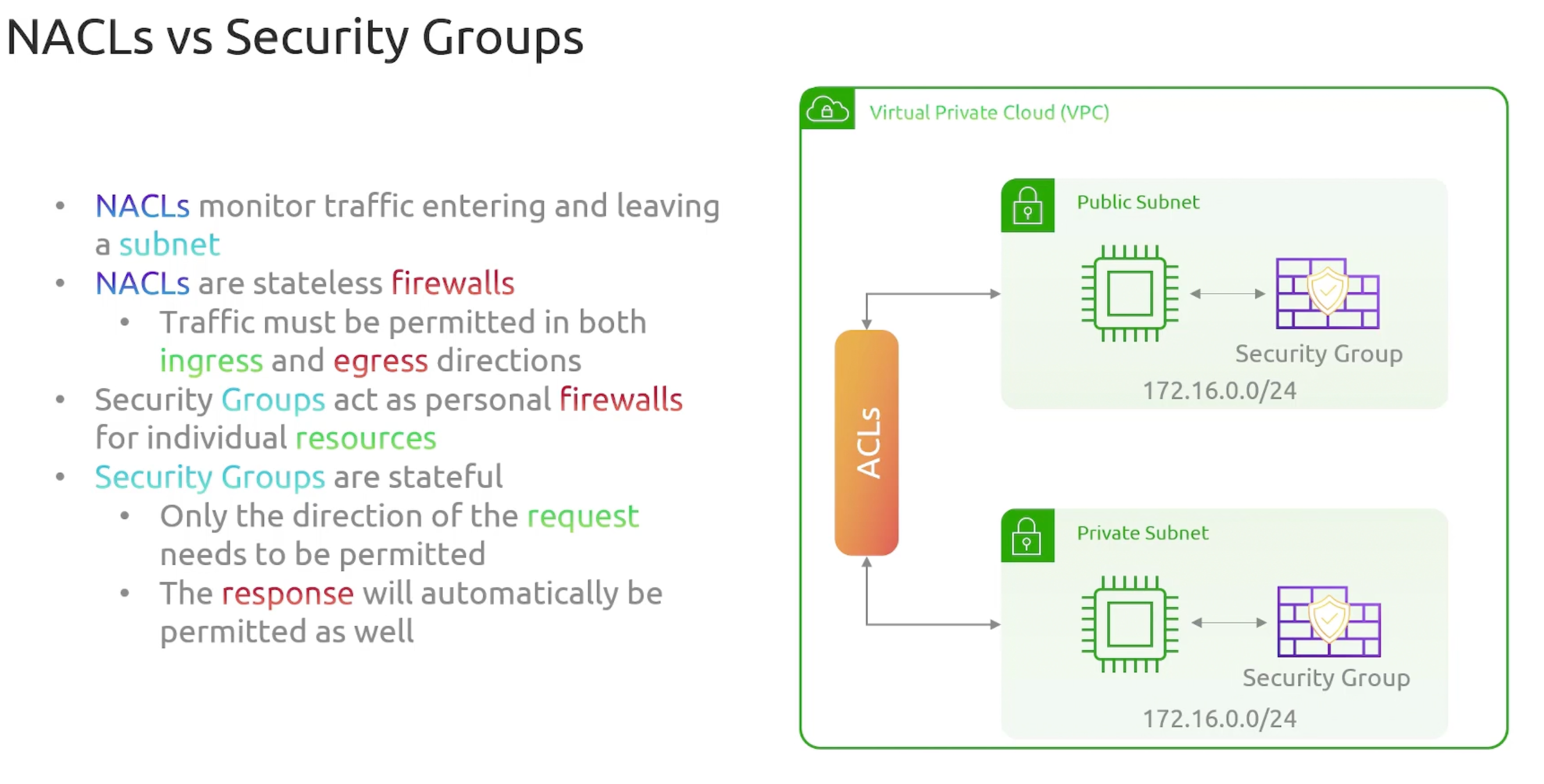
Security Groups and NACLs
Security Groups and NACLs act as firewalls.
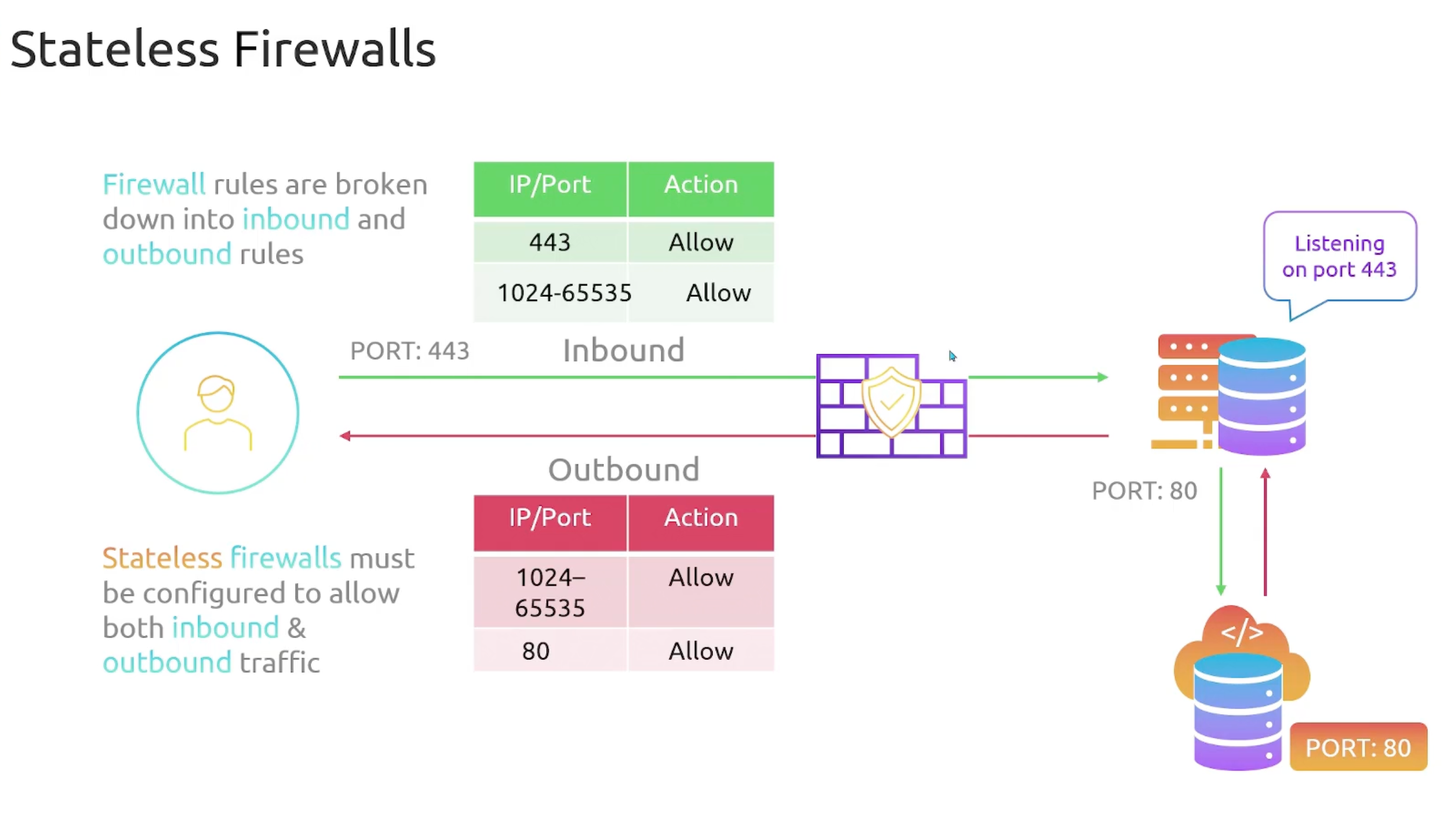
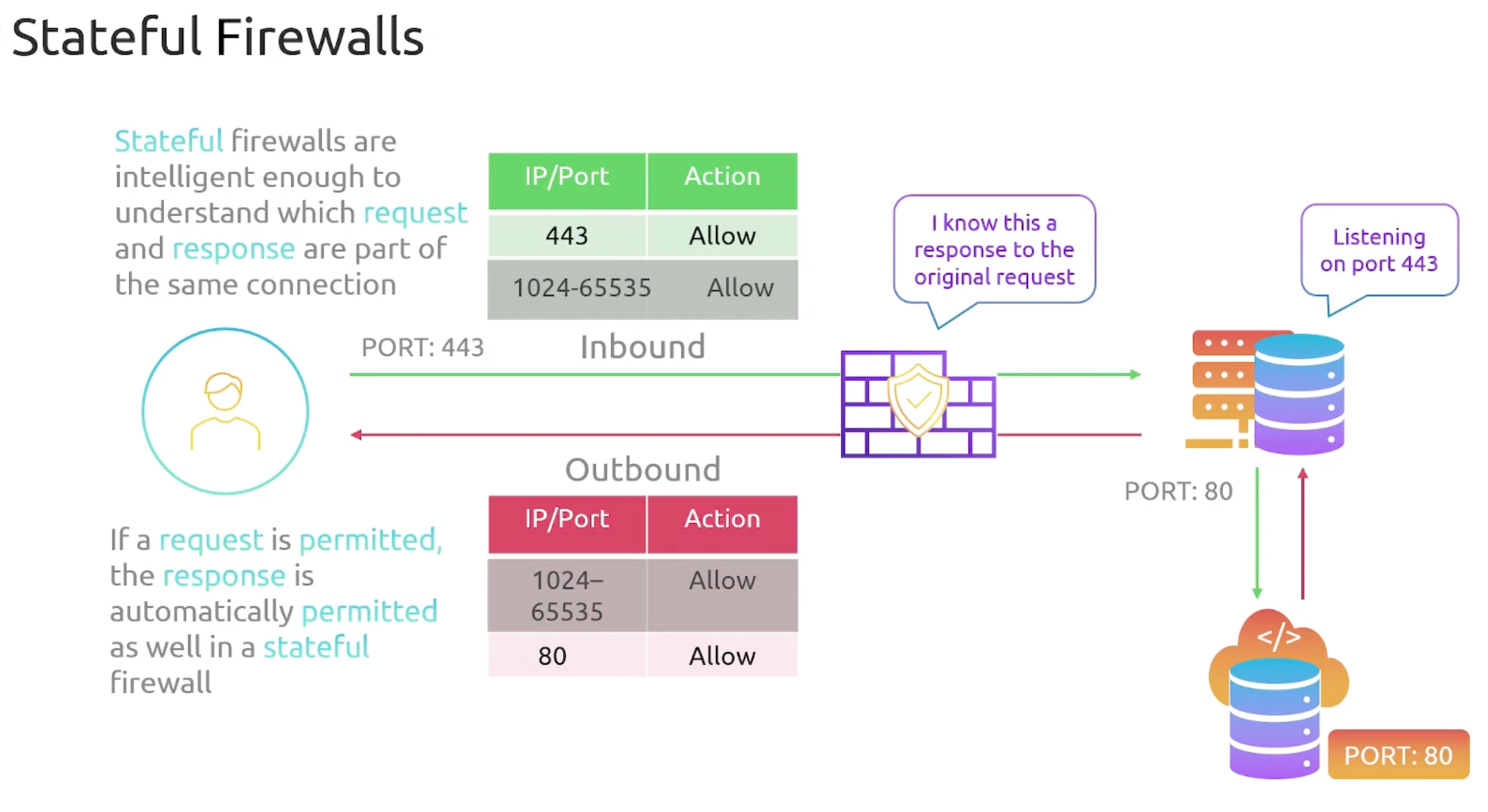
Firewall Types
- Stateless Firewall
- Stateful Firewall
NACLs
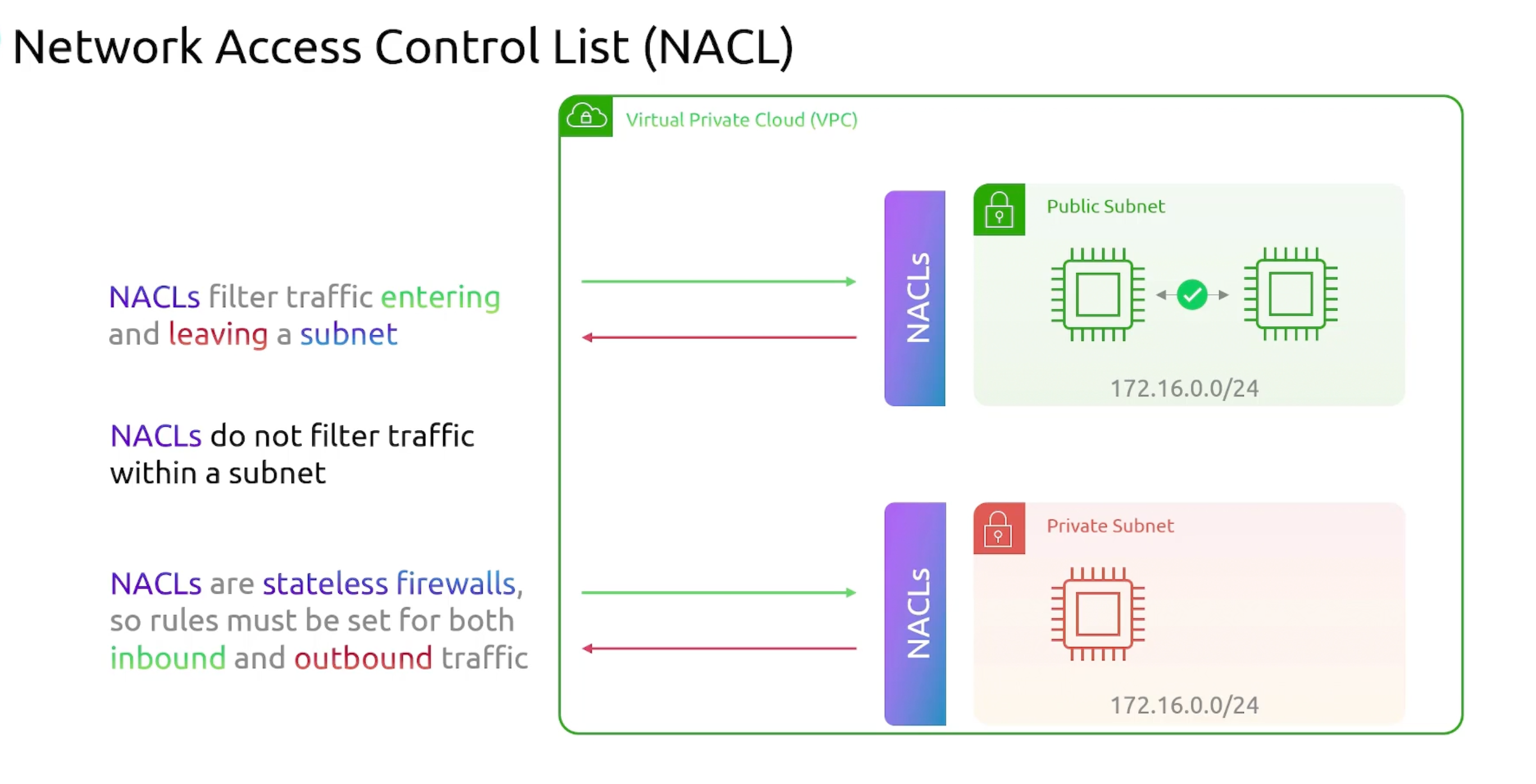
- Purpose: filter traffic at the subnet level. Meaning filtering traffic entering and leaving the subnet.
- NACLs are
statelessfirewalls by default. - NACLs don't filter traffic within a subnet.
- NACLs stands for
Network Access Control Lists. Every subnet in a VPC must be associated with a NACL.
You can have multiple subnets associated with the same NACL. But a subnet can only be associated with one NACL at a time.
- Amazon Domain Name Service (DNS).
- Amazon Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
- Amazon EC2 instance metadata.
- Amazon ECS task metadata endpoints.
- License activation for Windows instances.
- Amazon Time Sync Service.
- Reserved IP addresses used by default VPC router.
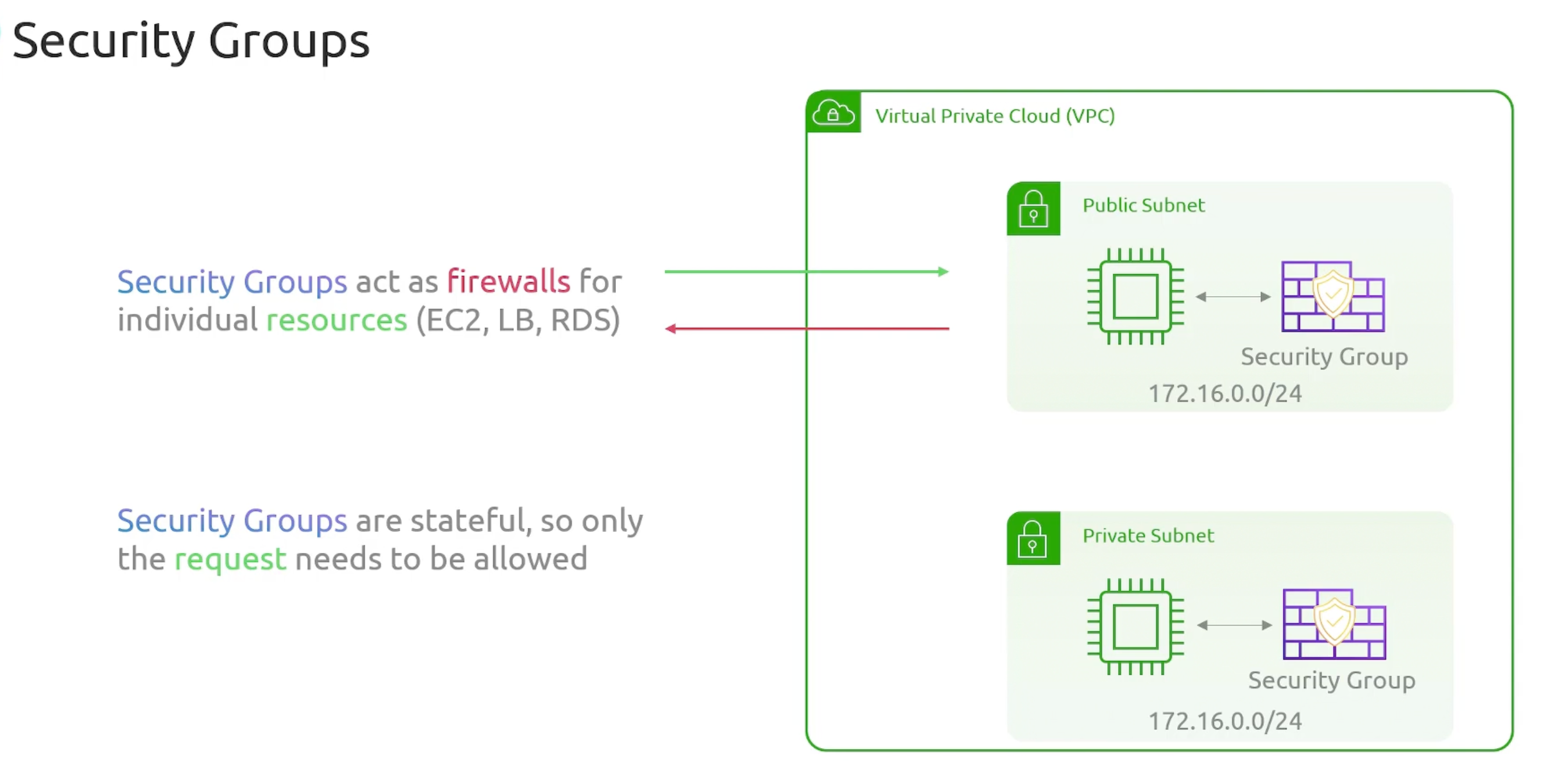
Security Groups
- Purpose: filter traffic at individual resources level
EC2, LB, RDS...etc. - Security Groups are
statefulfirewalls by default. - By default, all inbound traffic is
deniedand all outbound traffic isallowed. - Specific to a VPC.
Instead of hardcoding Private IP addresses in the source field, you can use the security group ID of the source security group. E.g. database security group allows traffic from web security group.
NACLs vs Security Groups
- Security Groups when there are no rules, it
deniesall traffic. - NACLs rules are either
allowordenytraffic. - NACKs have
numberedrules. Ordered and evaluated in order. The smaller the earlier. - You can assign multiple security groups to a single resource. Rules get
Merged.
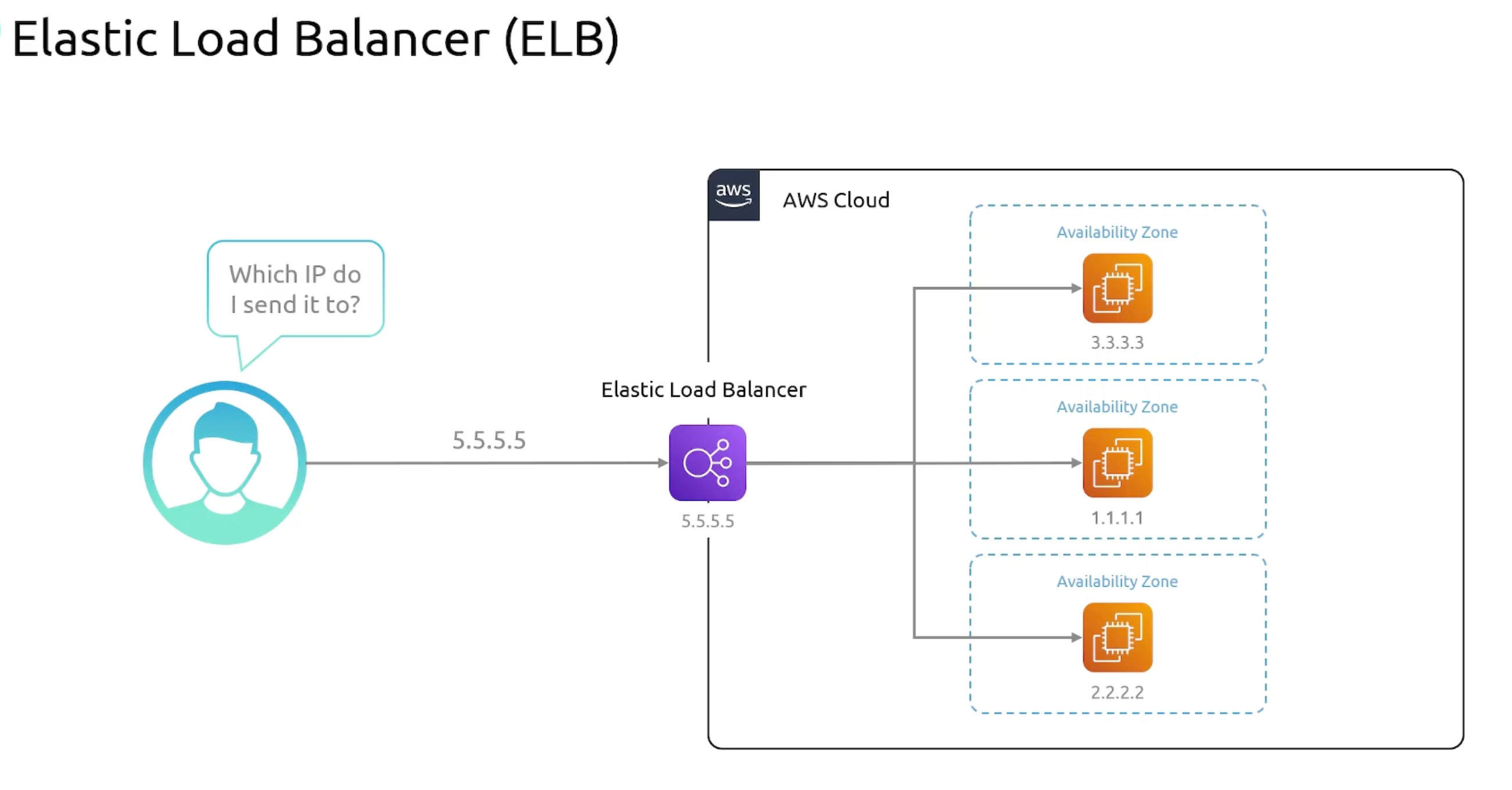
Elastic Load Balancer
- AWS load balancers service.
- AWS offers three types of load balancers:
- Application Load Balancer.
- Network Load Balancer.
- Classic Load Balancer.
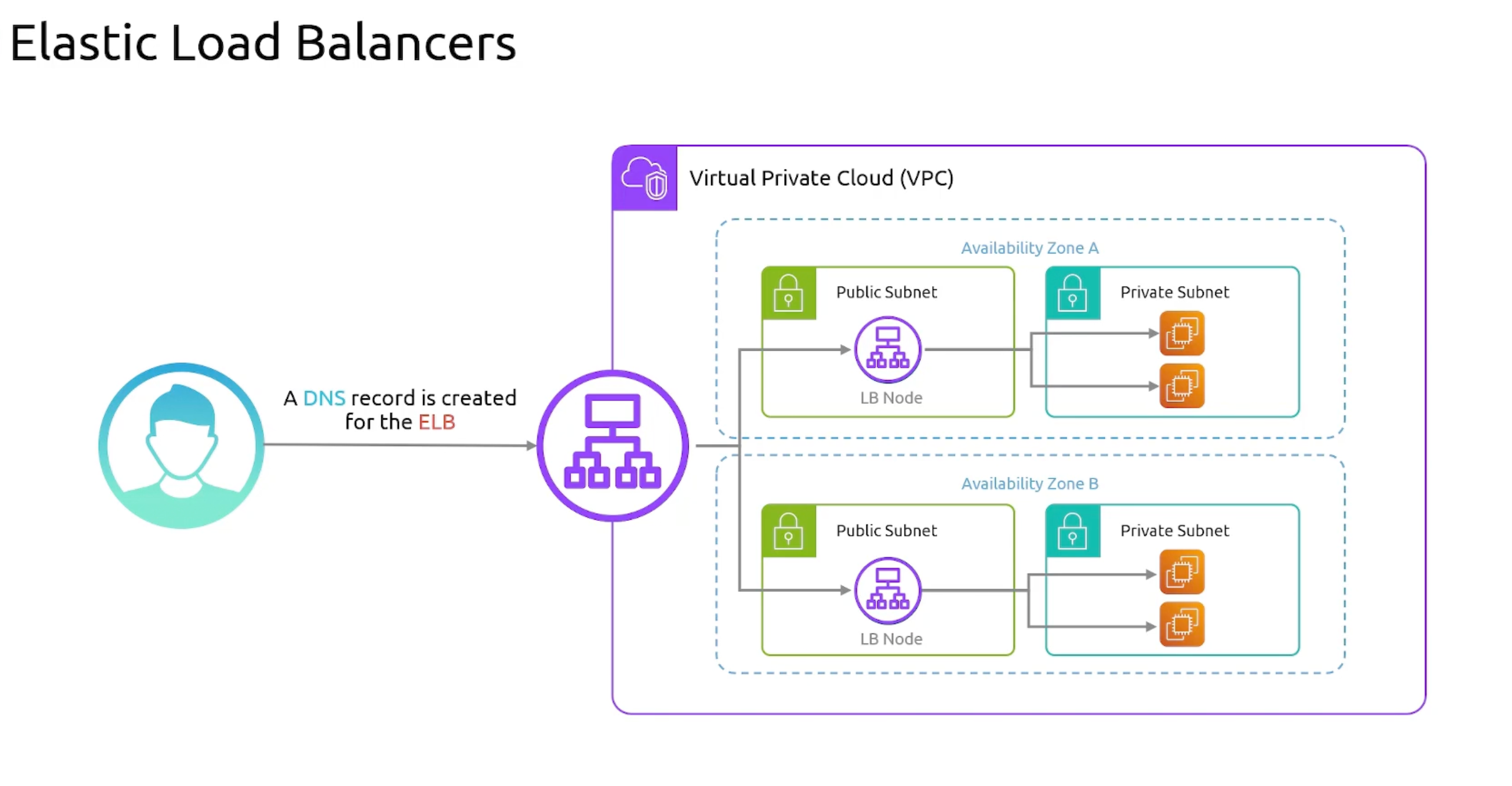
- ELB Overview
- ELB Nodes
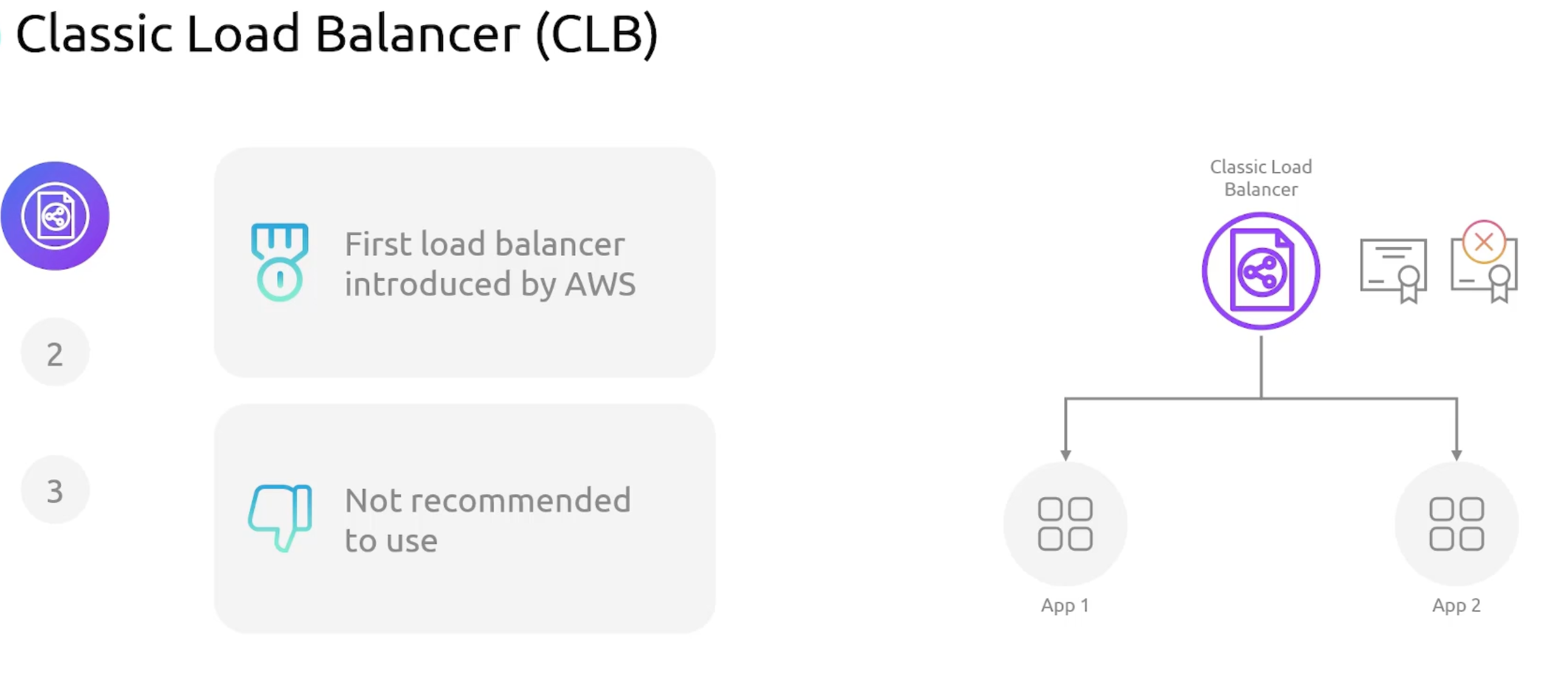
Classic Load Balancer
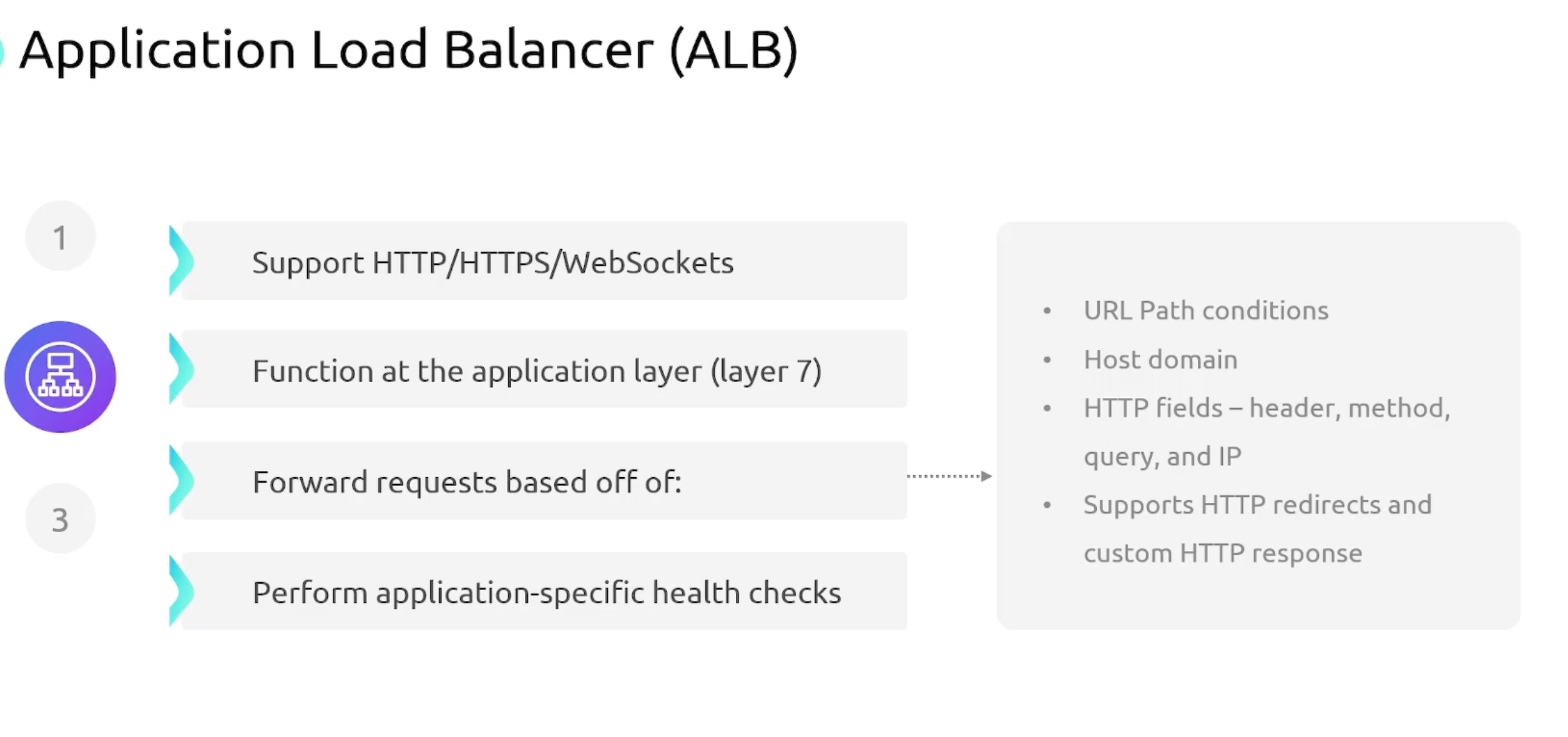
Application Load Balancer
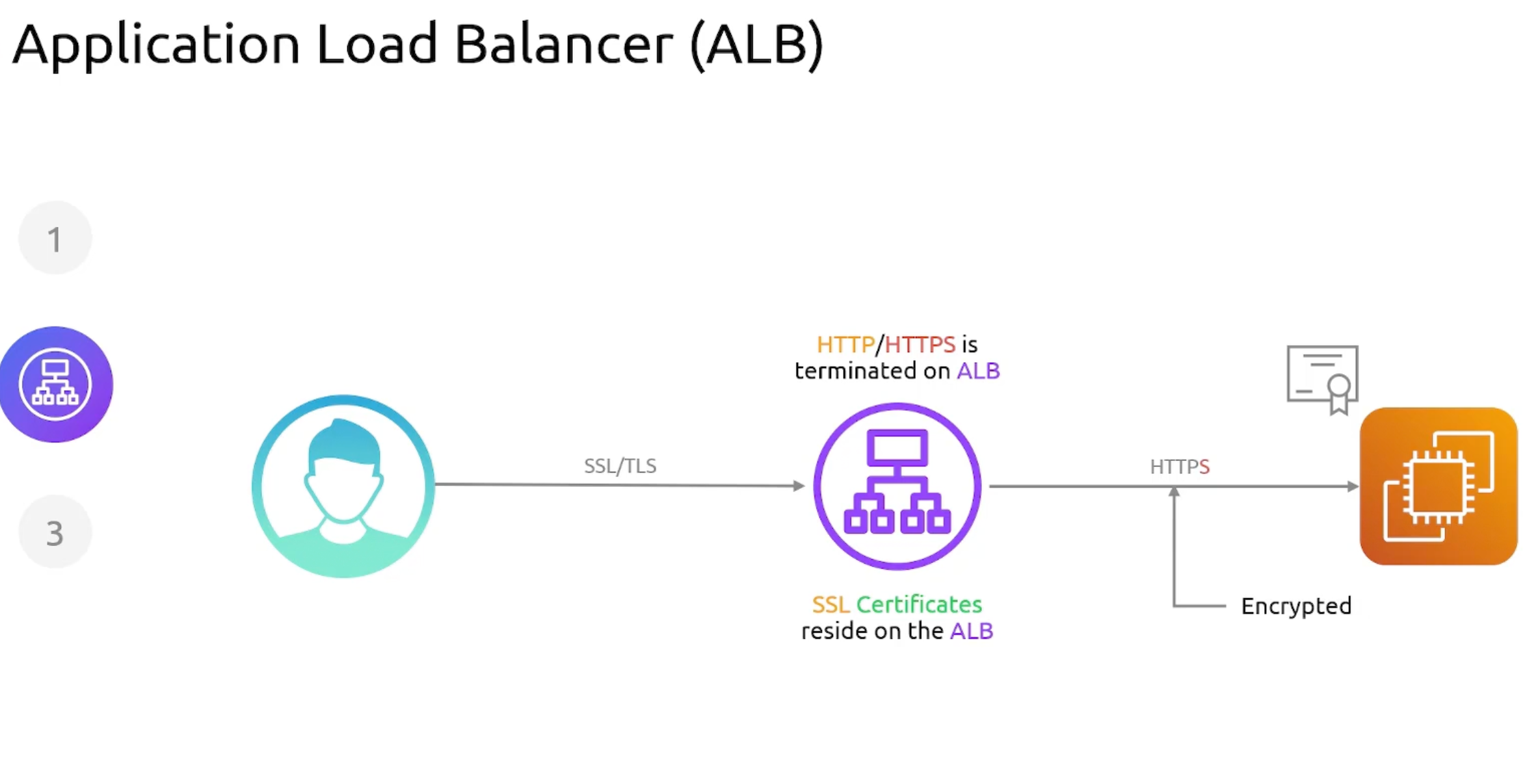
- Application LB
- Certificate Termination
Network Load Balancer
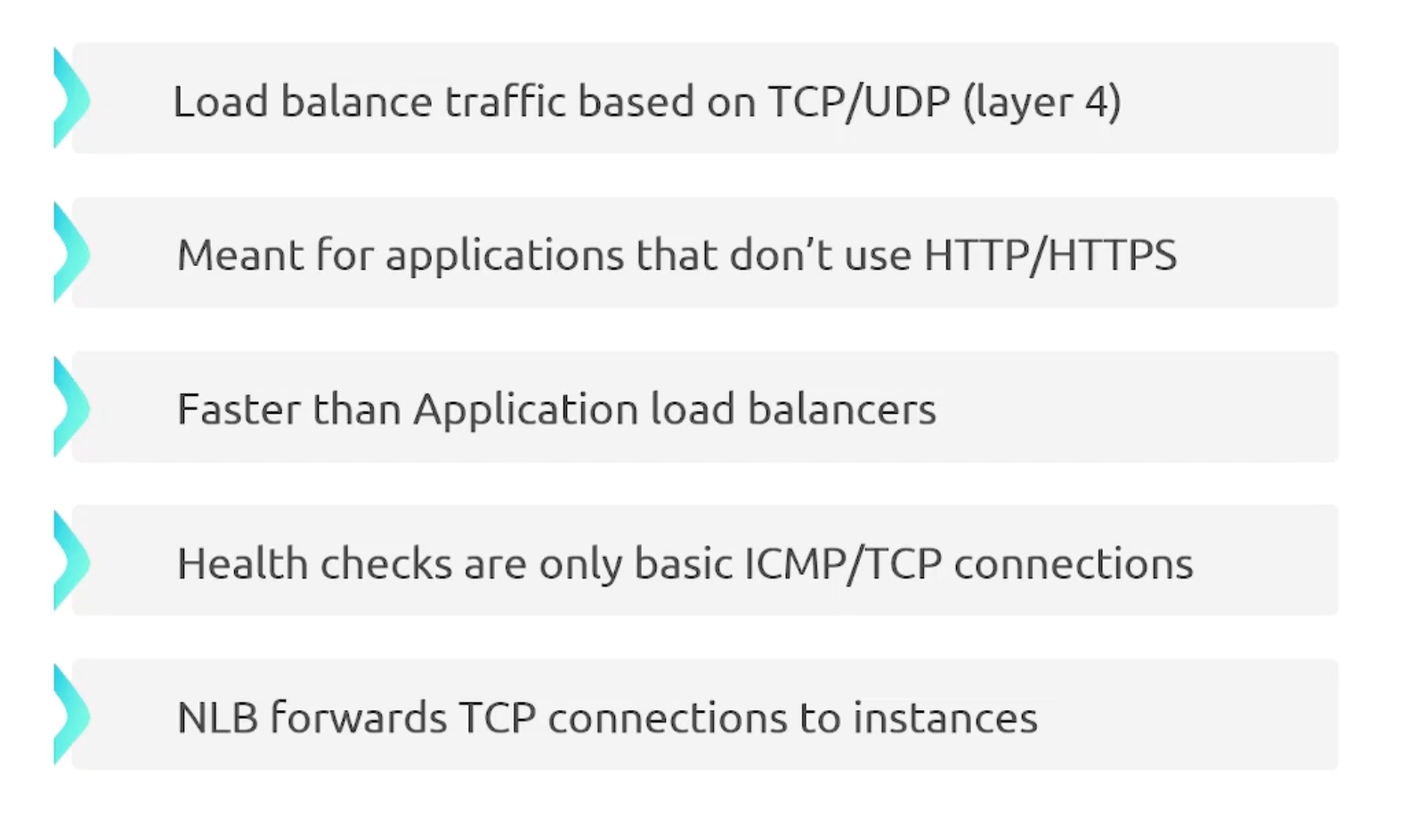
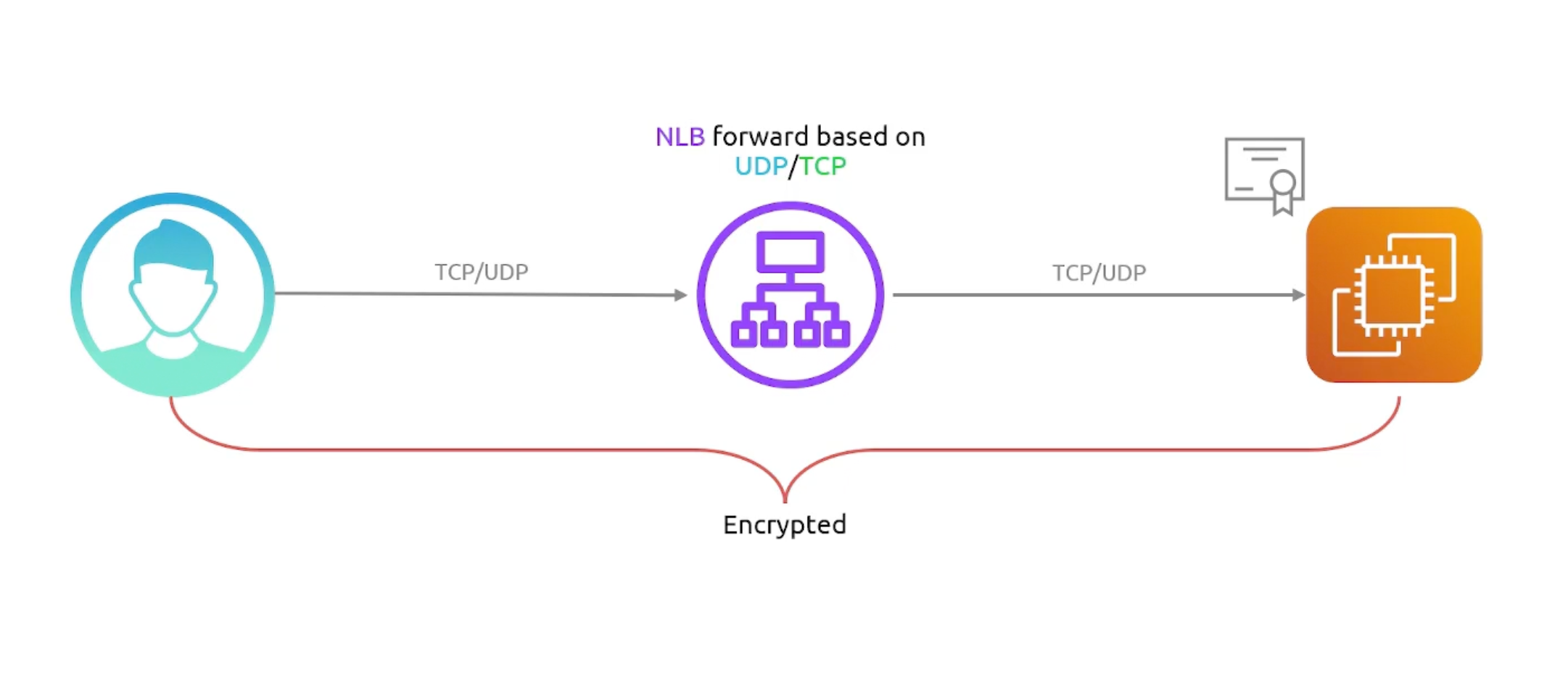
- Network LB
- Certificate Termination
Cross-Zone Load Balancing
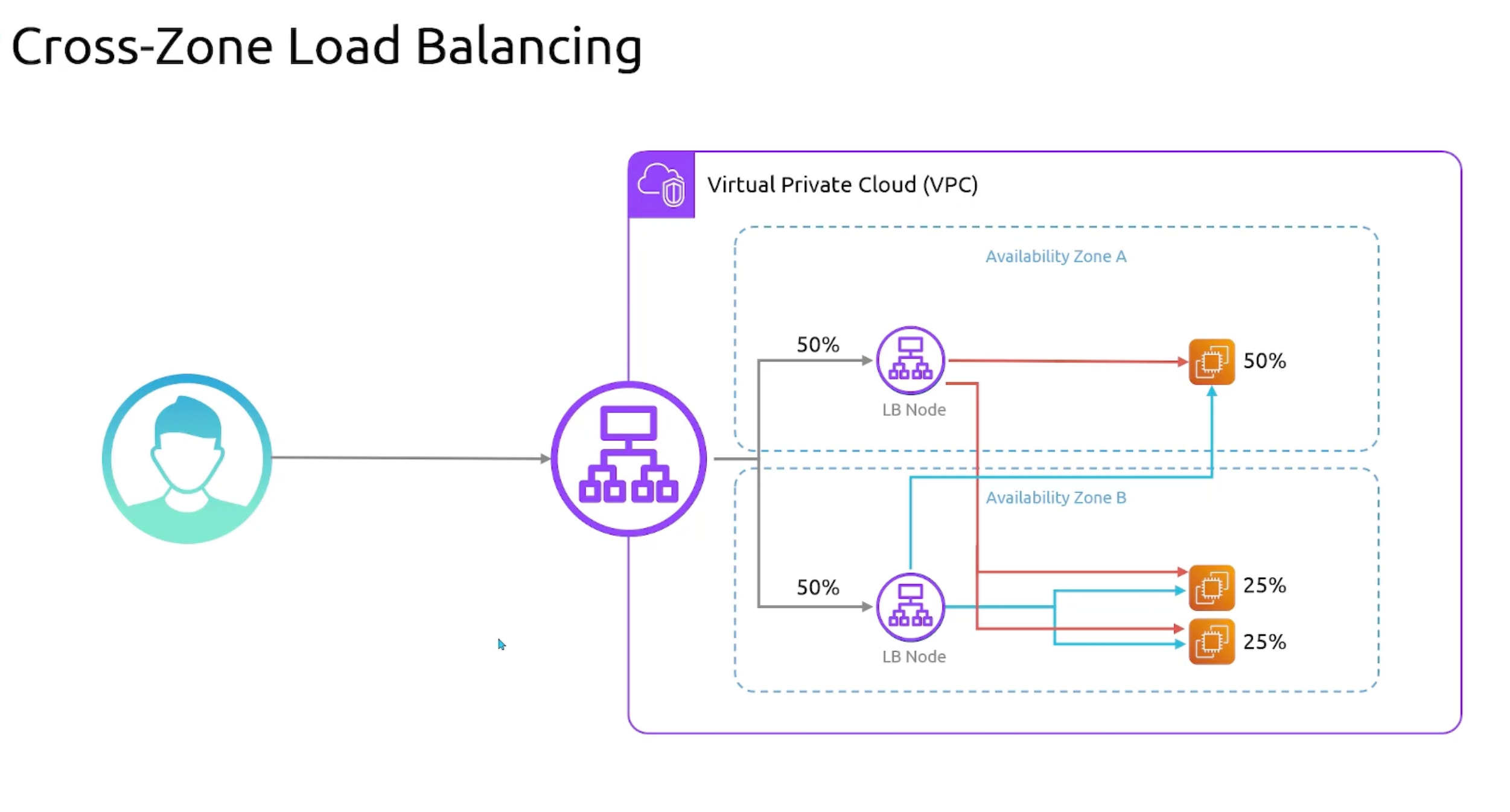
Deployment Modes
- Public Load Balancers:
- Deployed on public subnets.
- Access by users across public internet.
- Private/Internal Load Balancers:
- Deployed on private subnets.
- Accessible only from organization's aws network.
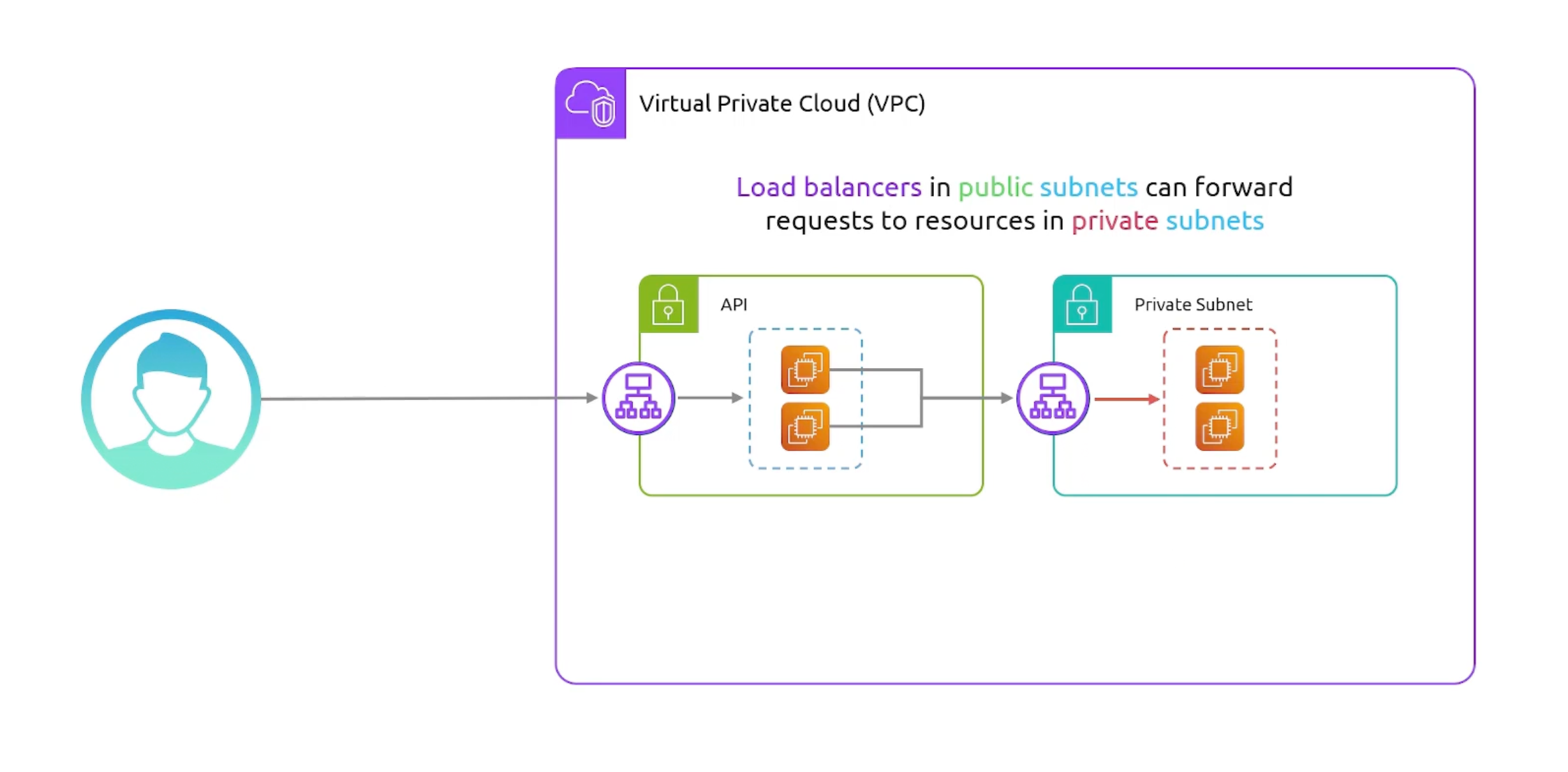
ELB Architecture Example
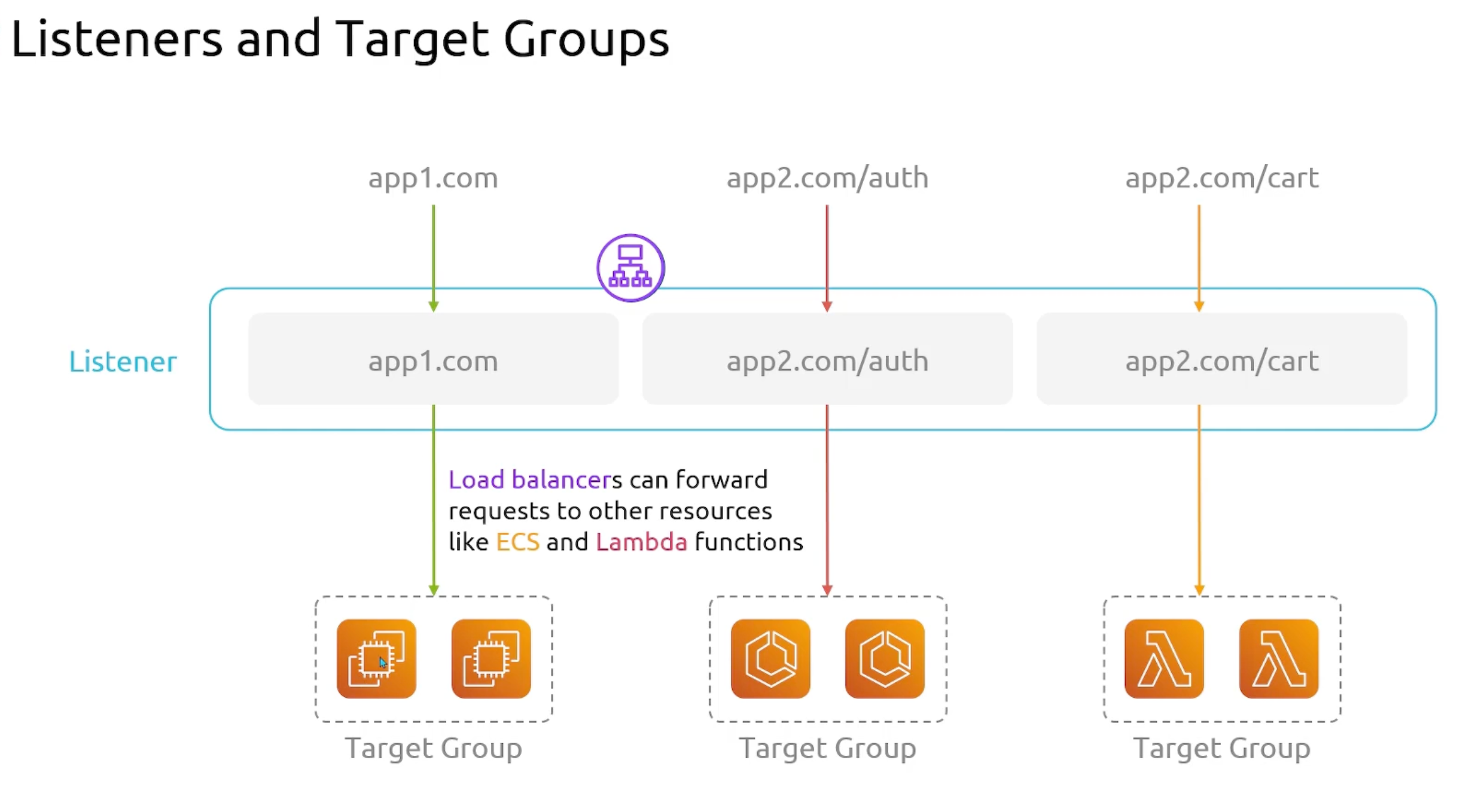
Listeners and Target Groups
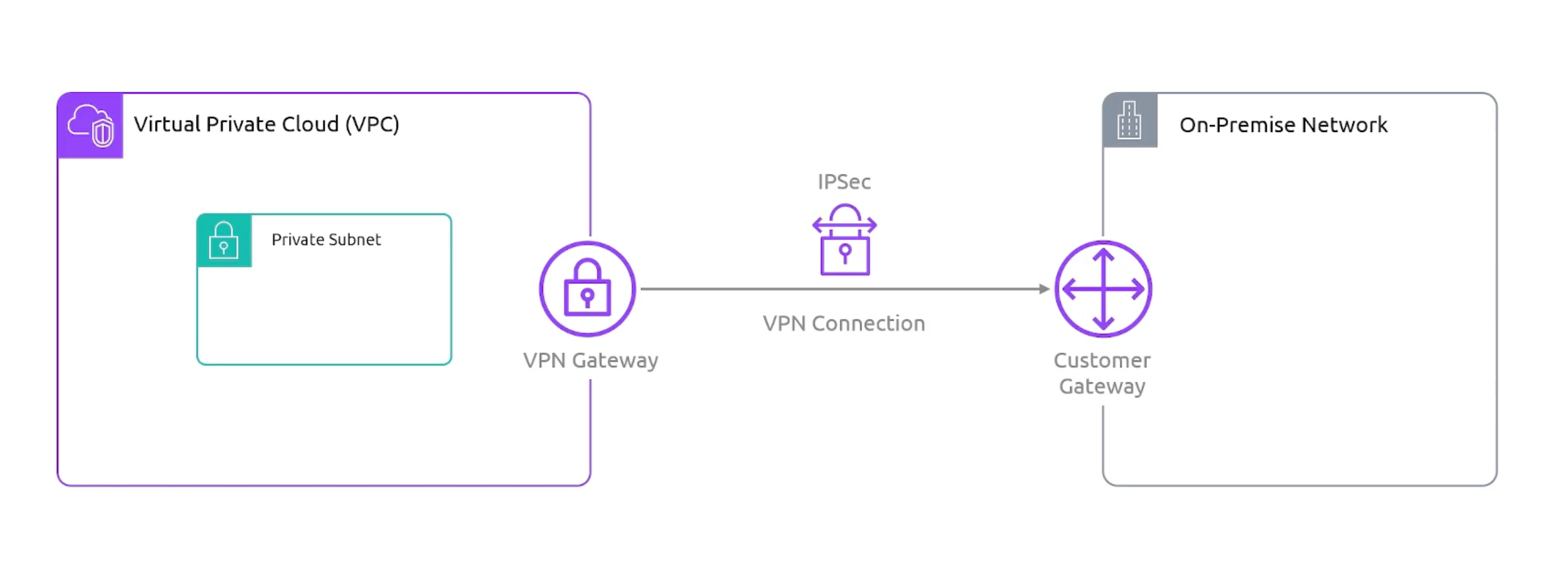
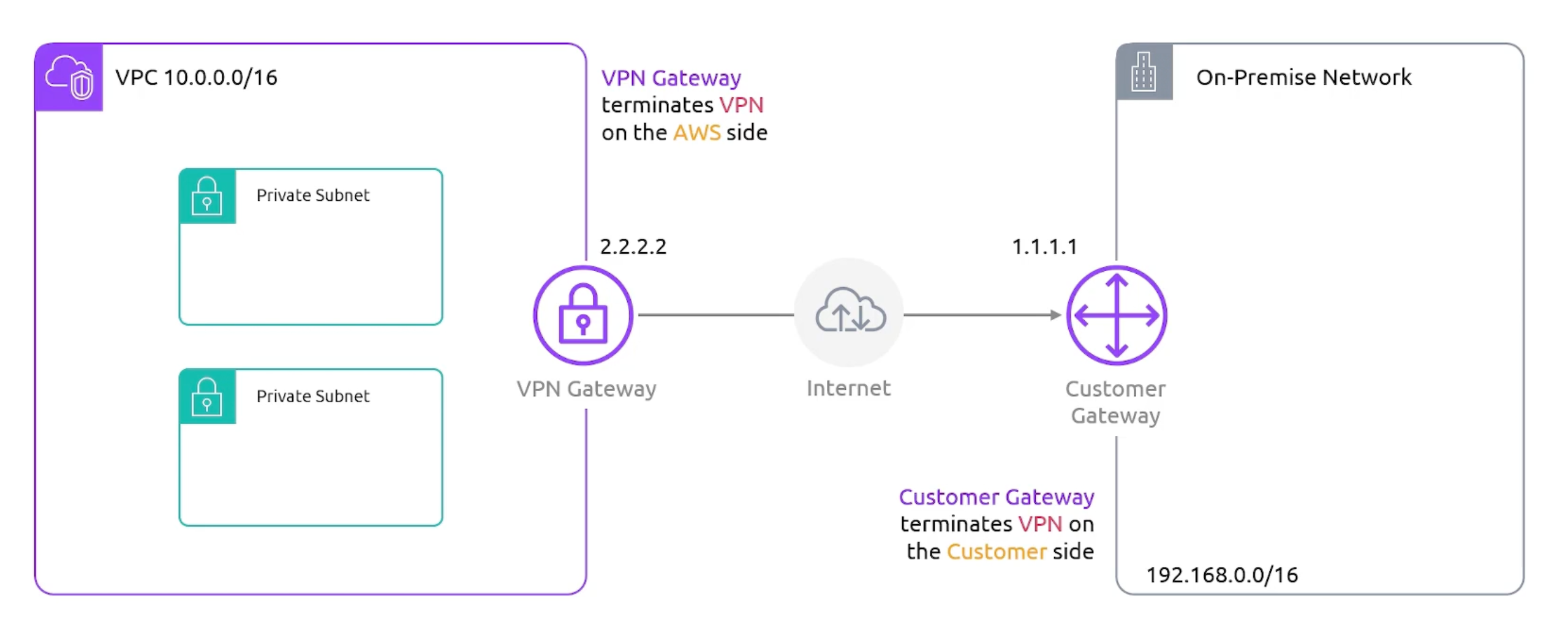
VPN
- Stands for
Virtual Private Network. - VPN Connects VPCs to on-premises data centers.
- A virtual private gateway is the Amazon-side endpoint for your VPN, attachable to
oneVPC. And it willterminate the connection. - Customer Gateway is the on-premises side endpoint for your VPN. And it will
terminate the connection.
- VPN Overview
- VPN Detailed
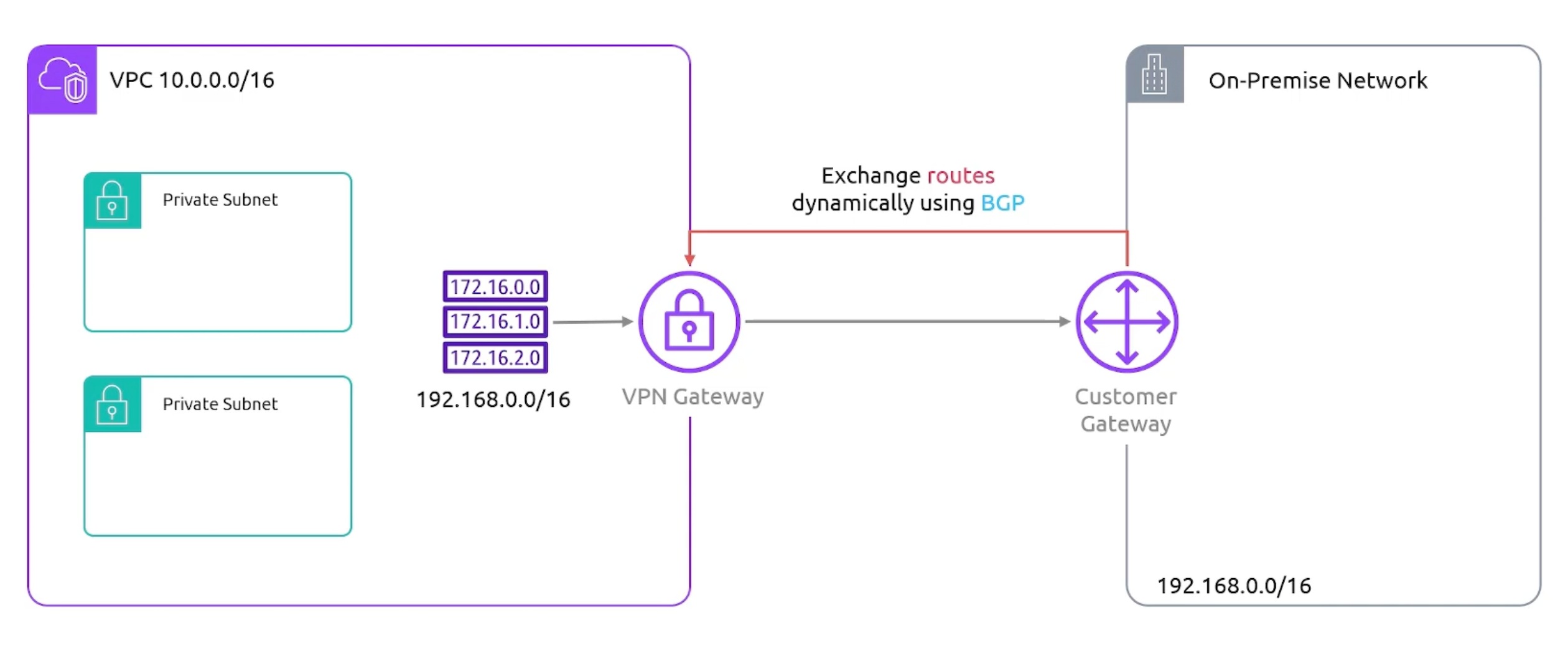
VPN Routing
- On-premises network can be set
staticallyin a route table. Ordynamicallyexchanged via BGP. Border Gateway Protocol - BGProuting protocol.
VPN Pricing
- Charged for each available VPN connection per hour.
- Charged for data transfer out from the AWS side to the internet.
- Per hour for each VPN connection.
- Egress data out of the AWS side to the internet.
VPN Gateway Limits
- Maximum bandwidth per VPN tunnel: 1.25 Gbps.
- Maximum packets per second: 140,000 packet.
- Maximum transmission unit: 1,466 bytes.
You can use ECMP to increase the bandwidth of your VPN connection. Equal Cost Multi-Path routing. Across multiple VPN tunnels.
Direct Connect
- A dedicated network connection from your on-premises data center to AWS.
- You purchase a
portfrom aDirect Connectlocation AWS router.
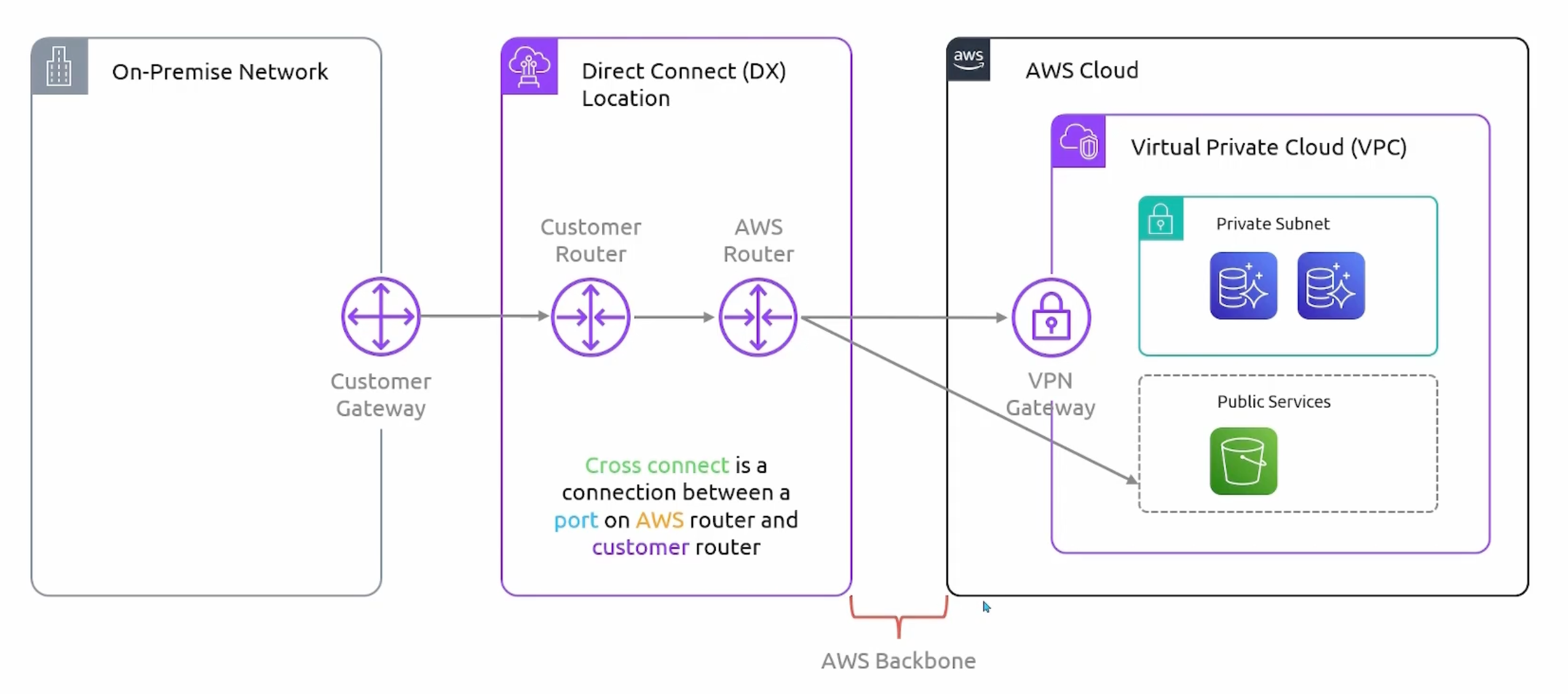
Direct Connect Pricing
- Charged for the port per hour.
- For Egress data out.
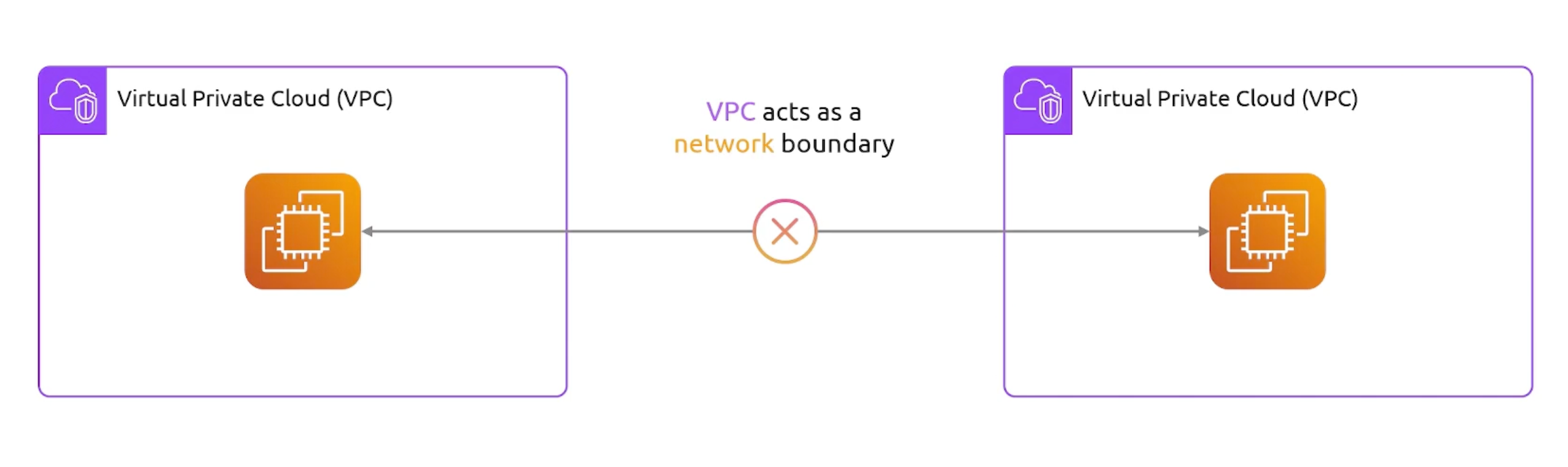
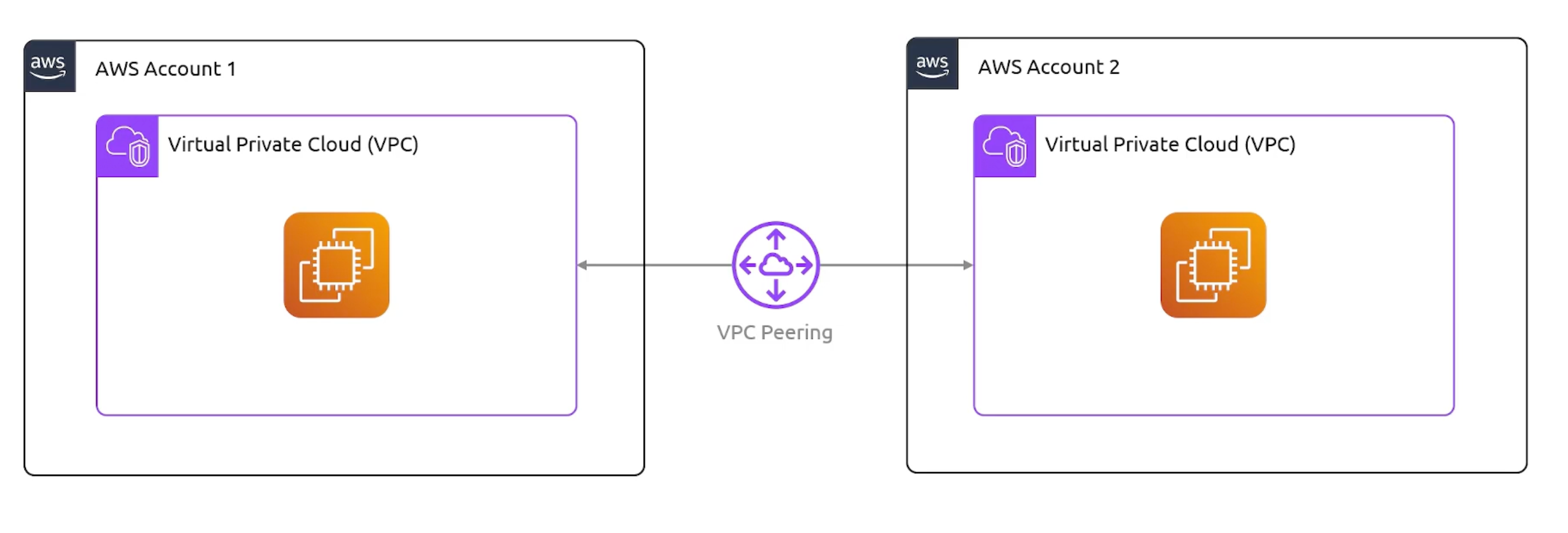
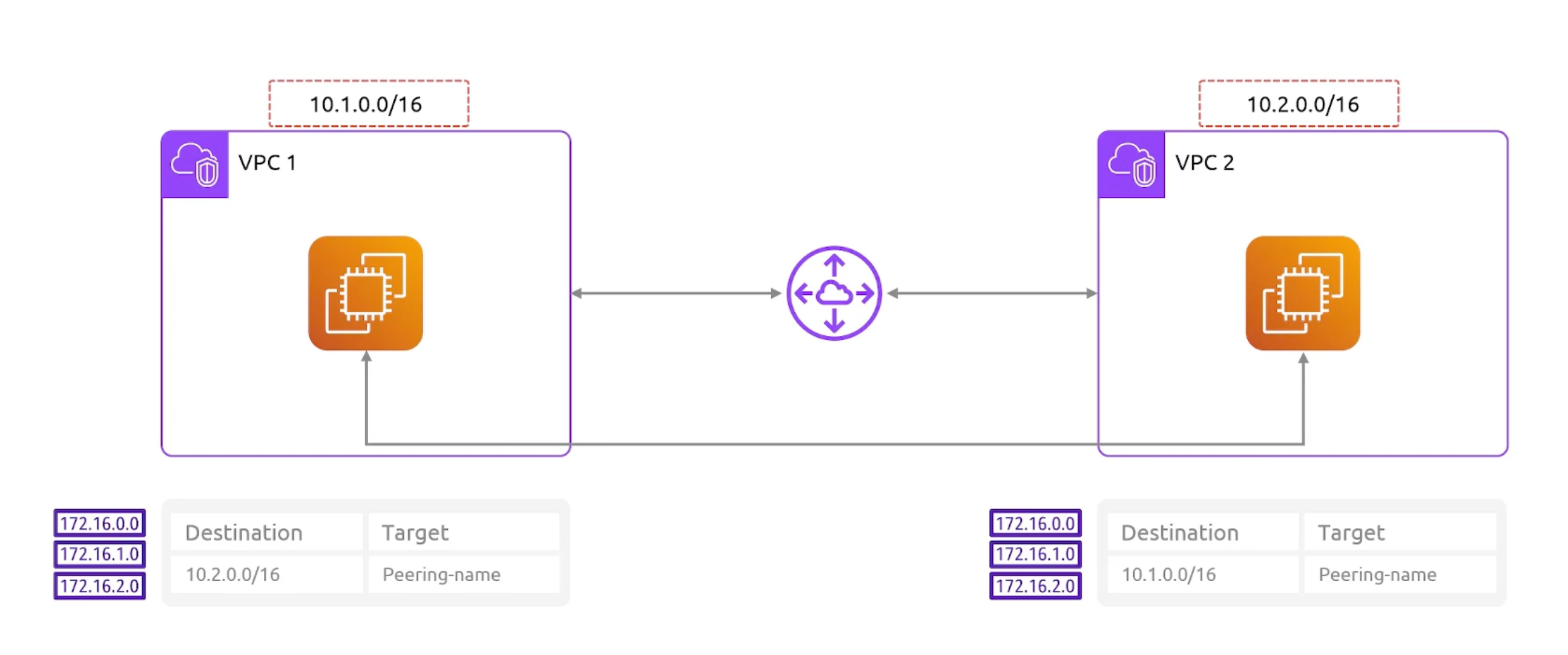
VPC Peering
- Connects two VPCs together.
- We can do peering across different accounts.
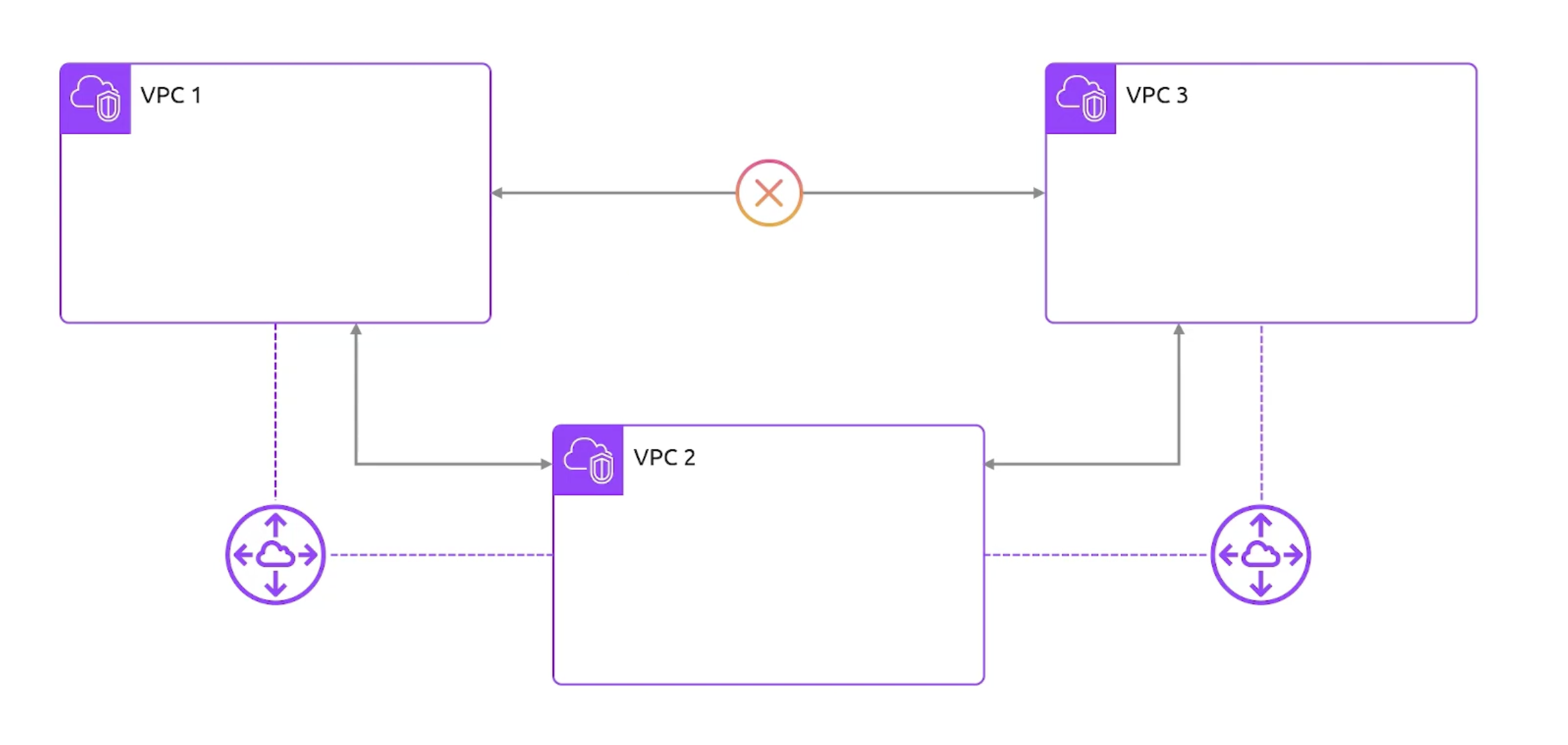
- transitive peering is not allowed.
Resources in a different VPC can't communicate with each other by default.
VPC Peering Pricing
- No cost:
- Actual VPC peering connection.
- Data transfer within the same AZ.
- Charged:
- Egress data across AZs.
VPC Peering Routing
Transitive VPC Peering
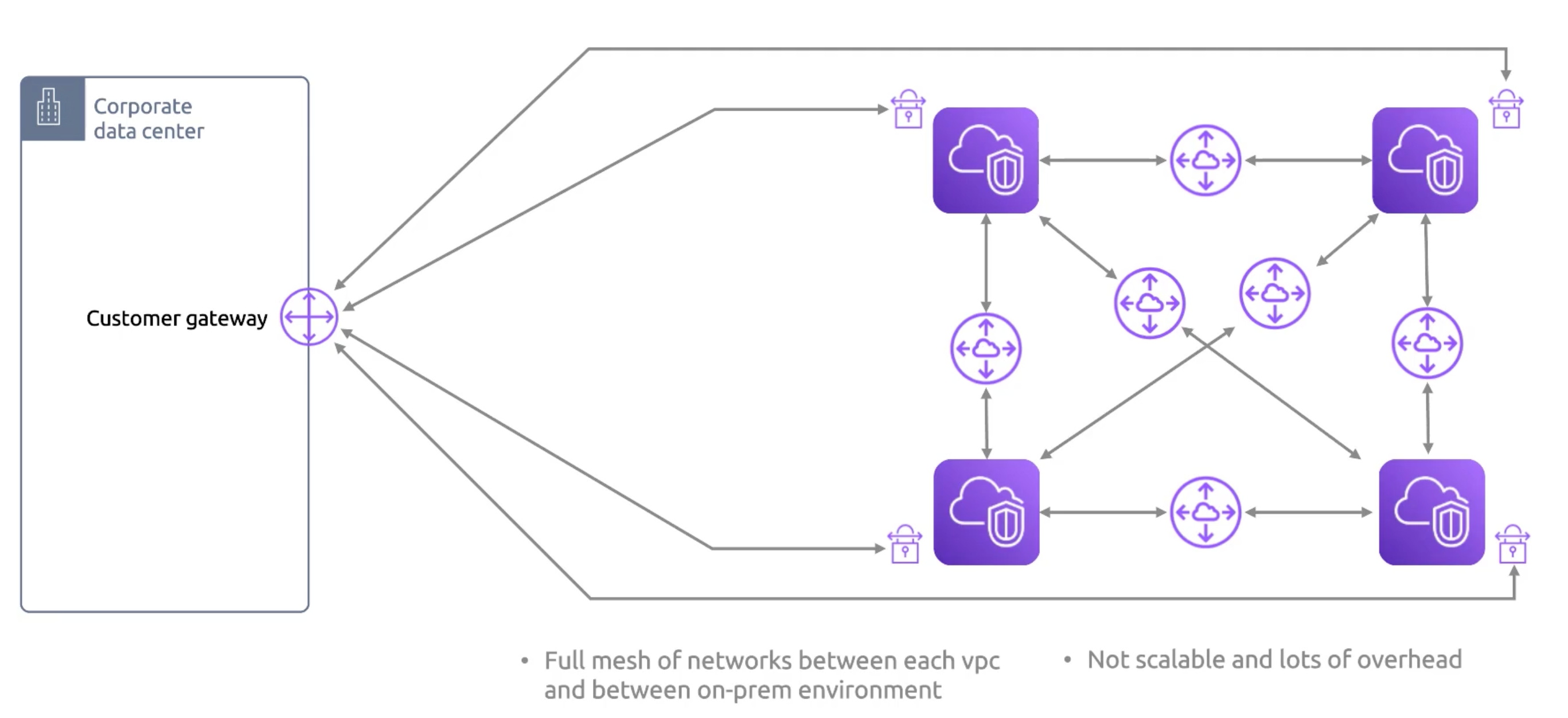
Transit Gateway
- VPCs by default can't talk to one another.
- Purpose: avoid having to maintain a full mesh of VPC peering connections.
VPC Peering and VPN connections don't scale well. Transit Gateway is the solution.
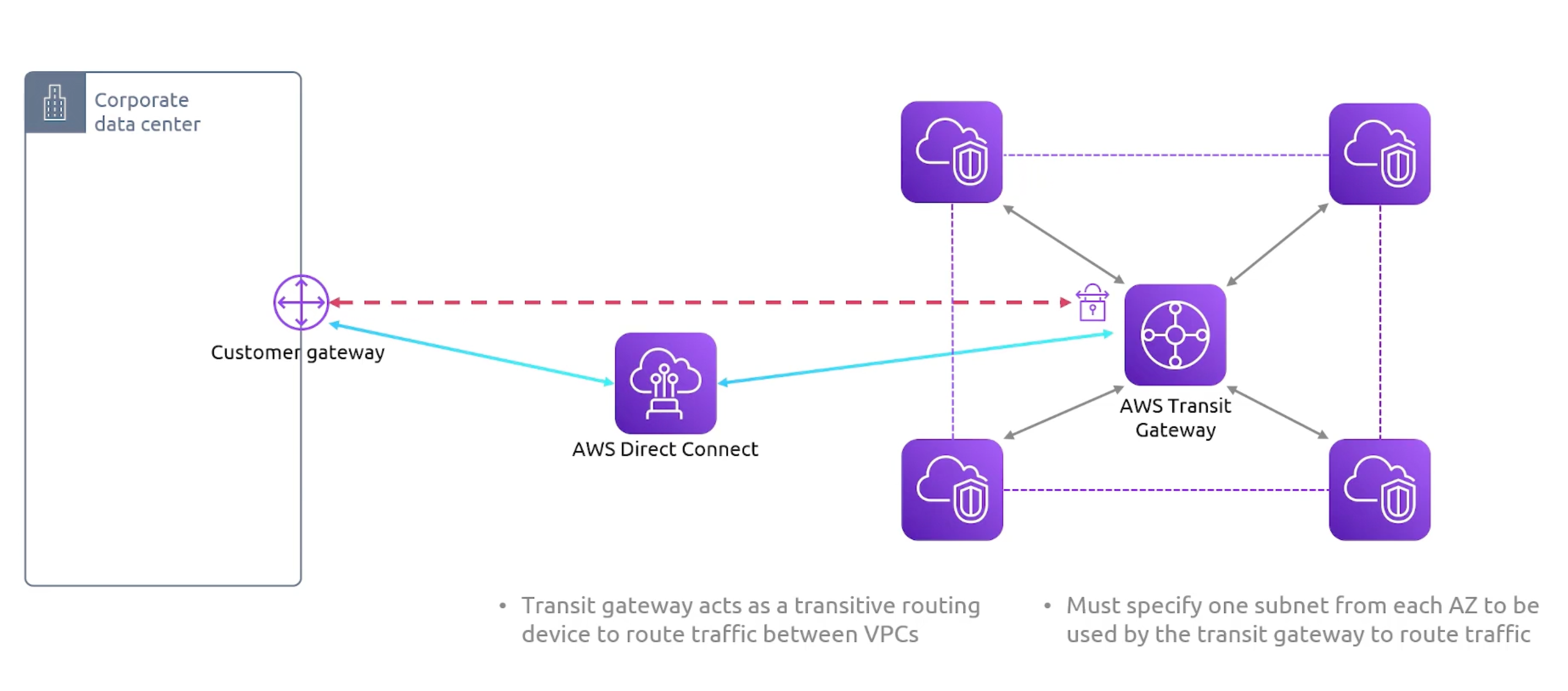
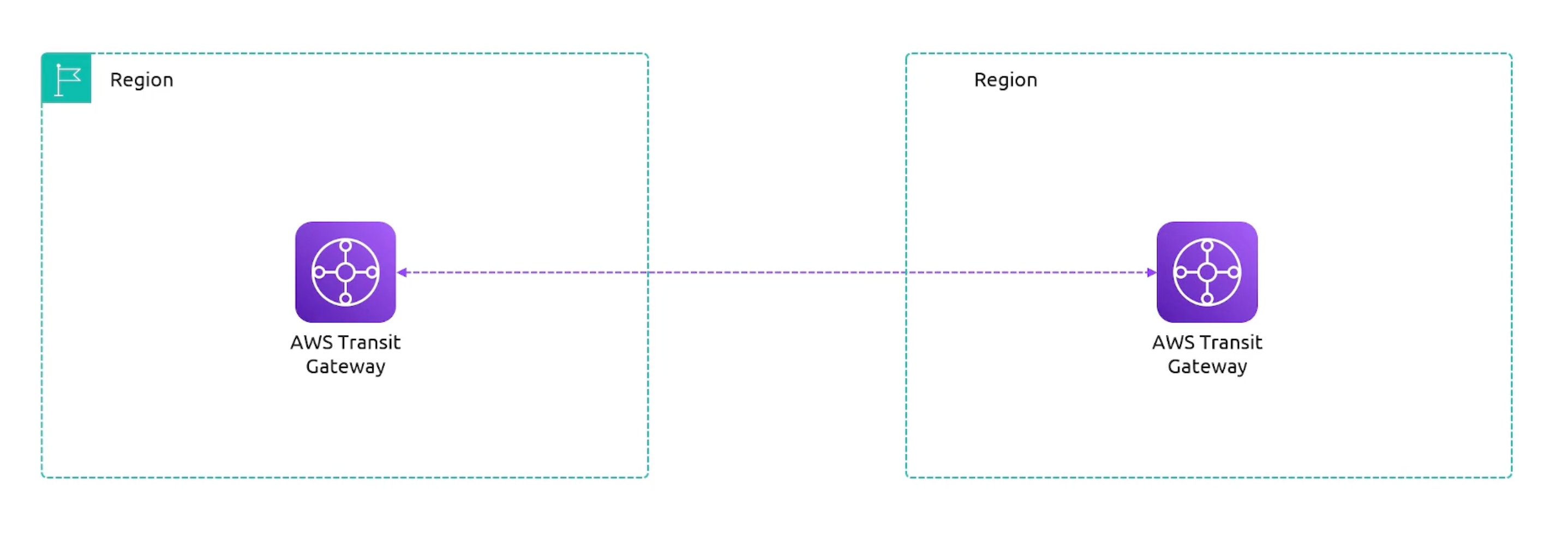
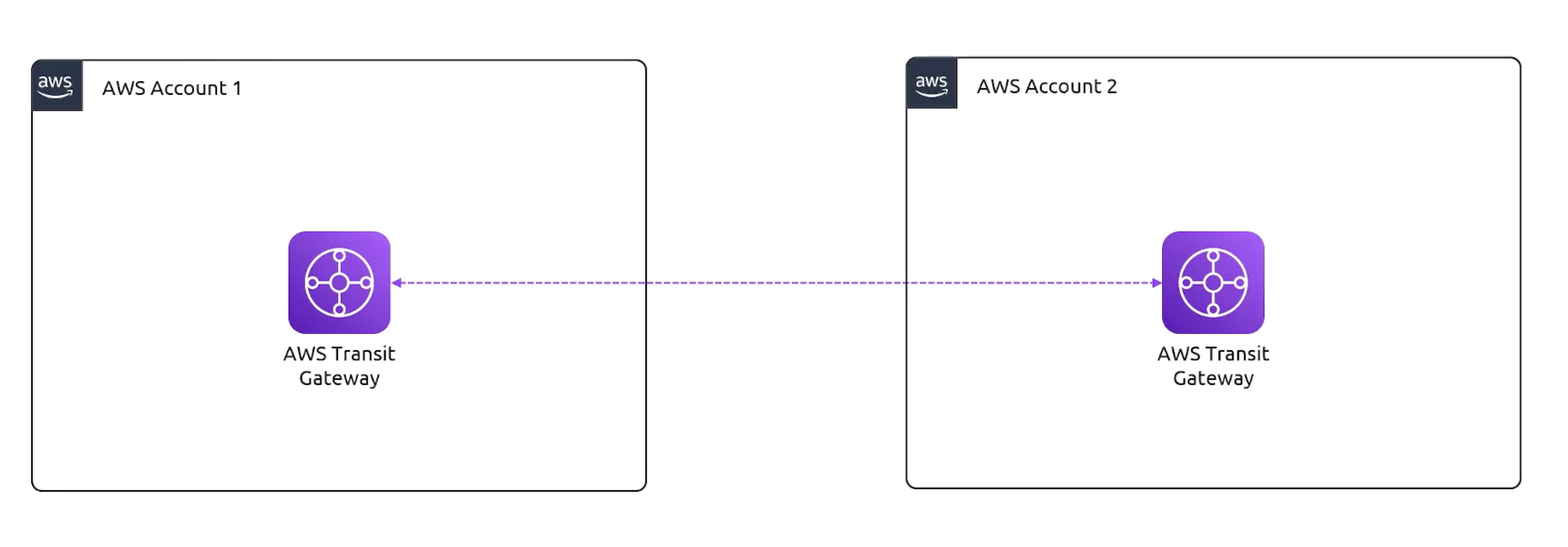
Transit Gateway Peerings
- Transit GW Peerings Regions
- Transit GW Peerings Accounts
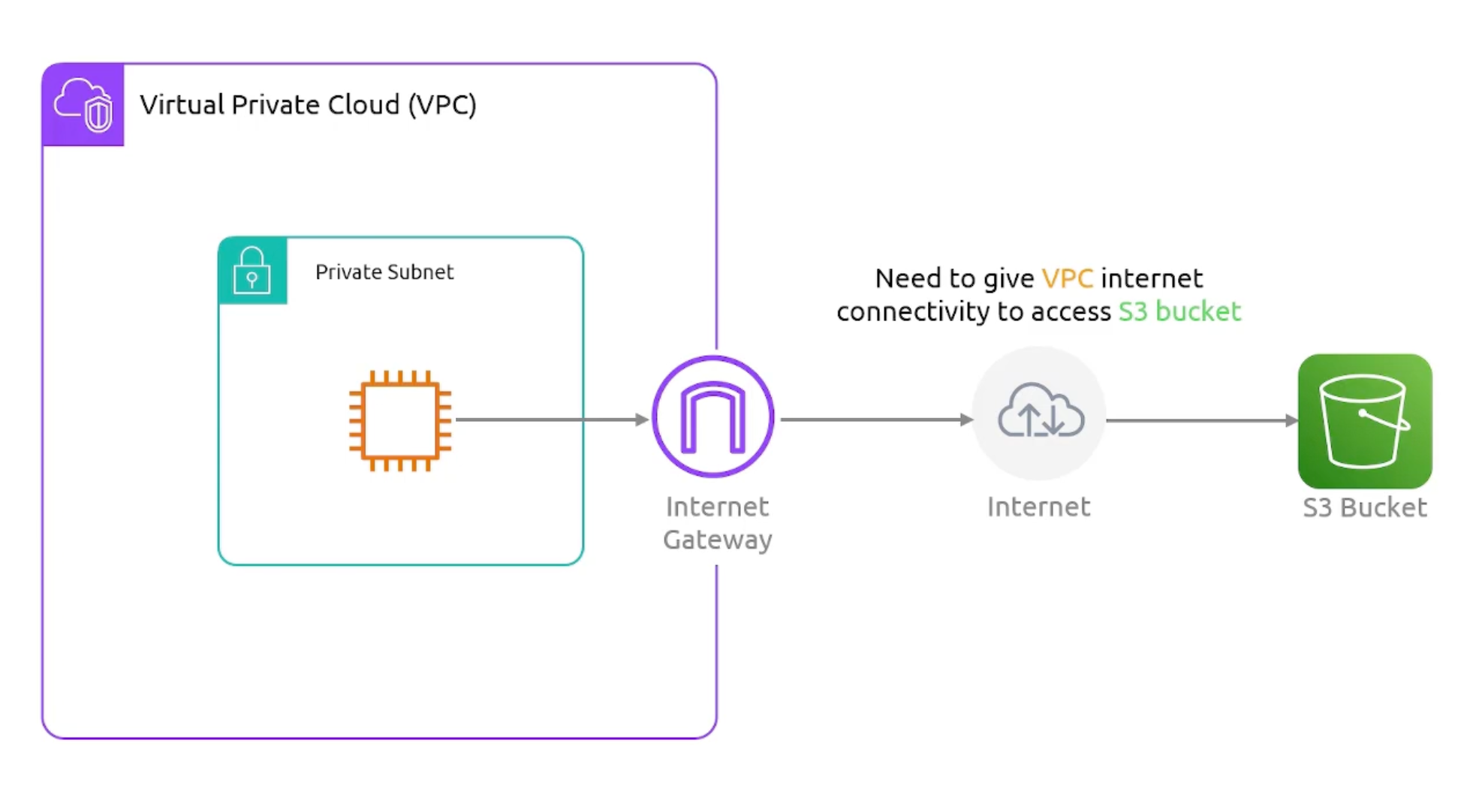
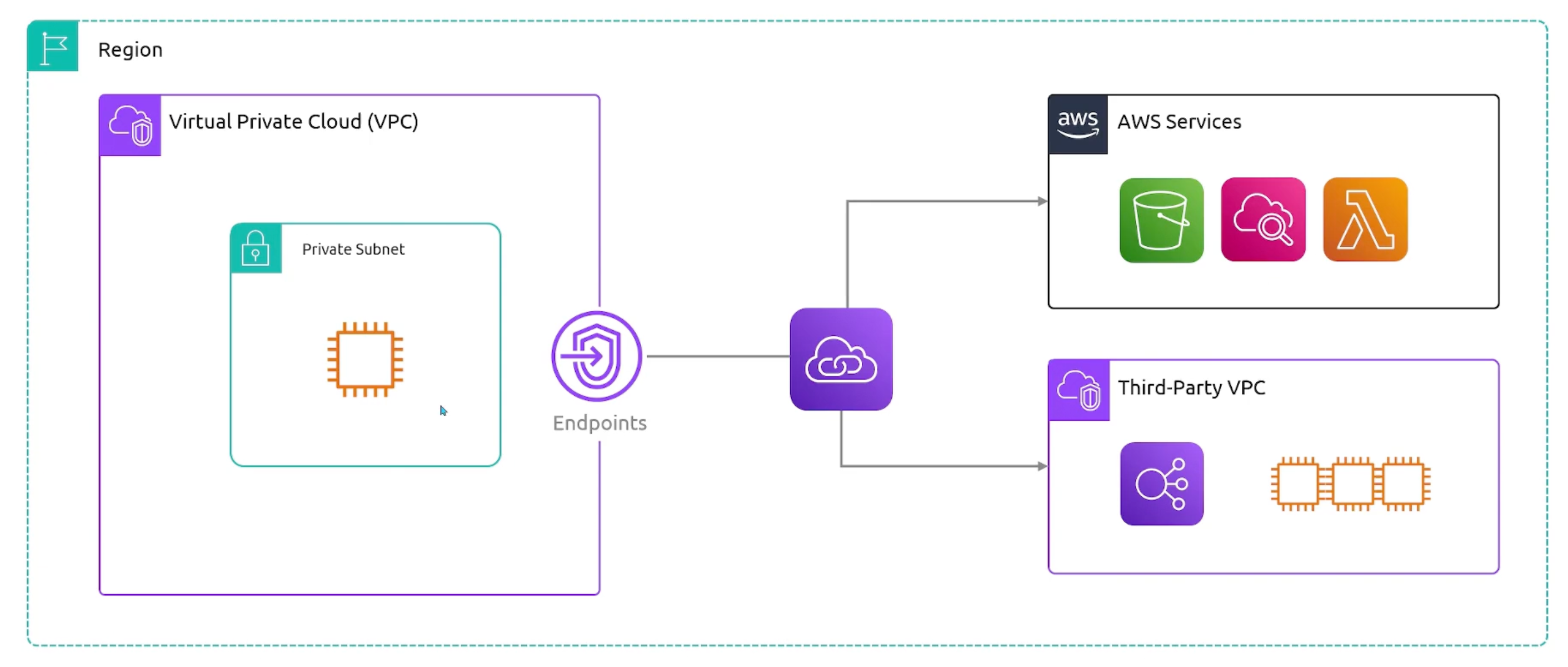
Private Link
- Problematic
- Implementation Diagram
CloudFront
- A
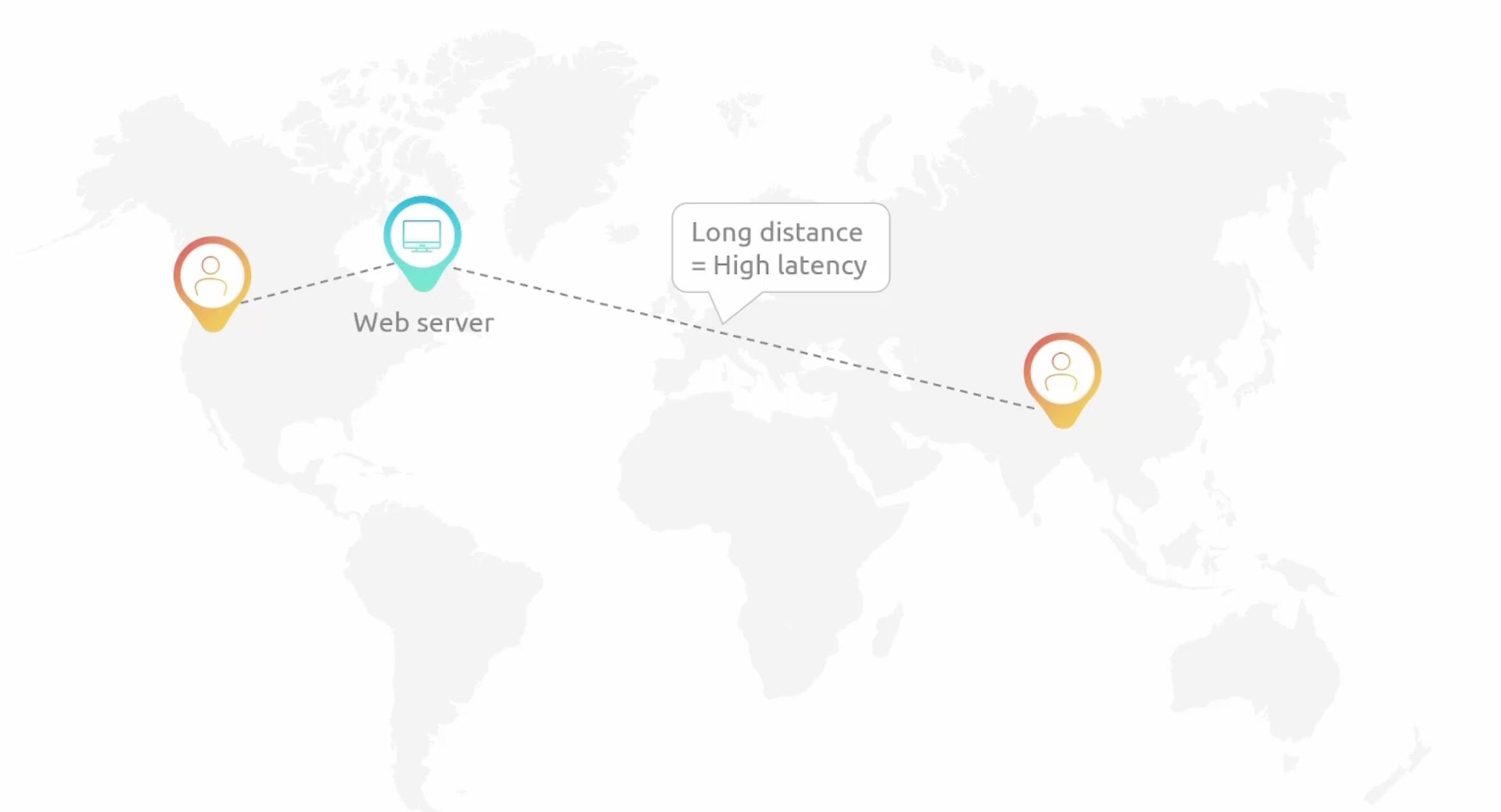
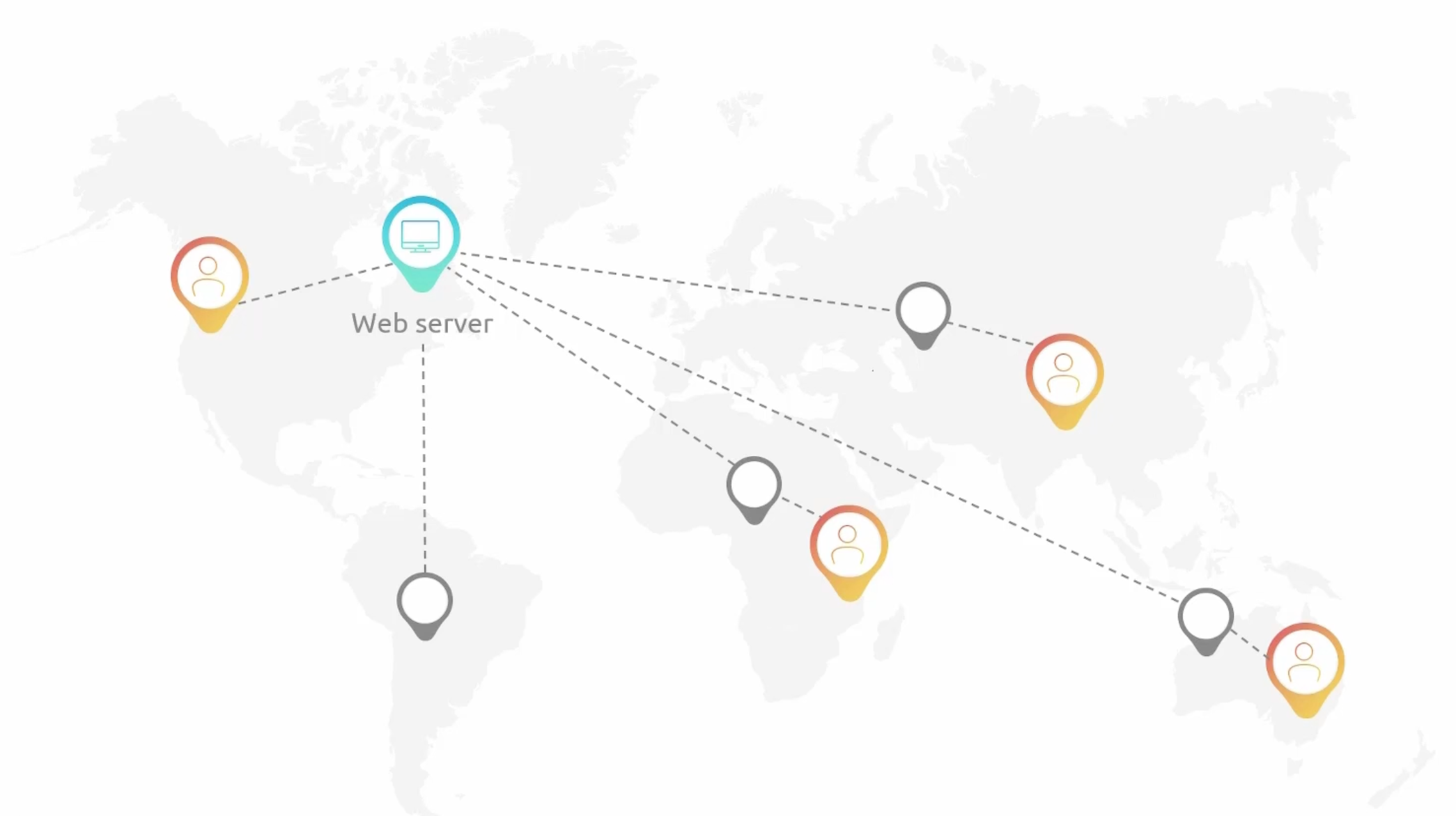
Content Delivery Network - CDN. - Purpose: to deliver content to users with low latency and high data transfer speeds.
Edge Locationsare the locations where content will be cached.- Use cases:
- Static websites.
- Video on demand.
- Streaming.
- Problem
- CloudFront Solution
Types of CloudFront Distributions
CloudFront Edge Locations
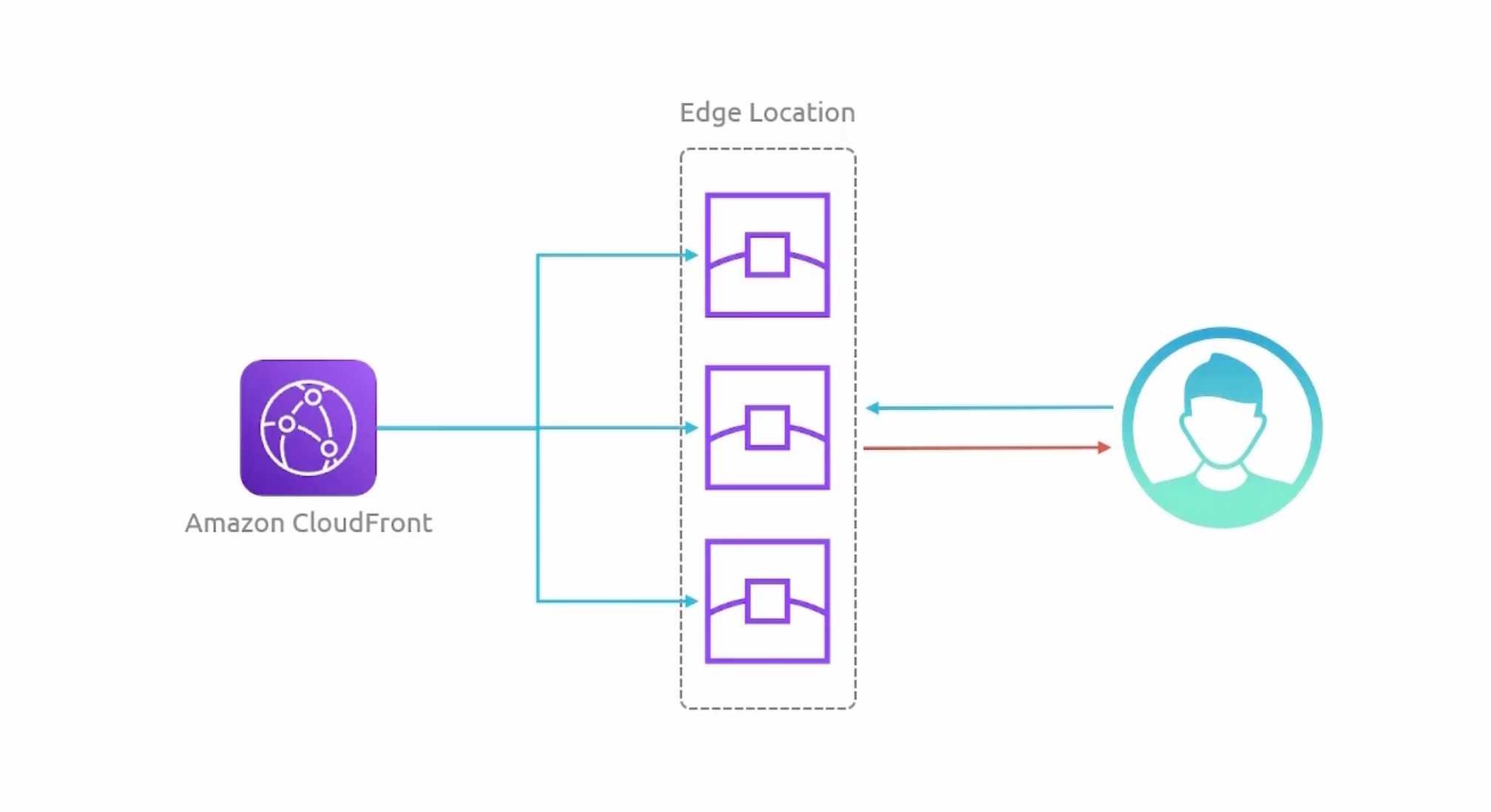
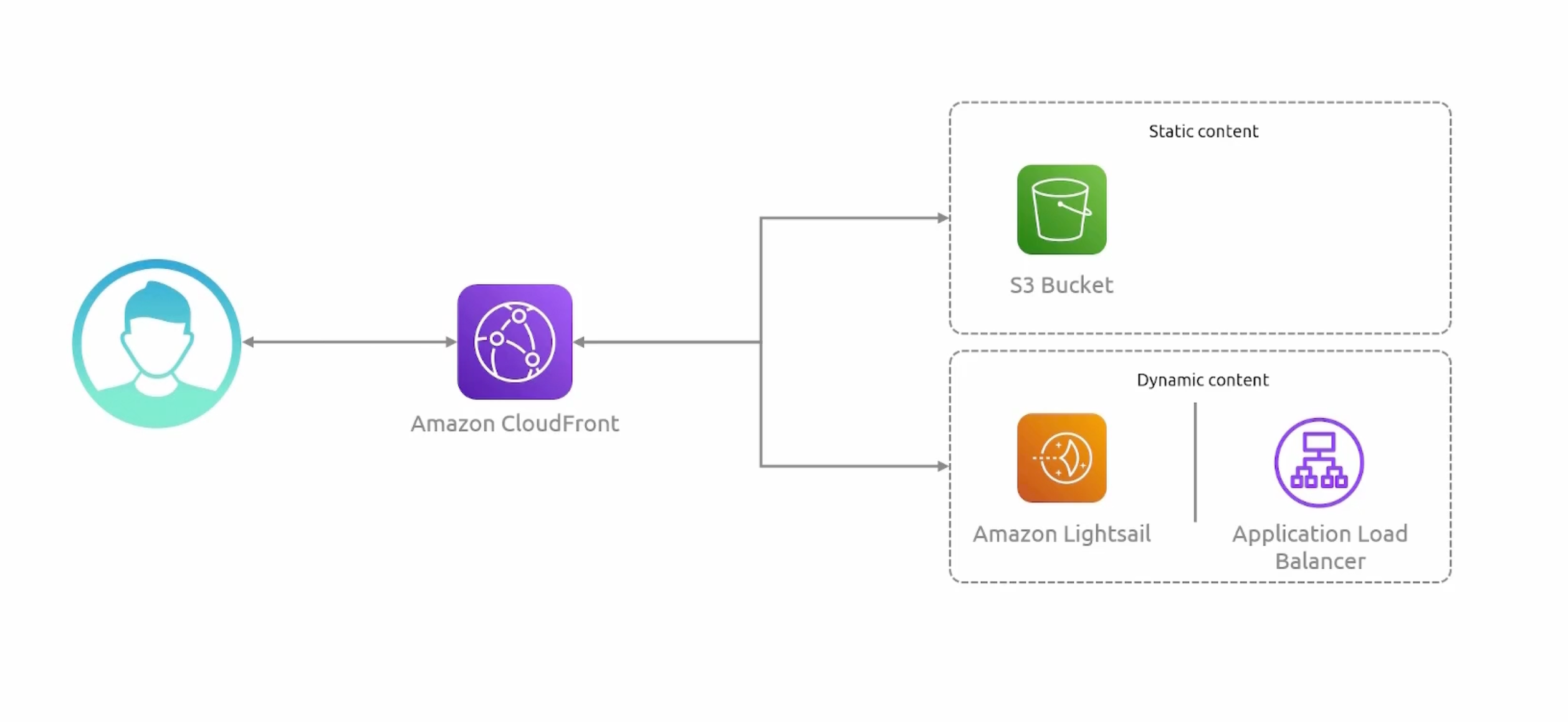
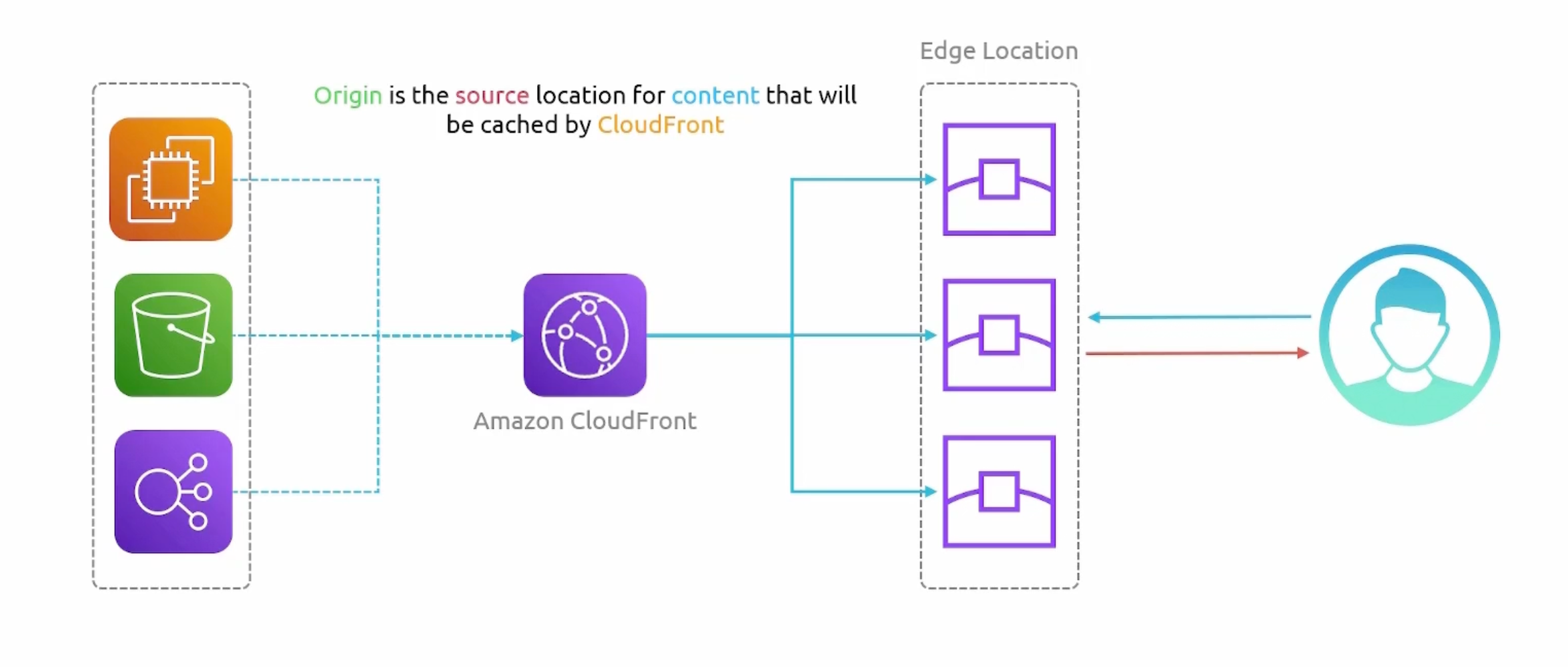
CloudFront Architecture
- Origin: the location of the original version of the content.
You can utilize Load Balancers or an HTTP server running on EC2 servers as a custom origin.
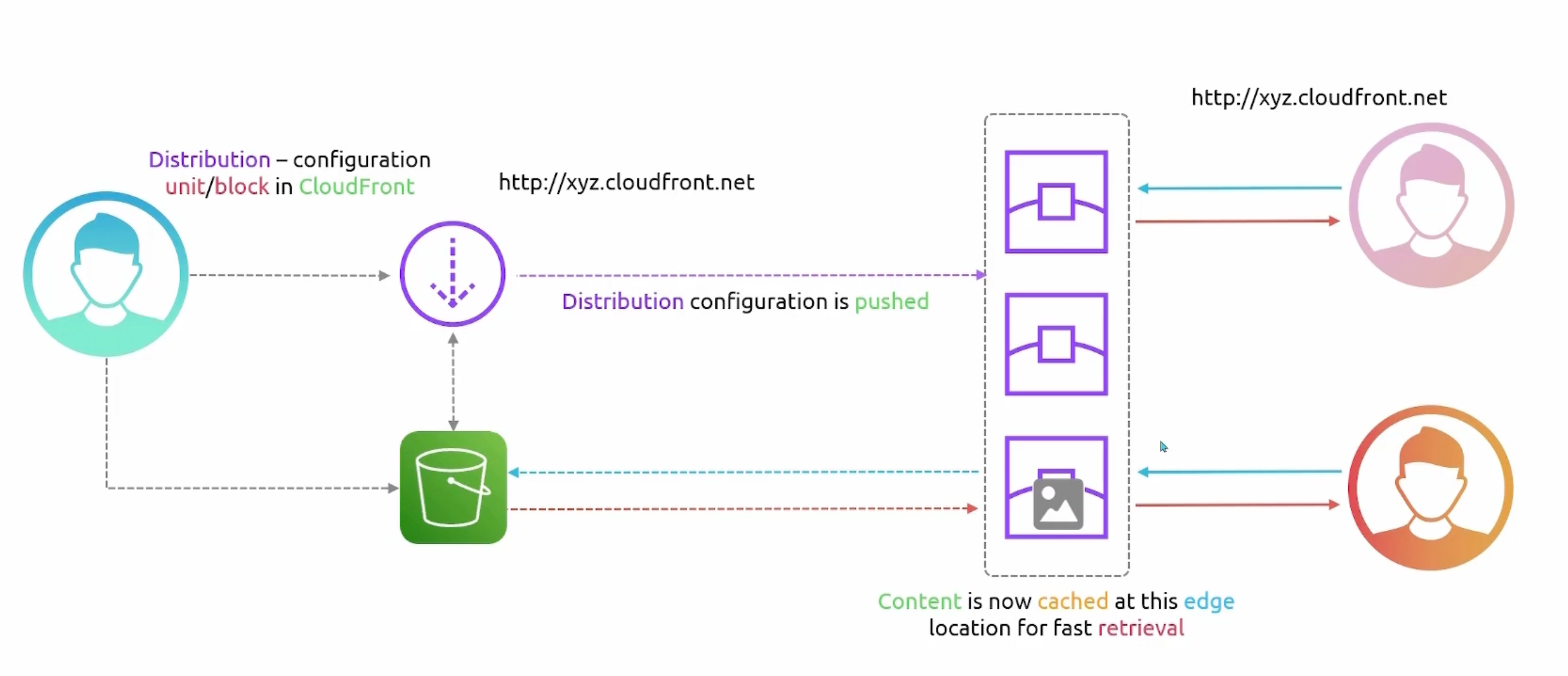
CloudFront TTL
- Cached content at an edge location remains for a set time known as time to live
TTL. - TTL value decides content validity before an edge location requests the origin.
- Default TTL is
24 hours. - Can have objects expire at a specific time.
CloudFront Cache Invalidation

CloudFront SSL/TLS and ACM

CloudFront Observability
- CloudFront exposes metrics to CloudWatch.
- Can enable extra metrics for an additional cost.
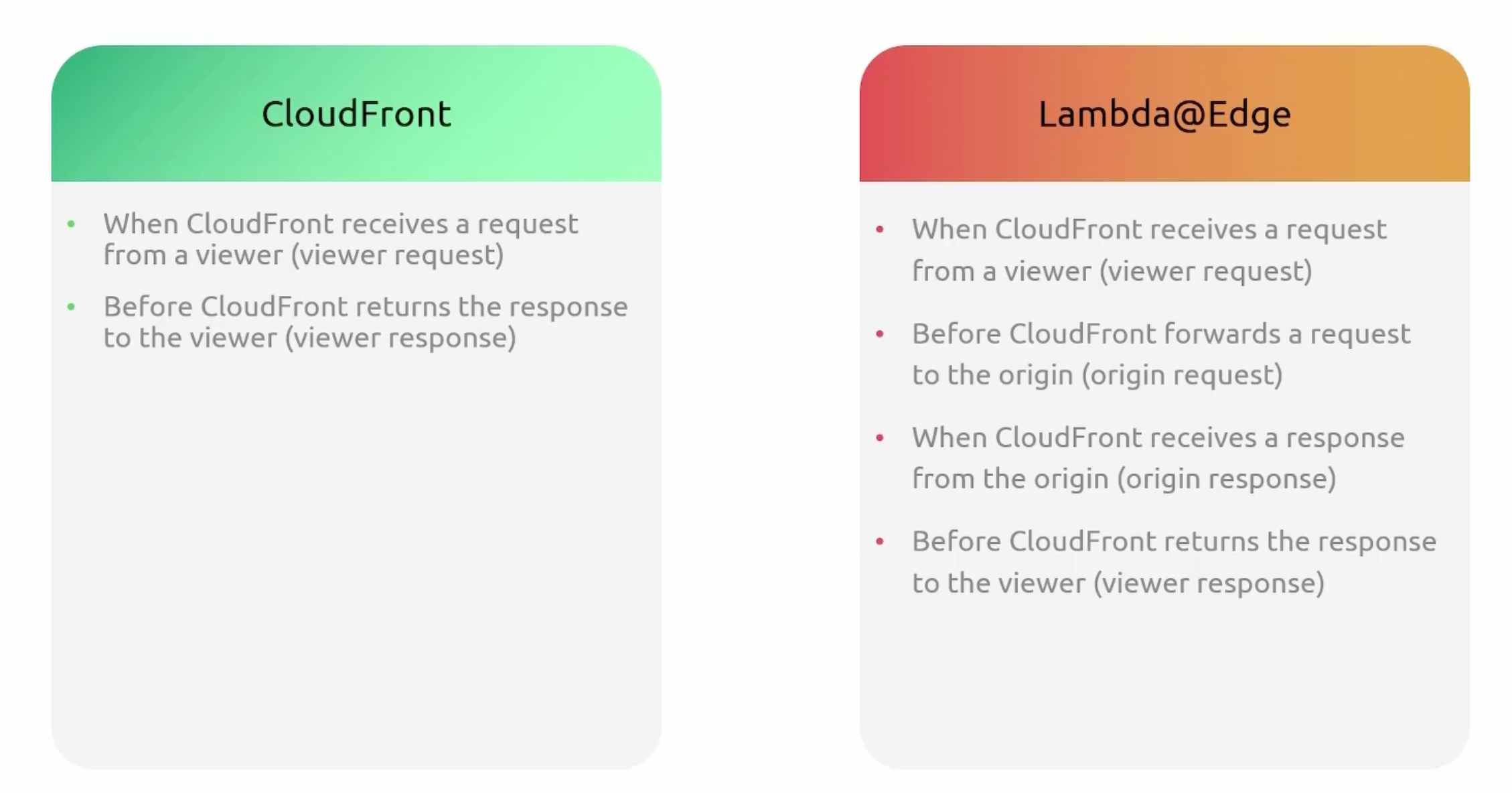
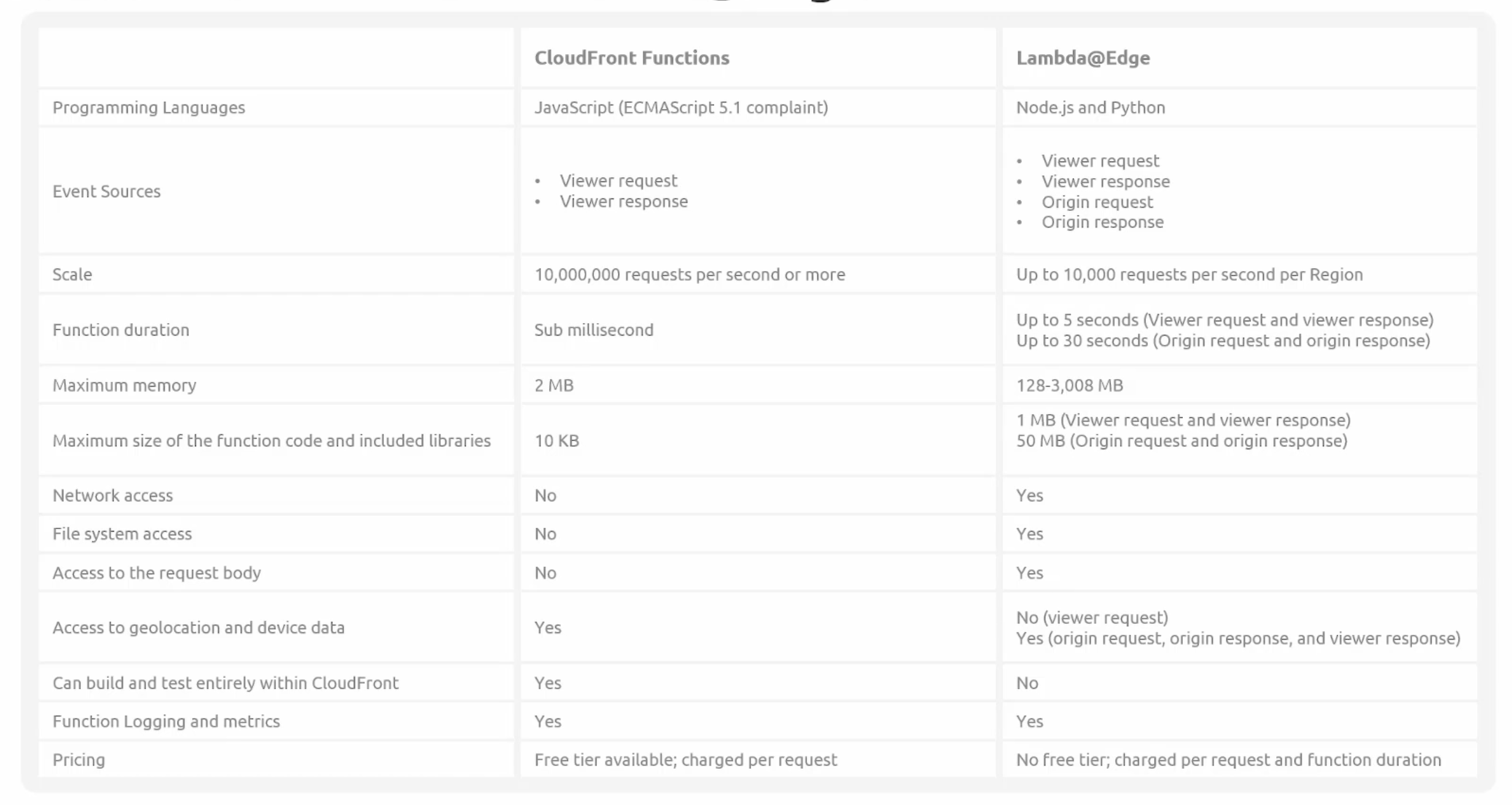
Lambda@Edge
- CloudFront functions, are ideal for:
- Lightweight functions.
- Cache key manipulations.
- Header manipulations.
- URL rewrites or redirects.
- Request authorization.
- Lambda@Edge, are ideal for:
- Long running functions, several milliseconds or more.
- Configurable CPU and memory functions.
- Functions that require external libraries.
- Network dependent functions.
- File system dependent or HTTP Request Access functions.
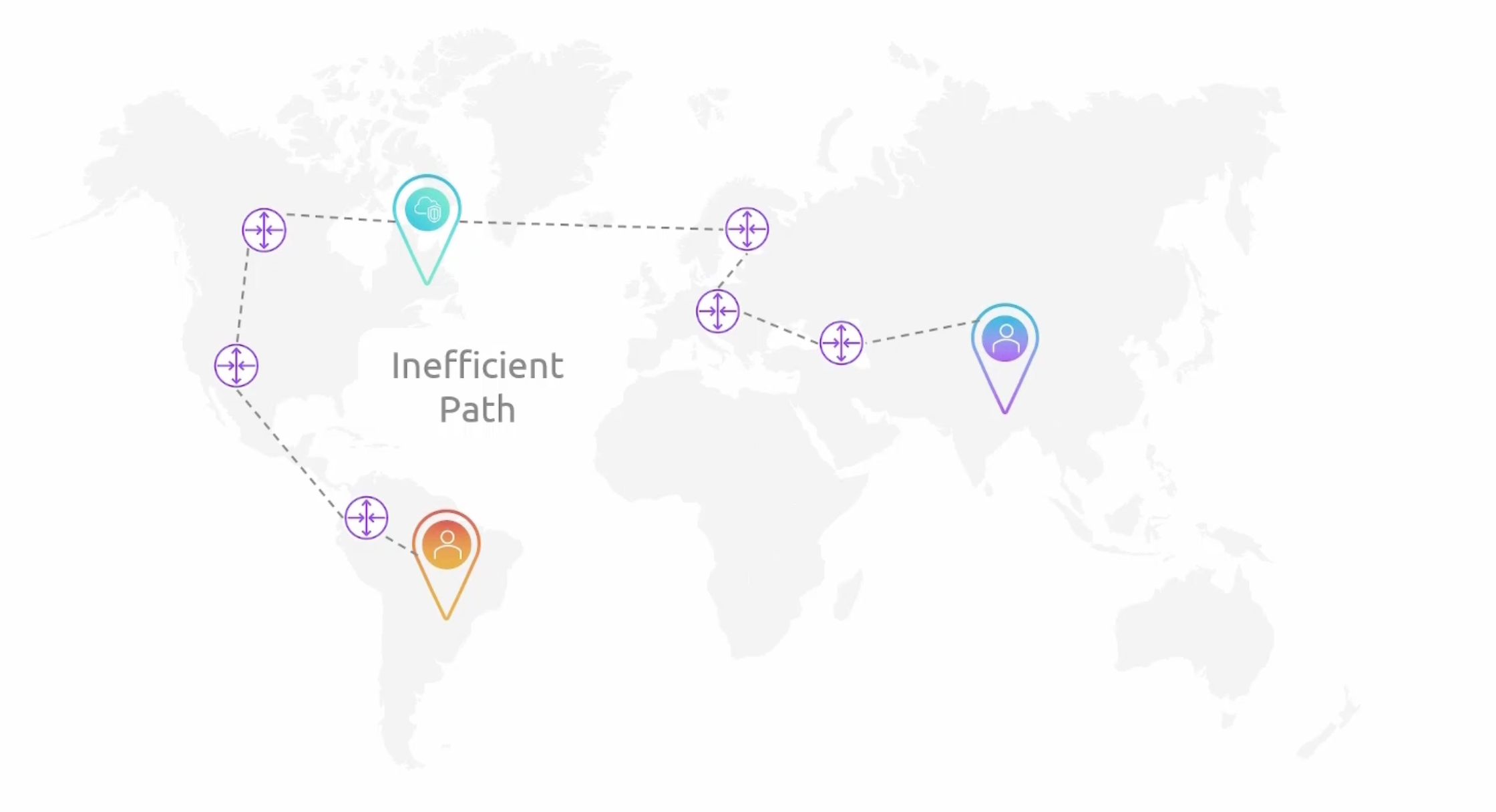
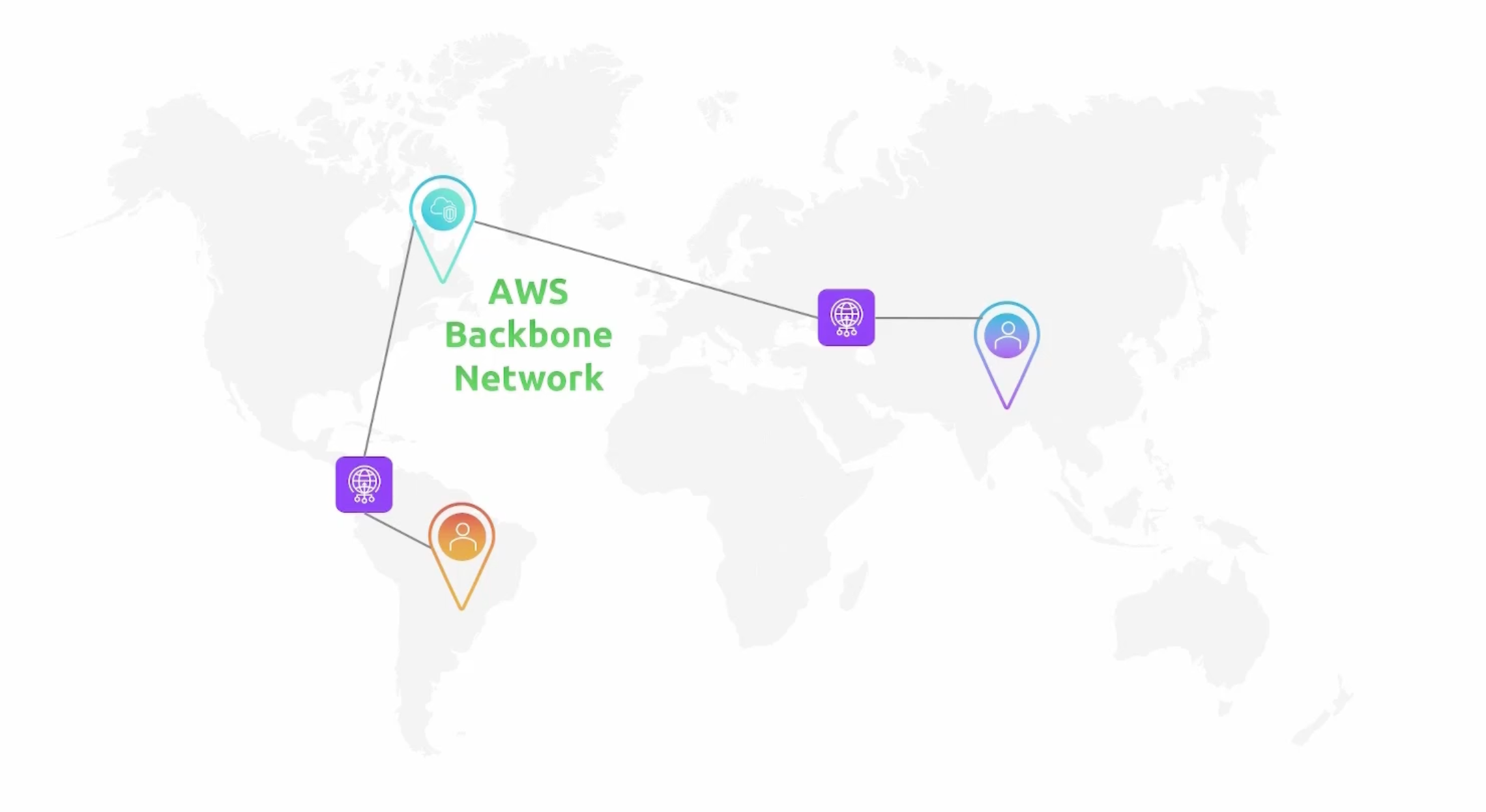
Global Accelerator
- Over Internet
- AWS Backbone
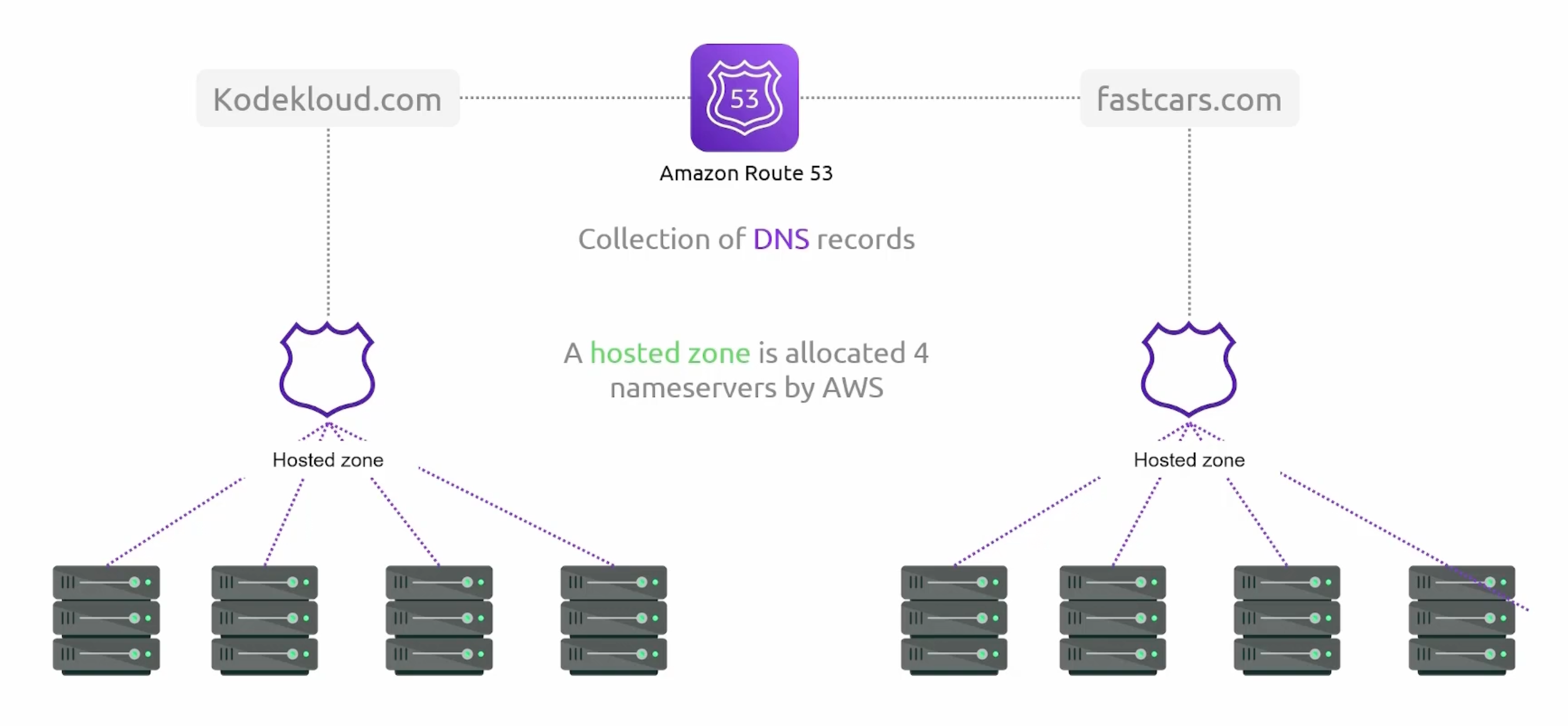
Route 53
When you create a record, you choose a routing policy, which determines how Amazon Route 53 responds to queries:
-
Simple routing policy – Use for a single resource that performs a given function for your domain, for example, a web server that serves content for the example.com website. You can use simple routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
-
Failover routing policy – Use when you want to configure active-passive failover. You can use failover routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
-
Geolocation routing policy – Use when you want to route traffic based on the location of your users. You can use geolocation routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
-
Geoproximity routing policy – Use when you want to route traffic based on the location of your resources and, optionally, shift traffic from resources in one location to resources in another location. You can use geoproximity routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
-
Latency routing policy – Use when you have resources in multiple AWS Regions and you want to route traffic to the Region that provides the best latency. You can use latency routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
-
IP-based routing policy – Use when you want to route traffic based on the location of your users, and have the IP addresses that the traffic originates from.
-
Multivalue answer routing policy – Use when you want Route 53 to respond to DNS queries with up to eight healthy records selected at random. You can use multivalue answer routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
-
Weighted routing policy – Use to route traffic to multiple resources in proportions that you specify. You can use weighted routing to create records in a private hosted zone.
Hosted Zones
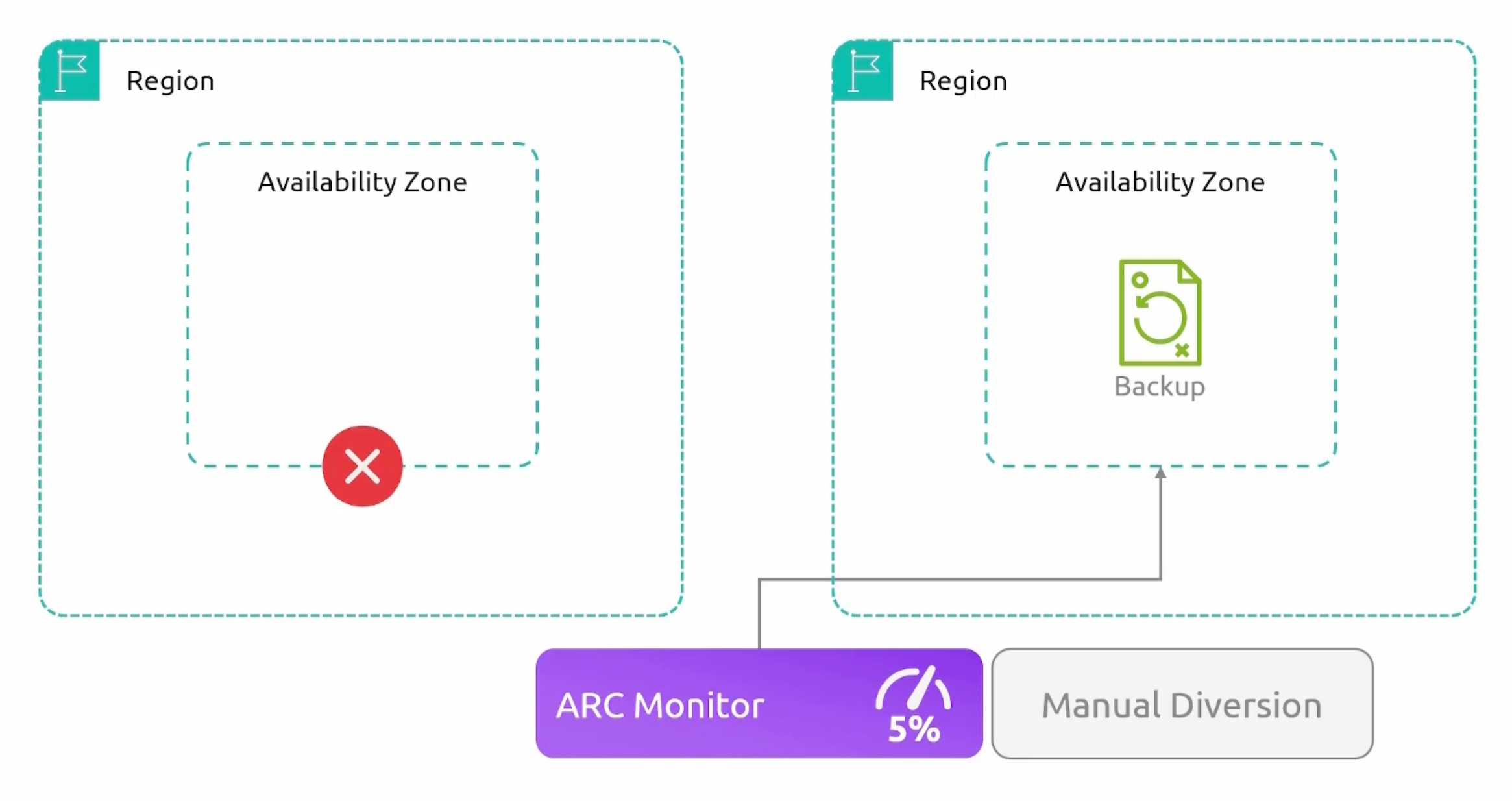
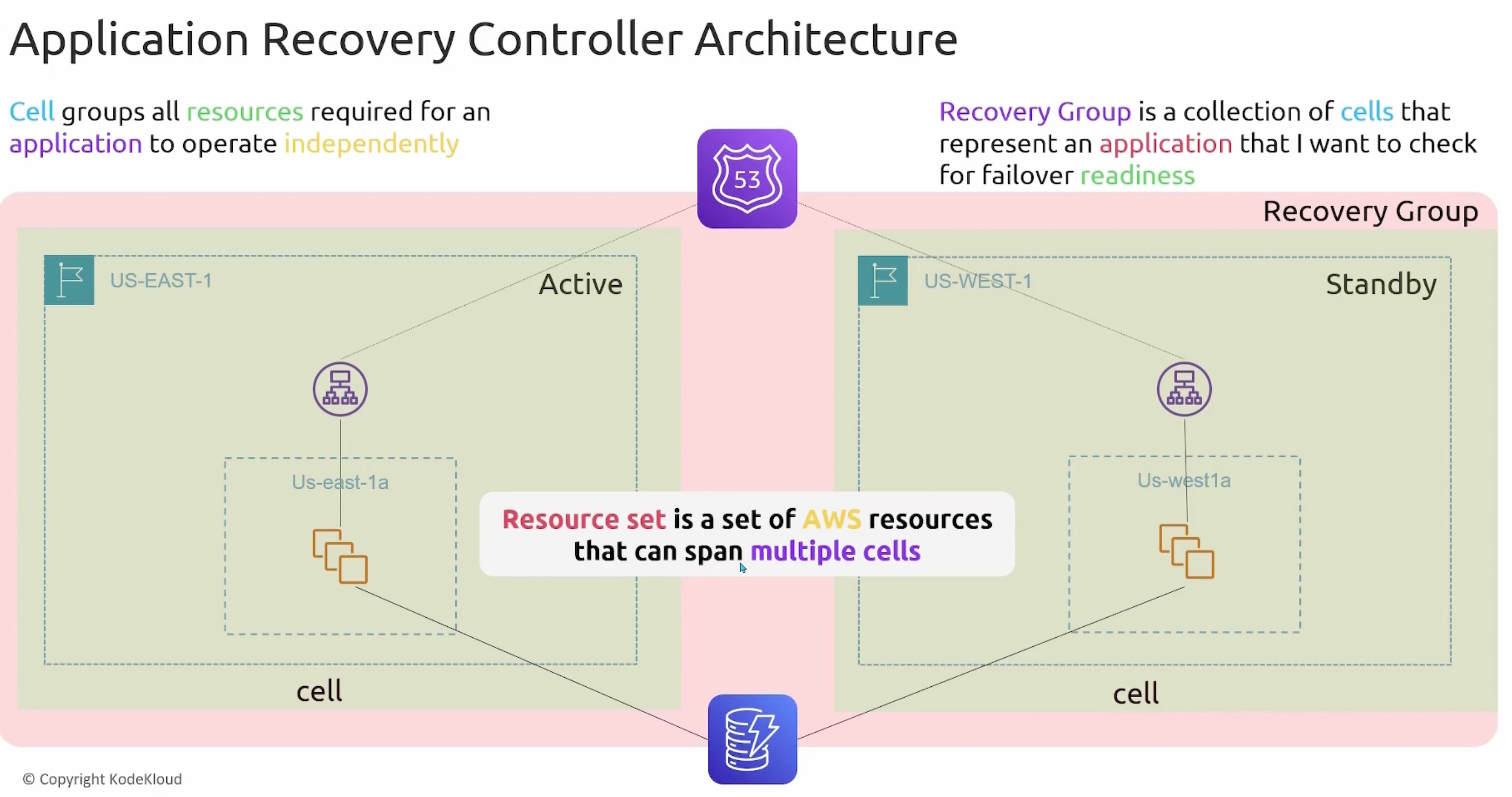
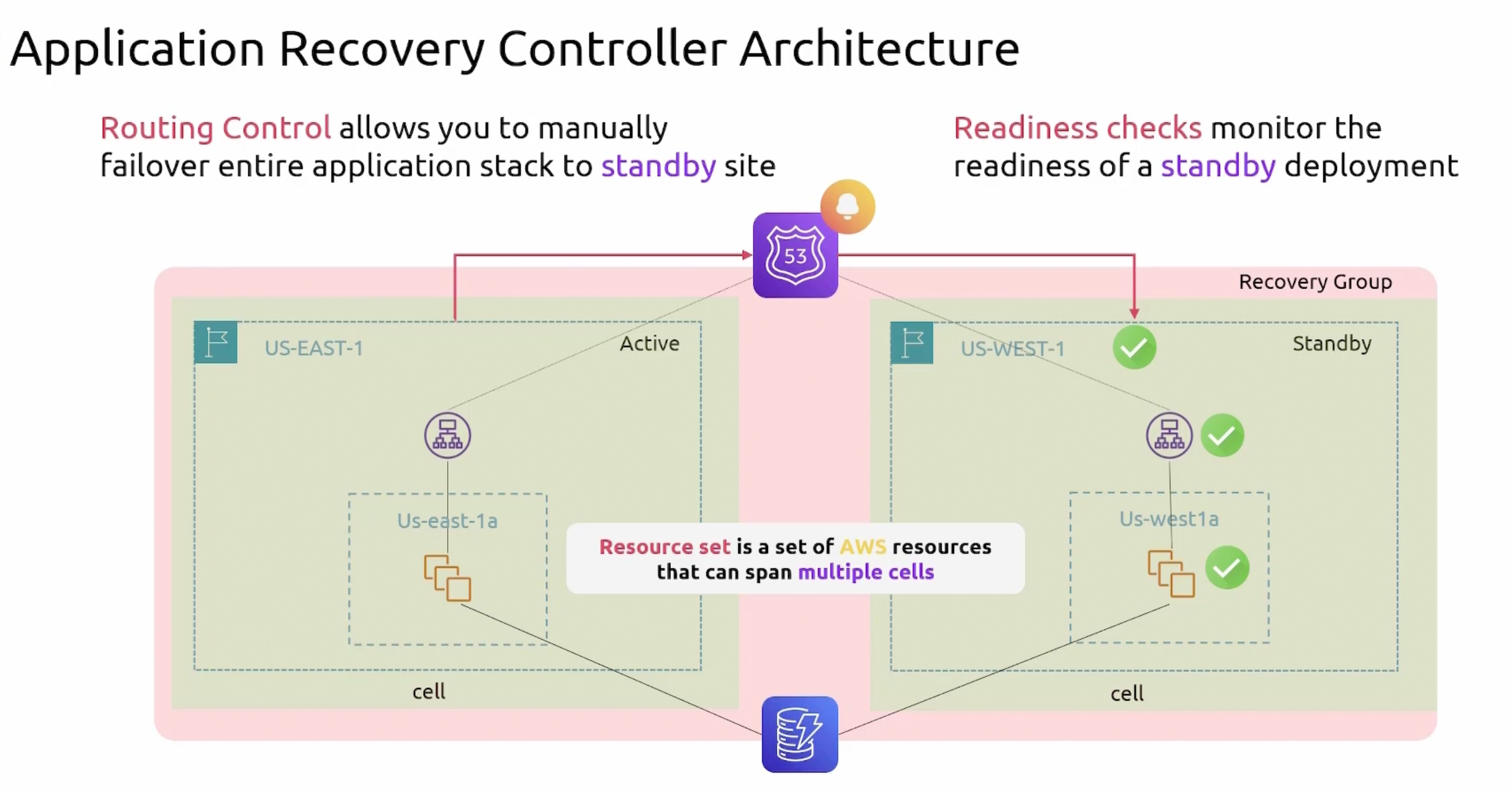
Application Recovery Controller
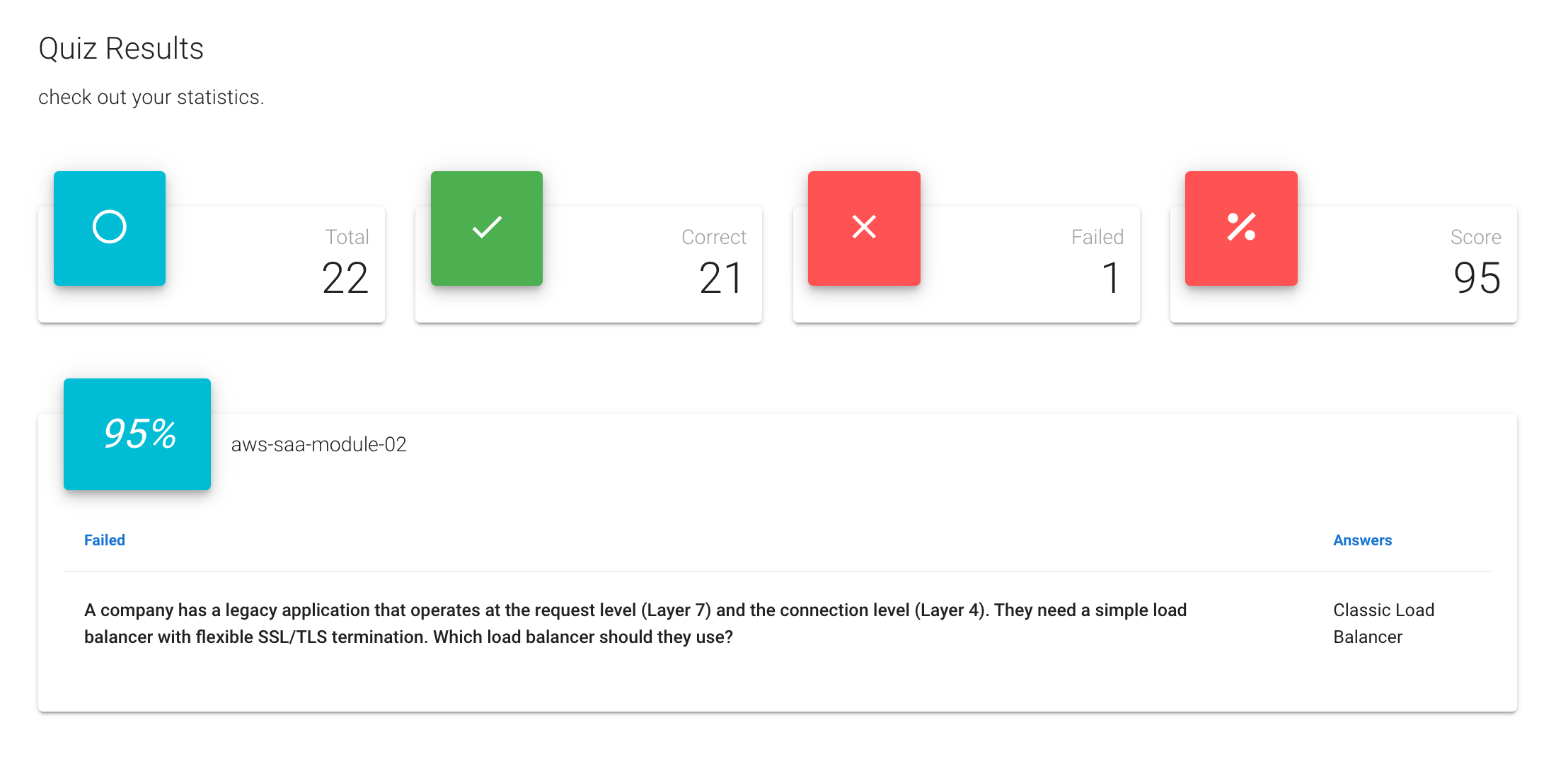
Questions Answered Wrong
Results